MODULE DESCRIPTOR Code: Alt Codes: Title:
... motion, forces, work, energy, momentum and impulse will be covered and explained in depth using examples from everyday phenomenon such as ‘Why do hurricane in the northern hemisphere rotate counter-clockwise?’, ‘What is the energy loss from two colliding snooker balls?”, “Where should a door-stopper ...
... motion, forces, work, energy, momentum and impulse will be covered and explained in depth using examples from everyday phenomenon such as ‘Why do hurricane in the northern hemisphere rotate counter-clockwise?’, ‘What is the energy loss from two colliding snooker balls?”, “Where should a door-stopper ...
Chapter 6 Guided Questions
... 3. After 3 seconds, how far as an object fallen? 4. What is the formula for the Velocity of a Falling Object? 5. In the formula, what is G equal to? 6. What force opposes the motion of objects through air? 7. What does air resistance depend upon? 8. What is Terminal Velocity? Explain how terminal ve ...
... 3. After 3 seconds, how far as an object fallen? 4. What is the formula for the Velocity of a Falling Object? 5. In the formula, what is G equal to? 6. What force opposes the motion of objects through air? 7. What does air resistance depend upon? 8. What is Terminal Velocity? Explain how terminal ve ...
Lecture 18
... DO NOT use Ff = sN. After solving, you will need to verify that the assumption was correct by checking if Ff sN. Case 2: Assume slipping and use Ff = kN as the 4th equation. In this case, aG ar. ...
... DO NOT use Ff = sN. After solving, you will need to verify that the assumption was correct by checking if Ff sN. Case 2: Assume slipping and use Ff = kN as the 4th equation. In this case, aG ar. ...
Newton`s Laws
... object increases with increased force and decreased with increased mass. • The acceleration of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inverse to the mass. The two people are pushing with the same power so they don't move. ...
... object increases with increased force and decreased with increased mass. • The acceleration of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inverse to the mass. The two people are pushing with the same power so they don't move. ...
Math 11 - BigEngine
... Section 5.1: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by GRAPHING When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) ...
... Section 5.1: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by GRAPHING When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) ...
Algebra - Militant Grammarian
... mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get from one point to the other. It takes a further 2.0 seconds to pass through th ...
... mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get from one point to the other. It takes a further 2.0 seconds to pass through th ...
CLASSICAL FIELD THEORY AND ELECTRODYNAMICS
... with the other components vanishing, t being the time since the origins of the frames K and K 0 overlapped and b referring to the closest distance of approach of the charge, assumed fixed on the x02 axis. 2. An alternative Lagrangian density for the electromagnetic field due to Enrico Fermi is ...
... with the other components vanishing, t being the time since the origins of the frames K and K 0 overlapped and b referring to the closest distance of approach of the charge, assumed fixed on the x02 axis. 2. An alternative Lagrangian density for the electromagnetic field due to Enrico Fermi is ...
Section 4
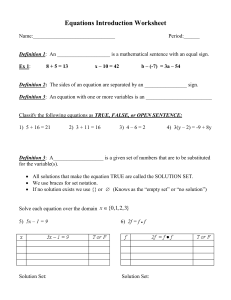
... Definition 3: A___________________ is a given set of numbers that are to be substituted for the variable(s). All solutions that make the equation TRUE are called the SOLUTION SET. We use braces for set notation. If no solution exists we use {} or (Knows as the “empty set” or “no solution”) S ...
... Definition 3: A___________________ is a given set of numbers that are to be substituted for the variable(s). All solutions that make the equation TRUE are called the SOLUTION SET. We use braces for set notation. If no solution exists we use {} or (Knows as the “empty set” or “no solution”) S ...
Possible Theory Questions
... 1. Unit conversion, built into the problems • Ch 3 2. Calculate speed, velocity, and acceleration • Ch 3 3. Problems using Newtons 2nd law, including where you have to combine forces applied at angles and opposing forces to find the total force on an object, in each direction. • Ch 4, Ch 5 4. ...
... 1. Unit conversion, built into the problems • Ch 3 2. Calculate speed, velocity, and acceleration • Ch 3 3. Problems using Newtons 2nd law, including where you have to combine forces applied at angles and opposing forces to find the total force on an object, in each direction. • Ch 4, Ch 5 4. ...
1) 3x+6=15 2) x2+2x=15
... 1) Find a common denominator for each fraction. 2) Drop denominators. 4) Solve the resulting equation. 5) Check for extraneous roots. **Extraneous roots are roots that when checked do not work. ...
... 1) Find a common denominator for each fraction. 2) Drop denominators. 4) Solve the resulting equation. 5) Check for extraneous roots. **Extraneous roots are roots that when checked do not work. ...
energy - RHIG - Wayne State University
... • Assume a force is acting between the two particles along a line joining them. • Particle positions described in some arbitrary reference frame as positions r1 and r2, or in terms of the CM frame position, R, and the relative position vector r = r1 - r2 . ...
... • Assume a force is acting between the two particles along a line joining them. • Particle positions described in some arbitrary reference frame as positions r1 and r2, or in terms of the CM frame position, R, and the relative position vector r = r1 - r2 . ...
Solving Equations Using the Addition and Multiplication Properties
... In this chapter, the equations we are solving are called linear equations in one variable or …rst-degree equations in one variable. For example, an equation such as 5x 2 = 6x is a linear equation in one variable. It is called linear or …rst degree because the exponent on each x is 1 and there is no ...
... In this chapter, the equations we are solving are called linear equations in one variable or …rst-degree equations in one variable. For example, an equation such as 5x 2 = 6x is a linear equation in one variable. It is called linear or …rst degree because the exponent on each x is 1 and there is no ...
Newton Review
... Speed = Distance/ Time; 20 ft/s = 200 ft/10 s 13. What is the acceleration of an object that goes from 50 m/s to 100 m/s in 10 seconds? ∆ speed/time = acceleration; 100 m/s – 50 m/s / 10 s = 50 m/s / 10 s = 5 m/s2 Fill in the blanks for the following questions below. 14. Air resistance is a kind of ...
... Speed = Distance/ Time; 20 ft/s = 200 ft/10 s 13. What is the acceleration of an object that goes from 50 m/s to 100 m/s in 10 seconds? ∆ speed/time = acceleration; 100 m/s – 50 m/s / 10 s = 50 m/s / 10 s = 5 m/s2 Fill in the blanks for the following questions below. 14. Air resistance is a kind of ...
Laws of Motion Test Name
... 2. A crumpled piece of paper hits the ground before a flat sheet of paper because a. the acceleration of gravity is greater on the crumpled paper. b. there is more air resistance against the flat paper. c. the crumpled paper is more massive. d. the crumpled paper is less massive. ...
... 2. A crumpled piece of paper hits the ground before a flat sheet of paper because a. the acceleration of gravity is greater on the crumpled paper. b. there is more air resistance against the flat paper. c. the crumpled paper is more massive. d. the crumpled paper is less massive. ...
5.1 Force changes motion
... Laws of Motion • 5.1 Newton’s First Law • 5.2 Newton’s Second Law • 5.3 Newton’s Third Law ...
... Laws of Motion • 5.1 Newton’s First Law • 5.2 Newton’s Second Law • 5.3 Newton’s Third Law ...