Physics Regents Review Sheet
... _____ the force used to lift an object upward _____ what you give an object when do work in lifting it up _____ what you give an object when you push an object along a table _____ what power is _____ how to calculate power _____ the relationship between power and time _____ the different types of en ...
... _____ the force used to lift an object upward _____ what you give an object when do work in lifting it up _____ what you give an object when you push an object along a table _____ what power is _____ how to calculate power _____ the relationship between power and time _____ the different types of en ...
Laws of Motion - physics teacher
... We have studied in the previous chapters, the motion of bodies loving with uniform, acceleration without taking into account the srnal factors that produced the acceleration. For centuries the problem of motion and its causes were a cen-|tral theme of natural philosophy. The Greek philosopher Ari_ _ ...
... We have studied in the previous chapters, the motion of bodies loving with uniform, acceleration without taking into account the srnal factors that produced the acceleration. For centuries the problem of motion and its causes were a cen-|tral theme of natural philosophy. The Greek philosopher Ari_ _ ...
Answers for chapters5,6 and 7
... (d) Plugging = 23° into the above result for F, with s = 0.42 and W = 180 N, yields F 70 N . 44. The magnitude of the acceleration of the car as it rounds the curve is given by v2/R, where v is the speed of the car and R is the radius of the curve. Since the road is horizontal, only the frictio ...
... (d) Plugging = 23° into the above result for F, with s = 0.42 and W = 180 N, yields F 70 N . 44. The magnitude of the acceleration of the car as it rounds the curve is given by v2/R, where v is the speed of the car and R is the radius of the curve. Since the road is horizontal, only the frictio ...
How? Newton`s second law of motion
... • No matter how far apart two objects are, the gravitational force between them never completely goes to zero. • Because the gravitational force between two objects never disappears, gravity is called a long-range force. ...
... • No matter how far apart two objects are, the gravitational force between them never completely goes to zero. • Because the gravitational force between two objects never disappears, gravity is called a long-range force. ...
PULLEYS - Mathematics with Mr Walters
... When two particles A and B collide, they exert equal and opposite forces, and hence impulses, on each other. The impulse that A exerts on B (equal to B’s change in momentum) is therefore equal and opposite to the impulse that B exerts on A (equal to A’s change in momentum). If these changes are equa ...
... When two particles A and B collide, they exert equal and opposite forces, and hence impulses, on each other. The impulse that A exerts on B (equal to B’s change in momentum) is therefore equal and opposite to the impulse that B exerts on A (equal to A’s change in momentum). If these changes are equa ...
Also except answer if student derive for particular two bodies.
... surface of a body produces a change in the shape of the body without any change in volume, then the stress set up in the body is called tangential stress. a) Strain :- The ratio of change in configuration to the original configuration is called strain. i.e. Strain = Change in configuration/ Original ...
... surface of a body produces a change in the shape of the body without any change in volume, then the stress set up in the body is called tangential stress. a) Strain :- The ratio of change in configuration to the original configuration is called strain. i.e. Strain = Change in configuration/ Original ...
S - Nuffield Foundation
... When a number of forces act on an object, the resultant force is the sum of these forces. For example, if forces F1, F2, and F3 act on an object, then the resultant force is F1 + F2 + F3. Newton's First Law of Motion A particle will remain at rest or continue to move uniformly in a straight line unl ...
... When a number of forces act on an object, the resultant force is the sum of these forces. For example, if forces F1, F2, and F3 act on an object, then the resultant force is F1 + F2 + F3. Newton's First Law of Motion A particle will remain at rest or continue to move uniformly in a straight line unl ...
Problem: 2nd Law and Pulleys (CM-1993)
... (A) speed of the object increases 9.8 m/s during each second (B) (B) speed of the object as it falls is 9.8 m/s (C) object falls 9.8 meters during each second (D) object falls 9.8 meters during the first second only (E) derivative of the distance with respect to time for the object equals 9.8 m/s2 ...
... (A) speed of the object increases 9.8 m/s during each second (B) (B) speed of the object as it falls is 9.8 m/s (C) object falls 9.8 meters during each second (D) object falls 9.8 meters during the first second only (E) derivative of the distance with respect to time for the object equals 9.8 m/s2 ...
Slide 1 - apphysicswarren
... object can be described using polar coordinates—r and θ— rather than x and y. The figure at left gives the conversion between the two descriptions. ...
... object can be described using polar coordinates—r and θ— rather than x and y. The figure at left gives the conversion between the two descriptions. ...
Projectile Motion-ppt
... 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
... 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
Final Solution-Phy 105-Fall2011-1
... c) Calculate the work done to spin the ring at w 50rpm about its diameter. 2) Solution: a) All parts of the ring are at the same distance R from the axis of rotation passing through its CM at its center and perpendicular to its plane. We consider a small part of the ring of mass mi located betwe ...
... c) Calculate the work done to spin the ring at w 50rpm about its diameter. 2) Solution: a) All parts of the ring are at the same distance R from the axis of rotation passing through its CM at its center and perpendicular to its plane. We consider a small part of the ring of mass mi located betwe ...
Topics 1, 2, 3, 4, 9 selected problems paper 1 take
... A liquid is heated in a well-insulated container. The power input to the liquid and its specific heat capacity are known. Which of the following quantities must be known in order to calculate the rate at which the temperature increases? A. ...
... A liquid is heated in a well-insulated container. The power input to the liquid and its specific heat capacity are known. Which of the following quantities must be known in order to calculate the rate at which the temperature increases? A. ...
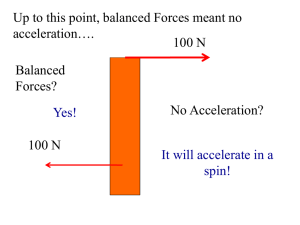
Unbalanced force system
... In order to nd the tension in the string, however, we need to consider individual block. Here, we consider block "A" for the simple reason that it is acted upon by a single force (T) in x-direction and analysis of force on block "A" will be simpler than that of block "B", which is acted by two forc ...
... In order to nd the tension in the string, however, we need to consider individual block. Here, we consider block "A" for the simple reason that it is acted upon by a single force (T) in x-direction and analysis of force on block "A" will be simpler than that of block "B", which is acted by two forc ...
Lecture 10 - Purdue Physics
... – Note: If vx is negative, the displacement is also negative. So, we count the area as negative. Lecture 10 ...
... – Note: If vx is negative, the displacement is also negative. So, we count the area as negative. Lecture 10 ...