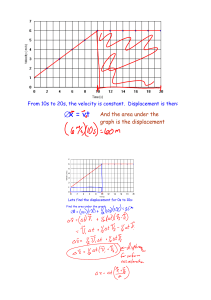
Learning Goal: To learn about the impulse-momentum
... Express your answer in terms of and . Use three significant figures in the numerical ...
... Express your answer in terms of and . Use three significant figures in the numerical ...
6.3 – Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination.
... 6.3 – Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination. Definitions of the Day (DODs) ...
... 6.3 – Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination. Definitions of the Day (DODs) ...
Isra University Faculty of Science Course Calendar 2016/2017
... Isra University Faculty of Science Course Calendar ...
... Isra University Faculty of Science Course Calendar ...
The Two-Body problem
... this to 2 degrees of freedom, (r, ϕ), and then to one, (r). Then, the problem with 1 degree of freedom can be solved using time translational invariance (conservation of E). 1 see ...
... this to 2 degrees of freedom, (r, ϕ), and then to one, (r). Then, the problem with 1 degree of freedom can be solved using time translational invariance (conservation of E). 1 see ...
Chapter3
... They undergo random thermal motions, known as diffusion, and each atom responds to all the forces acting on it according to Newton’s laws. The problem is that there are many atoms in hemoglobin and many solvent molecules that collide with them and need to be accounted for. Early crystal x-ray diffra ...
... They undergo random thermal motions, known as diffusion, and each atom responds to all the forces acting on it according to Newton’s laws. The problem is that there are many atoms in hemoglobin and many solvent molecules that collide with them and need to be accounted for. Early crystal x-ray diffra ...
Relativity, Inertia, and Equivalence Principle
... Objects in motion remain moving at constant velocity (straight line and constant speed), UNLESS …a net (unbalanced) force acts ...
... Objects in motion remain moving at constant velocity (straight line and constant speed), UNLESS …a net (unbalanced) force acts ...
EFFECT OF CENTRIFUGAL AND CORIOLIS FORCES DUE TO
... Hence, due to coriolis force, the particle dropped vertically downwards suffers a deviation along positive x-axis i.e. towards east. The displacement of the particle will be maximum for λ=0 i.e. at the equator. ...
... Hence, due to coriolis force, the particle dropped vertically downwards suffers a deviation along positive x-axis i.e. towards east. The displacement of the particle will be maximum for λ=0 i.e. at the equator. ...
Course Syllabus
... Catalog Description including pre- and co-requisites: supporting data required for grade prerequisite of ‘C’ or higher. ...
... Catalog Description including pre- and co-requisites: supporting data required for grade prerequisite of ‘C’ or higher. ...
Lesson 6-6: Percent and Percentage Problems
... sentence to make the sentence true. Conditional equations - when not every element of the domain makes the sentence true. Identity - when every element of the domain satisfies an equation. Equivalent equations - Two equations that have the same solution set. ...
... sentence to make the sentence true. Conditional equations - when not every element of the domain makes the sentence true. Identity - when every element of the domain satisfies an equation. Equivalent equations - Two equations that have the same solution set. ...
On the Shoulders of Giants”
... While it is important to note that there is an association of H with E, it is equally important to note that these two are not necessarily the same value or even the same type of quantity! ...
... While it is important to note that there is an association of H with E, it is equally important to note that these two are not necessarily the same value or even the same type of quantity! ...
Relevant Equations
... U1-2: Work of a non-conservative variable force ΔT = change in kinetic energy ΔVg = change in potential energy ΔVe = change in potential energy (for a spring) g = gravitational constant (9.81 meters per second squared or 32.2 feet per second squared) h = height above or below reference datum (can be ...
... U1-2: Work of a non-conservative variable force ΔT = change in kinetic energy ΔVg = change in potential energy ΔVe = change in potential energy (for a spring) g = gravitational constant (9.81 meters per second squared or 32.2 feet per second squared) h = height above or below reference datum (can be ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... On Earth, gravity and friction are unbalanced forces that often change an object’s motion. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia, and the greater the force required to change its motion. Example: The tennis ball thrown in the air will continue until the force of gravity ...
... On Earth, gravity and friction are unbalanced forces that often change an object’s motion. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia, and the greater the force required to change its motion. Example: The tennis ball thrown in the air will continue until the force of gravity ...
Chapter 3 Review
... ____________________ 1. Newton’s Second Law shows the relationship between force, mass, and __________________. _____________________ 2. _______________ is the force that opposes motion. _____________________ 3. _____________ friction is experienced when a box is pushed across a floor. _____________ ...
... ____________________ 1. Newton’s Second Law shows the relationship between force, mass, and __________________. _____________________ 2. _______________ is the force that opposes motion. _____________________ 3. _____________ friction is experienced when a box is pushed across a floor. _____________ ...