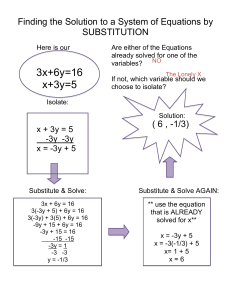
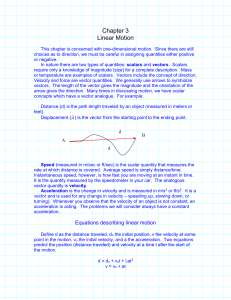
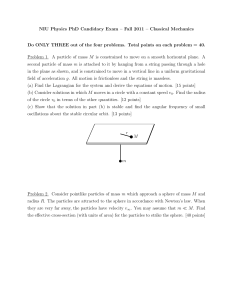
Forces and Motion Study Guide
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... To verify Newton’s second law of motion using a tickertimer, weights and a small trolley. The second law of motion can be written F=m·a W here F : F orce m : mass a : acceleration ...
... To verify Newton’s second law of motion using a tickertimer, weights and a small trolley. The second law of motion can be written F=m·a W here F : F orce m : mass a : acceleration ...
Notes - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... It is the quantity measured by the speedometer in your car. The analogous vector quantity is velocity. Acceleration is the change in velocity and is measured in m/s2 or ft/s2. It is a vector and is used for any change in velocity – speeding up, slowing down, or turning). Whenever you observe that th ...
... It is the quantity measured by the speedometer in your car. The analogous vector quantity is velocity. Acceleration is the change in velocity and is measured in m/s2 or ft/s2. It is a vector and is used for any change in velocity – speeding up, slowing down, or turning). Whenever you observe that th ...
Two-Body Central
... the two-body central force problem? Relative position, r Position of center of mass, R, where ...
... the two-body central force problem? Relative position, r Position of center of mass, R, where ...
Formula Sheet - Blank File
... (chose a common origin for all point masses so all positions (all xi and xcm) are relative to that origin.) ...
... (chose a common origin for all point masses so all positions (all xi and xcm) are relative to that origin.) ...
Dr. Zeemo has a brief guide to Newton`s Three Laws of Motion.
... II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleratio ...
... II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleratio ...
Equations of Motion Computational Physics Orbital Motion
... dependent on position only: Angular Momentum conserved; Motion in a plane. ...
... dependent on position only: Angular Momentum conserved; Motion in a plane. ...
Worksheet - 2
... 7.Derive the equation of motion for position-time relation S=ut+1/2 at2 8.Derive graphically the position-velocity equation of motion v2-u2=2as 9. A ball is dropped from a height of 50m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10m/sec2 a) With what velocity will it strike the ground? b) A ...
... 7.Derive the equation of motion for position-time relation S=ut+1/2 at2 8.Derive graphically the position-velocity equation of motion v2-u2=2as 9. A ball is dropped from a height of 50m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10m/sec2 a) With what velocity will it strike the ground? b) A ...
Phy221 E1Review
... e. Given an equation describing the motion of an object, utilize differentiation and/or integration to represent the other kinematic variables as functions of time. 4. Kinematics in multiple dimensions: Analyze and represent. a. Find the vector representation of an object’s position, velocity, and a ...
... e. Given an equation describing the motion of an object, utilize differentiation and/or integration to represent the other kinematic variables as functions of time. 4. Kinematics in multiple dimensions: Analyze and represent. a. Find the vector representation of an object’s position, velocity, and a ...
Physics PHYS 352 Mechanics II Problem Set #4
... A pendulum is constructed by attaching a mass m to a string of length . The upper end of the string is connected to the uppermost part of a vertical disk of radius R ( R ) as in the figure. ...
... A pendulum is constructed by attaching a mass m to a string of length . The upper end of the string is connected to the uppermost part of a vertical disk of radius R ( R ) as in the figure. ...
PHYS4330 Theoretical Mechanics HW #8 Due 25 Oct 2011
... (3) (See Taylor 7.49.) A mass m with charge q moves in a uniform constant magnetic field B = Bẑ. Prove that B = ∇ × A where A = 12 B × r. (You can do this in a coordinateindependent way, only assuming that B is a constant field, and using some vector identities.) Show that A = 12 Bρφ̂ in cylindrica ...
... (3) (See Taylor 7.49.) A mass m with charge q moves in a uniform constant magnetic field B = Bẑ. Prove that B = ∇ × A where A = 12 B × r. (You can do this in a coordinateindependent way, only assuming that B is a constant field, and using some vector identities.) Show that A = 12 Bρφ̂ in cylindrica ...
Physics 200A Theoretical Mechanics Fall 2013 Topics
... coupled oscillators, normal coordinates and modes, etc., intuition from symmetry b.) Parametric oscillators and instability c.) Pondermotive potential and force ...
... coupled oscillators, normal coordinates and modes, etc., intuition from symmetry b.) Parametric oscillators and instability c.) Pondermotive potential and force ...
T - UniMAP Portal
... The 3 kg disk is D is attached to the end of a cord as shown. The other end of the cord is attached to a ball-and-socket joint located at the center of the platform. If the platform is rotating rapidly, and the disk is placed on it and released from rest as shown, determine the time it takes for the ...
... The 3 kg disk is D is attached to the end of a cord as shown. The other end of the cord is attached to a ball-and-socket joint located at the center of the platform. If the platform is rotating rapidly, and the disk is placed on it and released from rest as shown, determine the time it takes for the ...