Chapter6
... subplot(3,2,i),plot(xp,yp,xb(i),yb(i),'o');axis([0 xmax 0 ymax]); xlabel('x(m)');ylabel('y(m)') end ...
... subplot(3,2,i),plot(xp,yp,xb(i),yb(i),'o');axis([0 xmax 0 ymax]); xlabel('x(m)');ylabel('y(m)') end ...
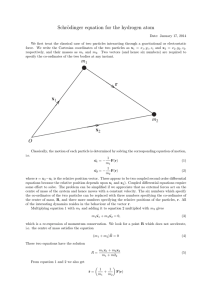
Sect. 2.4, Part I
... block & plane is μs = 0.4. At what angle, θ, will block start sliding (if it is initially at rest)? (Work on board!) ...
... block & plane is μs = 0.4. At what angle, θ, will block start sliding (if it is initially at rest)? (Work on board!) ...
for reference Name Period ______ Date ______ Motion Notes from
... Acceleration: The rate of change in velocity. To calculate acceleration, use this equation: Acceleration = (Final Velocity) - (Original Velocity) / Time Deceleration: A term commonly used to mean a decrease in speed. Force: any push or pull. Forces cause a change in motion. Friction: a force tha ...
... Acceleration: The rate of change in velocity. To calculate acceleration, use this equation: Acceleration = (Final Velocity) - (Original Velocity) / Time Deceleration: A term commonly used to mean a decrease in speed. Force: any push or pull. Forces cause a change in motion. Friction: a force tha ...
Expectations for Ch 2 & 3
... ¤ How coordinate systems can be used in motion studies ¤ Terms such as displacement, magnitude, vectors ...
... ¤ How coordinate systems can be used in motion studies ¤ Terms such as displacement, magnitude, vectors ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #3, Due Wednesday,
... (b) Assume that a solution is of the form xi = Ai eαt , substitute it into the set of differential equations and write the resulting system of algebraic equations in matrix form, Ax = 0. (c) Write an expression for the characteristic polynomial of which α must be a root in order to satisfy the matri ...
... (b) Assume that a solution is of the form xi = Ai eαt , substitute it into the set of differential equations and write the resulting system of algebraic equations in matrix form, Ax = 0. (c) Write an expression for the characteristic polynomial of which α must be a root in order to satisfy the matri ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... solve problems using Newton’s 2nd Law Fnet ma provide examples of Newton’s 3rd Law of action-reaction force pairs FAonB = -FBonA explain the advantages and disadvantages of static and kinetic friction in situations involving various planes (e.g. a horizontal plane, a variety of inclined plan ...
... solve problems using Newton’s 2nd Law Fnet ma provide examples of Newton’s 3rd Law of action-reaction force pairs FAonB = -FBonA explain the advantages and disadvantages of static and kinetic friction in situations involving various planes (e.g. a horizontal plane, a variety of inclined plan ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... o To demonstrate an understanding of the forces involved in uniform circular motion and motion in a plane. o To analyze 1D and 2D forces acting on an object that will determine the motion of that object. o To investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, forces involved in uniform circular mot ...
... o To demonstrate an understanding of the forces involved in uniform circular motion and motion in a plane. o To analyze 1D and 2D forces acting on an object that will determine the motion of that object. o To investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, forces involved in uniform circular mot ...
EQUATIONS OF MOTION
... If the forces can be resolved directly from the free-body diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian vector formulation of ...
... If the forces can be resolved directly from the free-body diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian vector formulation of ...
Newton`s Laws
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion • The greater the acceleration of an object, the greater the force required to change its motion. ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion • The greater the acceleration of an object, the greater the force required to change its motion. ...
Answers
... Divergence occurs when the denominator of the above equation becomes zero. This allows the critical speed for divergence to be determined as ...
... Divergence occurs when the denominator of the above equation becomes zero. This allows the critical speed for divergence to be determined as ...
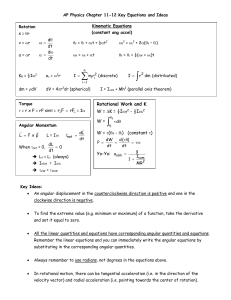
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... To find the extreme value (e.g. minimum or maximum) of a function, take the derivative and set it equal to zero. ...
... To find the extreme value (e.g. minimum or maximum) of a function, take the derivative and set it equal to zero. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 19. Explain Legendre transformation. Discuss how the transformation equations can be obtained from the generating functions of type F 1 and F2. 20. What are action angle variables? Explain how they can be used to obtain the frequencies of periodic motion. 21. Discuss the double pendulum and obtain i ...
... 19. Explain Legendre transformation. Discuss how the transformation equations can be obtained from the generating functions of type F 1 and F2. 20. What are action angle variables? Explain how they can be used to obtain the frequencies of periodic motion. 21. Discuss the double pendulum and obtain i ...
• Introduction
... solve these equations for each unknown quantity. Finally, substitute the numerical values of the known quantities (including the units) in the equations and calculate each of the unknown quantities. • Linear momentum and angular momentum The linear momentum or amount of motion p of a particle of mas ...
... solve these equations for each unknown quantity. Finally, substitute the numerical values of the known quantities (including the units) in the equations and calculate each of the unknown quantities. • Linear momentum and angular momentum The linear momentum or amount of motion p of a particle of mas ...