Navier-Stokes Equations
... where Re is a dimensionless parameter known as the Reynolds number. Pressure is a parameter fixed by the observer, so it follows that the only other force is inertia force. Furthermore, the relative magnitudes of the pressure and inertial forces are describe by the Reynolds number, defined as ...
... where Re is a dimensionless parameter known as the Reynolds number. Pressure is a parameter fixed by the observer, so it follows that the only other force is inertia force. Furthermore, the relative magnitudes of the pressure and inertial forces are describe by the Reynolds number, defined as ...
Mechanics 1: Motion in a Central Force Field
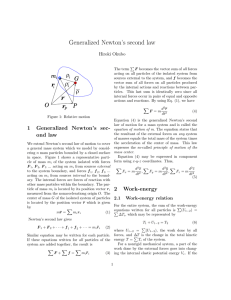
... field, a central force field. Central forces are very important in physics and engineering. For example, the gravitional force of attraction between two point masses is a central force. The Coulomb force of attraction and repulsion between charged particles is a central force. Because of their impor ...
... field, a central force field. Central forces are very important in physics and engineering. For example, the gravitional force of attraction between two point masses is a central force. The Coulomb force of attraction and repulsion between charged particles is a central force. Because of their impor ...
Solve Rational Equations
... 5: Remove any factors equal to 1, and write the result in simpli…ed form. 6: Solve the resulting equation. 7: Check all possible solutions in the original equation. Example 1: (Solving rational expressions) Solve the following equations. ...
... 5: Remove any factors equal to 1, and write the result in simpli…ed form. 6: Solve the resulting equation. 7: Check all possible solutions in the original equation. Example 1: (Solving rational expressions) Solve the following equations. ...
Section 1.2
... A total of $24,000 is invested, some in stocks and some in bonds. If the amount invested in bonds is half that invested in stocks, how much is invested in each category? ...
... A total of $24,000 is invested, some in stocks and some in bonds. If the amount invested in bonds is half that invested in stocks, how much is invested in each category? ...
24 Slides
... motion will stay in motion and objects at rest will stay at rest…unless a force acts on them. The ball will stay at rest (not move) unless the dog moves it. ...
... motion will stay in motion and objects at rest will stay at rest…unless a force acts on them. The ball will stay at rest (not move) unless the dog moves it. ...
of an object
... falling and in space. Explain how free-fall acceleration and terminal velocity are connected. Describe the difference between mass and weight and their connection to gravity. Explain how projectile motion works and how we use it to our advantage in sports and in space ...
... falling and in space. Explain how free-fall acceleration and terminal velocity are connected. Describe the difference between mass and weight and their connection to gravity. Explain how projectile motion works and how we use it to our advantage in sports and in space ...
Newton`s first law of motion
... speed of the parachutist is zero. However he will immediately be acted upon by his weight acting vertically downwards and since the external resultant force is not zero he will accelerate downwards. As the parachutist’s speed increases so does the air resistance. This opposes the downwards force of ...
... speed of the parachutist is zero. However he will immediately be acted upon by his weight acting vertically downwards and since the external resultant force is not zero he will accelerate downwards. As the parachutist’s speed increases so does the air resistance. This opposes the downwards force of ...
presentation source
... “Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it.” What does this really mean? ...
... “Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it.” What does this really mean? ...
Examples 2.1 - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... The break-even point occurs at a monthly usage of 100 minutes. b. The graph of the equations shows that for monthly usage under 100 minutes, Plan 2 is less expensive. So, Jeremy should probably choose Plan 2. ...
... The break-even point occurs at a monthly usage of 100 minutes. b. The graph of the equations shows that for monthly usage under 100 minutes, Plan 2 is less expensive. So, Jeremy should probably choose Plan 2. ...
2-1 Solving Systems of Equations in Two Variables
... The break-even point occurs at a monthly usage of 100 minutes. b. The graph of the equations shows that for monthly usage under 100 minutes, Plan 2 is less expensive. So, Jeremy should probably choose Plan 2. ...
... The break-even point occurs at a monthly usage of 100 minutes. b. The graph of the equations shows that for monthly usage under 100 minutes, Plan 2 is less expensive. So, Jeremy should probably choose Plan 2. ...
The Aristotelian approach
... - why motion is sometimes with constant speed and why sometimes motion is with variable speed ? - why sometimes motion is on straight line, and why sometimes has curved trajectory? - can we write up some simple laws that would allow us to PREDICT what kind of motion will a particle have under well-c ...
... - why motion is sometimes with constant speed and why sometimes motion is with variable speed ? - why sometimes motion is on straight line, and why sometimes has curved trajectory? - can we write up some simple laws that would allow us to PREDICT what kind of motion will a particle have under well-c ...
PHYSICS SAE 4
... Newton’s Laws is to draw the free body diagram Be sure to include only the forces acting on the object of interest Include any field forces acting on the object Do not assume the normal force equals the weight ...
... Newton’s Laws is to draw the free body diagram Be sure to include only the forces acting on the object of interest Include any field forces acting on the object Do not assume the normal force equals the weight ...