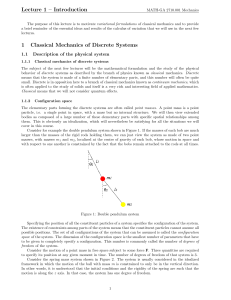
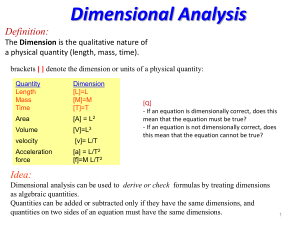
M - Otterbein University
... • If we know which force is acting on an object of known mass we can calculate (predict) its motion • Qualitatively: – objects subject to a constant force will speed up (slow down) in that direction – Objects subject to a force perpendicular to their motion (velocity!) will not speed up, but change ...
... • If we know which force is acting on an object of known mass we can calculate (predict) its motion • Qualitatively: – objects subject to a constant force will speed up (slow down) in that direction – Objects subject to a force perpendicular to their motion (velocity!) will not speed up, but change ...
3.4 Solving Equations with Variables on Both Sides
... • Some equations have variables on both sides • To solve these equations, you can first collect the variable terms on one side of the equation • Collecting the variable terms on the side with the greater variable coefficient will result in a positive coefficient ...
... • Some equations have variables on both sides • To solve these equations, you can first collect the variable terms on one side of the equation • Collecting the variable terms on the side with the greater variable coefficient will result in a positive coefficient ...
13_5elimination method by multiolication
... Previously, we learned how to solve systems of equations by using addition or subtraction which eliminated one of the variables. ...
... Previously, we learned how to solve systems of equations by using addition or subtraction which eliminated one of the variables. ...
Topics covered in PH112 - Rose
... Topics covered in PH112 Angular position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration Equations of motion in terms of angular variables Linear and angular variables Rotational kinetic energy and rotational inertia Parallel-axis theorem Torque, moment arm, line of action of F Newton’s second law in angu ...
... Topics covered in PH112 Angular position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration Equations of motion in terms of angular variables Linear and angular variables Rotational kinetic energy and rotational inertia Parallel-axis theorem Torque, moment arm, line of action of F Newton’s second law in angu ...
Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Problems: SHOW YOUR WORK
... 36. Calculate the acceleration (in m/sec2) of a missile that goes from 0 km/s to 8.8 km/s in 2 sec. How does this compare to the acceleration of gravity? (about 10 m/s2) ...
... 36. Calculate the acceleration (in m/sec2) of a missile that goes from 0 km/s to 8.8 km/s in 2 sec. How does this compare to the acceleration of gravity? (about 10 m/s2) ...
vocabulary
... is the only force acting on it. A satellite in orbit is in free fall, as is a skydiver (if we neglect the effects of air resistance). ...
... is the only force acting on it. A satellite in orbit is in free fall, as is a skydiver (if we neglect the effects of air resistance). ...
given a space curve r(t)
... Velocity and Acceleration: assuming r(t) is position of an object in space; • the velocity of the object is v(t) = r0(t); • the speed of the object is v(t) = |v(t)| = |r0(t)|; • the acceleration of the object is a(t) = v0(t) = r00(t); • Newton’s Second Law of Motion: F = ma = mr00(t), for a force F ...
... Velocity and Acceleration: assuming r(t) is position of an object in space; • the velocity of the object is v(t) = r0(t); • the speed of the object is v(t) = |v(t)| = |r0(t)|; • the acceleration of the object is a(t) = v0(t) = r00(t); • Newton’s Second Law of Motion: F = ma = mr00(t), for a force F ...
Derivation of EMHD Equations
... vorticity. In the equation (9), the curl operation has eliminated the pressure ~ and ~ve , term for constant temperatures. Since equation (9) contains only B ...
... vorticity. In the equation (9), the curl operation has eliminated the pressure ~ and ~ve , term for constant temperatures. Since equation (9) contains only B ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Newton’s first law is often called the law of inertia. Every object continues in its state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. ...
... Newton’s first law is often called the law of inertia. Every object continues in its state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. ...
Chp+12+Quest REVISED 2012
... 1. What is an action force? 2. What is a reaction force? 3. What is a force pair? 4. Why don’t action/reaction forces cancel each other? 5. Why don’t we see equal effects from equal forces? 6. What does Newton’s third law of motion say? (4 ideas) 7. What is momentum? 8. What is the formula for findi ...
... 1. What is an action force? 2. What is a reaction force? 3. What is a force pair? 4. Why don’t action/reaction forces cancel each other? 5. Why don’t we see equal effects from equal forces? 6. What does Newton’s third law of motion say? (4 ideas) 7. What is momentum? 8. What is the formula for findi ...