Chapter 19 Outline The First Law of Thermodynamics
... • In the early 17th century, Johannes Kepler used Tycho Brahe’s observations of planetary motions to determine three empirical laws of planetary orbits. 1. Each planet moves in an elliptical orbit, with the sun at one focus of the ellipse. 2. A line from the sun to a given planet sweeps out equal ar ...
... • In the early 17th century, Johannes Kepler used Tycho Brahe’s observations of planetary motions to determine three empirical laws of planetary orbits. 1. Each planet moves in an elliptical orbit, with the sun at one focus of the ellipse. 2. A line from the sun to a given planet sweeps out equal ar ...
Unit 2 Forces Date ______ Hour ______ Practice Assessment Fill i
... ________________________4. The property of matter that resists a change in motion is ________________________5. According to Newton’s 2nd law of motion, force equals mass times ________________________6. The force of attraction that exists between all objects in the universe is _____________________ ...
... ________________________4. The property of matter that resists a change in motion is ________________________5. According to Newton’s 2nd law of motion, force equals mass times ________________________6. The force of attraction that exists between all objects in the universe is _____________________ ...
Jeopardy
... There two marbles of the same size, weight and density, yet one sinks in its container of liquid and the other floats in its container. Which of these describes the density of the different liquids? ...
... There two marbles of the same size, weight and density, yet one sinks in its container of liquid and the other floats in its container. Which of these describes the density of the different liquids? ...
Unit 06 Test Study Guide Part I. Force and Motion Review the Unit
... 1. Explain Newton’s First Law of Motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion, also known as the Law of Inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest until acted on by an unbalanced force, and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant direction and speed until acted on by a unba ...
... 1. Explain Newton’s First Law of Motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion, also known as the Law of Inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest until acted on by an unbalanced force, and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant direction and speed until acted on by a unba ...
activity 10 newton`s first law of motion
... BACKGROUND: The relationship between forces and the way objects move was described clearly for the first time by Sir Isaac Newton in his three Laws of Motion. NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION states: ...
... BACKGROUND: The relationship between forces and the way objects move was described clearly for the first time by Sir Isaac Newton in his three Laws of Motion. NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION states: ...
test one
... Differential Equations test one Monday, April 25, 2005 please show your work in order to get full credit ...
... Differential Equations test one Monday, April 25, 2005 please show your work in order to get full credit ...
Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object
... Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object Motion: Process of moving or being moved Gravity: The force that pulls things toward Earth Height: the measurement from base to top Distance: an amount of space between two things or people Surface: the outside part or uppermost layer o ...
... Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object Motion: Process of moving or being moved Gravity: The force that pulls things toward Earth Height: the measurement from base to top Distance: an amount of space between two things or people Surface: the outside part or uppermost layer o ...
MTH 212 Calculus III
... Consider a line in space through the point P( x1 , y1 , z1 ), in the direction of v = (the
direction vector). If the point Q (x, y, z) is on this line, then the vector PQ must be parallel with the
direction vector v.
Thus we can write:
...
... Consider a line in space through the point P( x1 , y1 , z1 ), in the direction of v =
Chapter 5 - galileo.harvard.edu
... dependence (?) • Example, low speeds (e.g. boat in water) • Terminal velocity – key? (a = 0) ...
... dependence (?) • Example, low speeds (e.g. boat in water) • Terminal velocity – key? (a = 0) ...
Newton Review
... 4. What is the force in Newton’s of an object whose mass is 100 kg and accelerates at 5 m/s2? F = ma; 500 N = 100 kg x 5 m/s2. 5. What is the acceleration of an object of 100 N that has a mass of 5 kg? 100N/5kg = 20 m/s2 6. What is matter? What is mass? What is volume? What is the volume of a box of ...
... 4. What is the force in Newton’s of an object whose mass is 100 kg and accelerates at 5 m/s2? F = ma; 500 N = 100 kg x 5 m/s2. 5. What is the acceleration of an object of 100 N that has a mass of 5 kg? 100N/5kg = 20 m/s2 6. What is matter? What is mass? What is volume? What is the volume of a box of ...
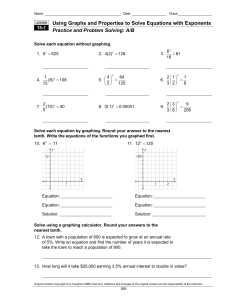
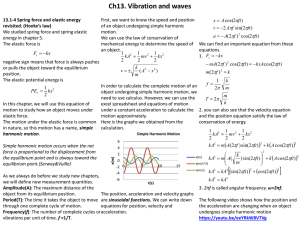
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... the equilibrium point and is always toward the kA m A( ) sin(2ft ) k A cos(2ft ) ...
... the equilibrium point and is always toward the kA m A( ) sin(2ft ) k A cos(2ft ) ...
Sect. 8.4
... between them F(r) = -U(r) = -(dU/dr)r • Started with a 6d, 2 body problem. By transforming to CM & relative coordinates (R,r) reduced it to 2, 3d 1 body problems. One (the CM motion, R) is trivial & free particlelike. The 2nd is for a “particle” with mass μ (m1m2)(m1+m2) = reduced mass interacti ...
... between them F(r) = -U(r) = -(dU/dr)r • Started with a 6d, 2 body problem. By transforming to CM & relative coordinates (R,r) reduced it to 2, 3d 1 body problems. One (the CM motion, R) is trivial & free particlelike. The 2nd is for a “particle” with mass μ (m1m2)(m1+m2) = reduced mass interacti ...
Ch-4-Lecture
... • Did not distinguish acceleration from velocity. • Believed that a heavy object would fall more quickly than a lighter object. • Earth-centered model of the solar system. ...
... • Did not distinguish acceleration from velocity. • Believed that a heavy object would fall more quickly than a lighter object. • Earth-centered model of the solar system. ...
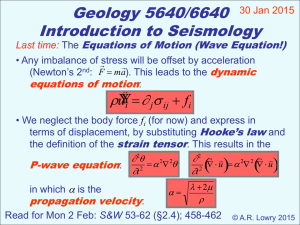
The Wave Equation & Velocity
... • Temperature • Fluid saturation = Vp, = Vs are much more sensitive to and than to ...
... • Temperature • Fluid saturation = Vp, = Vs are much more sensitive to and than to ...
Guide_Test1
... 1. What is Newton’s 3rd law? 2. Newton’s 3rd law is valid during an interaction. Action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. They act on different objects. 3. You should be able to state the action and reaction force during an interaction. For eg, motion of a rocket, ...
... 1. What is Newton’s 3rd law? 2. Newton’s 3rd law is valid during an interaction. Action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. They act on different objects. 3. You should be able to state the action and reaction force during an interaction. For eg, motion of a rocket, ...
MT 5500 - Loyola College
... 2. Where does the centre of gravity lie on a uniform solid tetrahedron? 3. State the principle of virtual work. 4. The maximum velocity of a particle moving in a simple harmonic motion is 2ft/sec and its period is ...
... 2. Where does the centre of gravity lie on a uniform solid tetrahedron? 3. State the principle of virtual work. 4. The maximum velocity of a particle moving in a simple harmonic motion is 2ft/sec and its period is ...
45 m/s - Madison Public Schools
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity until acted upon by a net force. ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity until acted upon by a net force. ...