Quiz 1 Force and Vectors Static Equilibrium Problem Solving
... Next Reading Assignment: W03D1 Young and Freedman: University Physics (Review) 5.1-5.3 Experiment 1: Force and Motion ...
... Next Reading Assignment: W03D1 Young and Freedman: University Physics (Review) 5.1-5.3 Experiment 1: Force and Motion ...
Newton`s Laws Vocabulary
... Gravity – the force of attraction that moves bodies towards the center of the earth. Inertia – the tendency of a body to preserve its state of rest or motion unless acted upon by an external force. Newton (N) – the unit for the amount of force an object contains. Traction – a kind of friction that a ...
... Gravity – the force of attraction that moves bodies towards the center of the earth. Inertia – the tendency of a body to preserve its state of rest or motion unless acted upon by an external force. Newton (N) – the unit for the amount of force an object contains. Traction – a kind of friction that a ...
Lecture Notes for Section 13.4 (Equation of Motion)
... diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian vector formulation of the second law is F = ma or Fx i + Fy j + Fz k = m(ax ...
... diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian vector formulation of the second law is F = ma or Fx i + Fy j + Fz k = m(ax ...
The Book we used
... final values of the momentum during the time interval dt over which the reaction pair interacts. ...
... final values of the momentum during the time interval dt over which the reaction pair interacts. ...
Conservation Of Linear Momentum
... final values of the momentum during the time interval dt over which the reaction pair interacts. ...
... final values of the momentum during the time interval dt over which the reaction pair interacts. ...
Name: Notes - 4.2 Newton`s First Law of Motion: Inertia 1. State
... 3. Why does an object given a push across a surface slow down? Why is this in agreement with Newton’s 1st Law? ...
... 3. Why does an object given a push across a surface slow down? Why is this in agreement with Newton’s 1st Law? ...
Lecture Notes for Section 13.4 (Equation of Motion)
... diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian vector formulation of the second law is F = ma or Fx i + Fy j + Fz k = m(ax ...
... diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian vector formulation of the second law is F = ma or Fx i + Fy j + Fz k = m(ax ...
Ch. 2-3
... 2. Newton was the first to discover the notion of _________ or an object’s resistance to motion. 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is __ ...
... 2. Newton was the first to discover the notion of _________ or an object’s resistance to motion. 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is __ ...
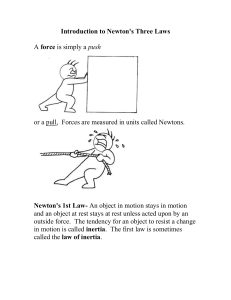
Introduction to Newton`s Three Laws
... Newton's 2nd Law- F=MA where F is force, M is mass, and A is acceleration. According to this equation, 1 newton equals _________________. Newton's 3rd Law- For every action there is an equal and ...
... Newton's 2nd Law- F=MA where F is force, M is mass, and A is acceleration. According to this equation, 1 newton equals _________________. Newton's 3rd Law- For every action there is an equal and ...
SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 11 Learning Targets
... c) A volleyball is spiked d) A football is caught 4. State the law of universal gravitation. 5. Explain how mass and distance affect gravitational force. 6. What is projectile motion? 7. List the two components of projectile motion. 8. List Newton’s Three Laws of Motion. 9. Give an example of each o ...
... c) A volleyball is spiked d) A football is caught 4. State the law of universal gravitation. 5. Explain how mass and distance affect gravitational force. 6. What is projectile motion? 7. List the two components of projectile motion. 8. List Newton’s Three Laws of Motion. 9. Give an example of each o ...