Physics 117
... density, fall at the same rate in a vacuum. To determine this, Galileo performed various experiments in which he dropped objects from a certain height. He wrote down his discoveries about motion in his book, De Motu, which means "On ...
... density, fall at the same rate in a vacuum. To determine this, Galileo performed various experiments in which he dropped objects from a certain height. He wrote down his discoveries about motion in his book, De Motu, which means "On ...
Chapter 3: The Basics of Classical Mechanics
... of classical mechanics to this problem would be to divide it into two parts. The first of these would be to write the equations of motion for an object moving under the influence of an arbitrary collection of mass points. The second part then consists of solving those equations. Therefore it is appr ...
... of classical mechanics to this problem would be to divide it into two parts. The first of these would be to write the equations of motion for an object moving under the influence of an arbitrary collection of mass points. The second part then consists of solving those equations. Therefore it is appr ...
presentation source
... in Cartesian coordinates for an object moving under the influence of a two-dimensional central force of the form F=k/r2, where k is a constant. b) What difficulty you will encounter if you would like to derive the Newton equations of motion in polar coordinates? y ...
... in Cartesian coordinates for an object moving under the influence of a two-dimensional central force of the form F=k/r2, where k is a constant. b) What difficulty you will encounter if you would like to derive the Newton equations of motion in polar coordinates? y ...
Problem set 11
... Classical Mechanics 2, Spring 2016 CMI Problem set 11 Due by the beginning of lecture on Monday April 4, 2016 Force free motion of a rigid body, Euler angles ...
... Classical Mechanics 2, Spring 2016 CMI Problem set 11 Due by the beginning of lecture on Monday April 4, 2016 Force free motion of a rigid body, Euler angles ...
Physics 50 Lecture Final Review
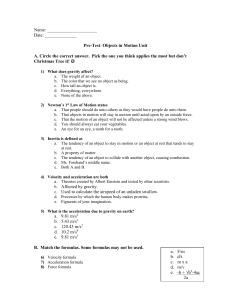
... a) What is a vector quantity? b) What is a scalar quantity? c) Know how to add vectors graphically (geometrically) and using component method. d) What are unit vectors? What are they used for? e) Know how to calculate displacement, velocity (average), and acceleration (average) vectors. f) How do yo ...
... a) What is a vector quantity? b) What is a scalar quantity? c) Know how to add vectors graphically (geometrically) and using component method. d) What are unit vectors? What are they used for? e) Know how to calculate displacement, velocity (average), and acceleration (average) vectors. f) How do yo ...
Name - forehandspace
... C. Use the WORD BANK to fill in the blanks in the paragraph. Some words may be used once, twice or not at all. Today in class Sarah and Michael are doing an experiment with a rocket. They first write down their (9)______________which they came to by using their knowledge from doing research. Mich ...
... C. Use the WORD BANK to fill in the blanks in the paragraph. Some words may be used once, twice or not at all. Today in class Sarah and Michael are doing an experiment with a rocket. They first write down their (9)______________which they came to by using their knowledge from doing research. Mich ...
Mon, Mar 17
... The following is a DE of a different type since it contains the dependent variable: y ' = .08y Say in words what this says! Note that we don’t see the independent variable at all – let’s call it t . What is a solution to this equation? And how can we find it? ...
... The following is a DE of a different type since it contains the dependent variable: y ' = .08y Say in words what this says! Note that we don’t see the independent variable at all – let’s call it t . What is a solution to this equation? And how can we find it? ...
Document
... Although most problems in celestial mechanics involve more than two bodies, many problems of practical interest can be accurately solved by just looking at two bodies at a time. When more than two bodies are involved, the problem is considerably more complicated, and, in this case, no general solut ...
... Although most problems in celestial mechanics involve more than two bodies, many problems of practical interest can be accurately solved by just looking at two bodies at a time. When more than two bodies are involved, the problem is considerably more complicated, and, in this case, no general solut ...
PHYS2101: General Physics I
... On successful completion of the course, the student will be able to explain physical phenomena based on the general concepts and to use general principles of physics in solving problems in electricity, magnetism and thermal physics. The student will also develop skills to use experimental apparatus ...
... On successful completion of the course, the student will be able to explain physical phenomena based on the general concepts and to use general principles of physics in solving problems in electricity, magnetism and thermal physics. The student will also develop skills to use experimental apparatus ...
Finding the Equation of a Line Given Two Points: Name Algebra 1
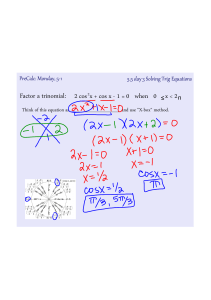
... A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with a same set of unknowns. In solving a system of equations, we try to find values for each of the unknowns that will satisfy every equation in the system. When solving a system containing two linear equations there will be one ordered ...
... A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with a same set of unknowns. In solving a system of equations, we try to find values for each of the unknowns that will satisfy every equation in the system. When solving a system containing two linear equations there will be one ordered ...
chapter 7 notes - School District of La Crosse
... III. Periodic motion-The motion of the object repeats itself. A pendulum, a Yo Yo A. circular motion-The product of 2 forces acting on an object. 1. F1- the outward force of inertiatangent to the motion of the object. 2. F2- the inward force called centripetal force. ...
... III. Periodic motion-The motion of the object repeats itself. A pendulum, a Yo Yo A. circular motion-The product of 2 forces acting on an object. 1. F1- the outward force of inertiatangent to the motion of the object. 2. F2- the inward force called centripetal force. ...
student notes - science
... His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x ...
... His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x ...