* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solve Rational Equations
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
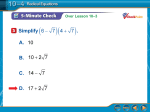
Math 35 6.7 "Solving Rational Equations" Objective: * Solve rational equations. Solve Rational Equations Solving Rational Equations 1. Factor all denominators. 2: Determine which numbers cannot be solutions of the equation. 3: Multiply both sides of the equation by the LCD. 4: Use the distributive property to remove parentheses. 5: Remove any factors equal to 1, and write the result in simpli…ed form. 6: Solve the resulting equation. 7: Check all possible solutions in the original equation. Example 1: (Solving rational expressions) Solve the following equations. 3 7 a) + =2 5 x+2 c) 2 x 3 = x x2 9 + 4 x+3 b) 1 1 = b 8 d) 2 2y 1 1 + = y + 4 y 2 + 2y 8 y 2 Page: 1 3 8b Notes by Bibiana Lopez Intermediate Algebra by Tussy and Gustafson 6.7 Example 2: (Solving rational expressions with opposite factors) 1 1 1 Solve the following equation. + = 6y 6 1 y 6 Solve Rational Equations with Extraneous Solutions When we multiply both sides of an equation by a quantity that contains a variable, we can get false solutions, called extraneous solutions. This happens when we multiply both sides of an equation by 0 and get a solution that gives a 0 in the denominator of a rational expression. Extraneous solutions must be discarded. Example 3: (Solving equations with extraneous solutions) Solve the following equations. t 3 1 2t = a) 3 t+2 t+2 b) Page: 2 3 x 4 + 2 18 + x + 5 x2 + x 20 =0 Notes by Bibiana Lopez