Systems Comprehensive
... 4) Solve these systems of equations using elimination. 3x – 2y = 1 2x + 3y = 8 2x + 2y = 4 -2x – 5y = -12 ...
... 4) Solve these systems of equations using elimination. 3x – 2y = 1 2x + 3y = 8 2x + 2y = 4 -2x – 5y = -12 ...
Motion in an Inverse-Square Central Force Field
... the equation of an ellipse if c < Km (and a circle if c = 0). If Km = c it is a parabola, and for Km < c it is an hyperbola (in particular, we always get hyperbolic orbits for a repulsive force). If the path of a particle is a closed orbit, then it must be an ellipse: this is Kepler’s second law. r= ...
... the equation of an ellipse if c < Km (and a circle if c = 0). If Km = c it is a parabola, and for Km < c it is an hyperbola (in particular, we always get hyperbolic orbits for a repulsive force). If the path of a particle is a closed orbit, then it must be an ellipse: this is Kepler’s second law. r= ...
Quick notes Giancoli #1
... 2. Purely rotational motion means that all points in an object moves in circles and the centers all lie on one line called the axis of rotation 3. To calculate the angular position we use the angle of a line in respect to a reference line such as the x-axis. If r is the radius of the circle and l is ...
... 2. Purely rotational motion means that all points in an object moves in circles and the centers all lie on one line called the axis of rotation 3. To calculate the angular position we use the angle of a line in respect to a reference line such as the x-axis. If r is the radius of the circle and l is ...
5.1 - Mass/Spring Systems
... After a mass is attached to a spring, it stretches the spring by an amount s to an ____________________ ____________ where it’s weight W is balanced by the restoring force F ks . Weight is defined by ____________ times ______________. _______________ can be measured in ...
... After a mass is attached to a spring, it stretches the spring by an amount s to an ____________________ ____________ where it’s weight W is balanced by the restoring force F ks . Weight is defined by ____________ times ______________. _______________ can be measured in ...
racing - MathinScience.info
... occurred in a situation. Motion can be determined by using the frame of reference to measure from point A to point B. The most common frame of reference is the horizon. ...
... occurred in a situation. Motion can be determined by using the frame of reference to measure from point A to point B. The most common frame of reference is the horizon. ...
Classical Mechanics and Minimal Action
... is minimal. The quantity S is referred to as the Action and the integrand L(q, q̇, t) the Lagrangian. The Lagrangian of a physical system is defined to be the difference between kinetic- and potential energy. That is, if T is the kinetic energy and V the potential energy, then L = T − V. The princip ...
... is minimal. The quantity S is referred to as the Action and the integrand L(q, q̇, t) the Lagrangian. The Lagrangian of a physical system is defined to be the difference between kinetic- and potential energy. That is, if T is the kinetic energy and V the potential energy, then L = T − V. The princip ...
... (Harder) Assume the medium is uncharged in its rest frame 0 . Using the Lorentz transformation and Eq. 3 show that ...
... (Harder) Assume the medium is uncharged in its rest frame 0 . Using the Lorentz transformation and Eq. 3 show that ...
Exercises #3
... •Problem 4. Plus air resistance. Now add in air resistance, which we model as a force depending linearly on the velocity. The modified equations are mz 00 (t) = −mg − bz 0 (t) mx00 (t) = −bx0 (t) Again solve for the range. Taking for definiteness the values g = 9.8m/s 2 , m = 1kg, b = .2N · s/m, wha ...
... •Problem 4. Plus air resistance. Now add in air resistance, which we model as a force depending linearly on the velocity. The modified equations are mz 00 (t) = −mg − bz 0 (t) mx00 (t) = −bx0 (t) Again solve for the range. Taking for definiteness the values g = 9.8m/s 2 , m = 1kg, b = .2N · s/m, wha ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... spring force and acceleration are zero. At maximum displacement, spring force and acceleration is a maximum and velocity is at zero. The negative sign in the equation signifies that the direction of the spring force is always opposite the direction of the mass’s displacement. The term k stands ...
... spring force and acceleration are zero. At maximum displacement, spring force and acceleration is a maximum and velocity is at zero. The negative sign in the equation signifies that the direction of the spring force is always opposite the direction of the mass’s displacement. The term k stands ...
Newton`s Second and Third Laws of Motion
... has more mass it accelerates at a lower rate because mass has inertia. ...
... has more mass it accelerates at a lower rate because mass has inertia. ...
lecture two
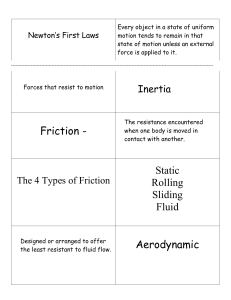
... Weight: The force due to gravity. Q:A person has weight 500N on the earth, what is his weight on Fg=w the moon? Location – mass –weight Earth 1kg 9.8N Moon 1kg 1.6N c M Space 1kg 0N w w Friction: resistance force for the relative motion. Static friction: when there is no Dynamic friction: When there ...
... Weight: The force due to gravity. Q:A person has weight 500N on the earth, what is his weight on Fg=w the moon? Location – mass –weight Earth 1kg 9.8N Moon 1kg 1.6N c M Space 1kg 0N w w Friction: resistance force for the relative motion. Static friction: when there is no Dynamic friction: When there ...