Rotational Motion
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
Ch. 13 notes 2017
... Newton told at least four people that he got the idea of universal gravitation by seeing an apple fall out of a tree. Nobody knows if it actually hit him on the head! Newton understood the concept of inertia, (what is inertia?) and he knew that things remained at constant speed in a straight line un ...
... Newton told at least four people that he got the idea of universal gravitation by seeing an apple fall out of a tree. Nobody knows if it actually hit him on the head! Newton understood the concept of inertia, (what is inertia?) and he knew that things remained at constant speed in a straight line un ...
Rotational Motion
... the resulting acceleration, and the proportionality constant r ris the mass. Newton’s second law can also be expressed for objects undergoing angular motion - in this case, " = I# . The applied torque generates an angular acceleration, and the two quantities are linearly proportional with a proporti ...
... the resulting acceleration, and the proportionality constant r ris the mass. Newton’s second law can also be expressed for objects undergoing angular motion - in this case, " = I# . The applied torque generates an angular acceleration, and the two quantities are linearly proportional with a proporti ...
Lesson 3
... by taking the square root of each side. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. is a perfect square ...
... by taking the square root of each side. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. is a perfect square ...
S = D
... Anything that has mass has (a)__________. Two things will affect the pull of gravity between 2 objects: One is the (b)________ of the objects and the other is the (c)________between the two objects. ...
... Anything that has mass has (a)__________. Two things will affect the pull of gravity between 2 objects: One is the (b)________ of the objects and the other is the (c)________between the two objects. ...
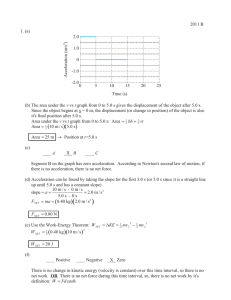
2011 B 1. (a) 2.0 0
... (b) Using the chalk, mark a starting line on the track. Using a tape metric measure or a meter stick, measure 10 m distances (marked by a chalk-line) up to, and including, 100 m (which is the finish line). Position one student, who has the starter's pistol, at the starting line. The ten other studen ...
... (b) Using the chalk, mark a starting line on the track. Using a tape metric measure or a meter stick, measure 10 m distances (marked by a chalk-line) up to, and including, 100 m (which is the finish line). Position one student, who has the starter's pistol, at the starting line. The ten other studen ...
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... examples of contact forces) and other forces are the result of action-at-a-distance interactions (gravitational, electrical, and magnetic forces). According to Newton, whenever objects A and B interact with each other, they exert forces upon each other. When you sit in your chair, your body exerts a ...
... examples of contact forces) and other forces are the result of action-at-a-distance interactions (gravitational, electrical, and magnetic forces). According to Newton, whenever objects A and B interact with each other, they exert forces upon each other. When you sit in your chair, your body exerts a ...
Calculating Velocity
... We can calculate the drag of Joe and his bike by using the following equation Eq. 7.62 CD = drag/ (1/2*r*V^2*A) Rearranging this equation, we solve for the drag. ...
... We can calculate the drag of Joe and his bike by using the following equation Eq. 7.62 CD = drag/ (1/2*r*V^2*A) Rearranging this equation, we solve for the drag. ...
NM3M03EAA.pdf - Mira Costa High School
... Step 1 Model each purchase with an equation. Cost of yearly subscription: y = _18_ Cost of one magazine: y = _3_ x, where x represents the number of magazines Step 2 Graph each equation. ...
... Step 1 Model each purchase with an equation. Cost of yearly subscription: y = _18_ Cost of one magazine: y = _3_ x, where x represents the number of magazines Step 2 Graph each equation. ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Notes 1 – Centripetal Acceleration
... Ok so we’ve figured out its speed, but is the mass accelerating? Remember that the mass is traveling at a constant speed. However, acceleration is defined as: ...
... Ok so we’ve figured out its speed, but is the mass accelerating? Remember that the mass is traveling at a constant speed. However, acceleration is defined as: ...
Chapter 2. Conservation of Energy
... solve problems involving them. In this chapter we introduce new quantities and concepts that are also related to forces and can advantageously be used to understand the dynamics of bodies and physical systems. The first quantity we study here is that of the work done on a body. In one-dimension or f ...
... solve problems involving them. In this chapter we introduce new quantities and concepts that are also related to forces and can advantageously be used to understand the dynamics of bodies and physical systems. The first quantity we study here is that of the work done on a body. In one-dimension or f ...
biomechanics2008
... Using this concept, explain why: a. The white ball in pool slows down after impacting the black. Some of the momentum of the white ball is passed on to the black ball. b. When suddenly braking in a car, your body moves forward (thankfully you are wearing a seatbelt). The momentum of the car is tran ...
... Using this concept, explain why: a. The white ball in pool slows down after impacting the black. Some of the momentum of the white ball is passed on to the black ball. b. When suddenly braking in a car, your body moves forward (thankfully you are wearing a seatbelt). The momentum of the car is tran ...