Document
... 4. A mountain climber, in the process of crossing between two cliffs by a rope, pauses to rest. She weighs 535 N. As the drawing shows, she is closer to the left cliff than to the right cliff, with the result that the tensions in the left and the right sides of the rope are not the same. Find the te ...
... 4. A mountain climber, in the process of crossing between two cliffs by a rope, pauses to rest. She weighs 535 N. As the drawing shows, she is closer to the left cliff than to the right cliff, with the result that the tensions in the left and the right sides of the rope are not the same. Find the te ...
Universal Gravitation Student Guide Activity 1 - Earth Gravity
... 6. Now comes the experimental part. The initial position for mass 1 should probably be 0. That gives us a reference point. The initial position for mass 2 should be somewhere farther away. Try 0.2 (that would be 20 cm). Remember that the gravitational force is very small. Now make the masses large ...
... 6. Now comes the experimental part. The initial position for mass 1 should probably be 0. That gives us a reference point. The initial position for mass 2 should be somewhere farther away. Try 0.2 (that would be 20 cm). Remember that the gravitational force is very small. Now make the masses large ...
Gravitational Fields (AIS) - Atlanta International School Moodle
... • The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their mean distances from the sun. T1 2 r1 3 ...
... • The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their mean distances from the sun. T1 2 r1 3 ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... You can tell the difference between a moving object and one that's still. But how would you define motion? An object is in motion when its position changes. Position is the location of an object in space, and it is always relative to a frame of reference. We use many words to express position, such ...
... You can tell the difference between a moving object and one that's still. But how would you define motion? An object is in motion when its position changes. Position is the location of an object in space, and it is always relative to a frame of reference. We use many words to express position, such ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
... Example: A potter’s wheel is rotating around a vertical axis through its center at a frequency of 2.00 rev/s. The wheel can be considered a uniform disk of mass 4.80 kg and diameter 0.360 m. The potter then throws a 3.10 kg chunk of clay, approximately shaped as a flat disk of radius 11.0 cm, onto ...
... Example: A potter’s wheel is rotating around a vertical axis through its center at a frequency of 2.00 rev/s. The wheel can be considered a uniform disk of mass 4.80 kg and diameter 0.360 m. The potter then throws a 3.10 kg chunk of clay, approximately shaped as a flat disk of radius 11.0 cm, onto ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
... Example: A potter’s wheel is rotating around a vertical axis through its center at a frequency of 2.0 rev/s. The wheel can be considered a uniform disk of mass 4.8 kg and diameter 0.36 m. The potter then throws a 3.1 kg chunk of clay, approximately shaped as a flat disk of radius 11 cm, onto the ce ...
... Example: A potter’s wheel is rotating around a vertical axis through its center at a frequency of 2.0 rev/s. The wheel can be considered a uniform disk of mass 4.8 kg and diameter 0.36 m. The potter then throws a 3.1 kg chunk of clay, approximately shaped as a flat disk of radius 11 cm, onto the ce ...
advanced higher content statements
... 2 State that an unbalanced torque produces an angular acceleration. 3 State that the angular acceleration produced by an unbalanced torque depends on the moment of inertia of the object. 4 Explain that the moment of inertia of an object depends on the mass of the object and the distribution of the m ...
... 2 State that an unbalanced torque produces an angular acceleration. 3 State that the angular acceleration produced by an unbalanced torque depends on the moment of inertia of the object. 4 Explain that the moment of inertia of an object depends on the mass of the object and the distribution of the m ...
Word
... The students attempt to pull the trolley up the ramp with constant velocity. (This can be quite difficult and may take a few tries.) They should compare the reading on the balance when the trolley is on the ramp and still to when it is pulled at constant velocity. They then pull the trolley with con ...
... The students attempt to pull the trolley up the ramp with constant velocity. (This can be quite difficult and may take a few tries.) They should compare the reading on the balance when the trolley is on the ramp and still to when it is pulled at constant velocity. They then pull the trolley with con ...
Force Summation
... The combination of force and time depends on the needs of the skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accele ...
... The combination of force and time depends on the needs of the skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accele ...
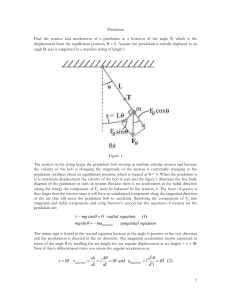
Pendulum
... The acceleration has two components; a radial component that always points along the string and a tangential component that points along the tangent toward the equilibrium. Since the acceleration is a vector it would be nice to express the components as a function of the angle . The tangential comp ...
... The acceleration has two components; a radial component that always points along the string and a tangential component that points along the tangent toward the equilibrium. Since the acceleration is a vector it would be nice to express the components as a function of the angle . The tangential comp ...
Dynamics Review Sheet Solutions
... 11. A child is riding on a merry-go-round. As the speed of the merry-go-round is doubled, the magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the child A. remains the same C. is halved B. is doubled D. is quadrupled 12. A 1,200-kilogram car traveling at 10 meters per second hits a tree that is brought ...
... 11. A child is riding on a merry-go-round. As the speed of the merry-go-round is doubled, the magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the child A. remains the same C. is halved B. is doubled D. is quadrupled 12. A 1,200-kilogram car traveling at 10 meters per second hits a tree that is brought ...
Momentum - Mr. Shaffer at JHS
... If momentum changes – what does not have to change? A) Mass B) Velocity C) Time When things change momentum, most of the time the object is changing its Velocity, and not its mass. Think about it… while walking down the hallway, if Wanted to change your momentum, would you change your mass or your s ...
... If momentum changes – what does not have to change? A) Mass B) Velocity C) Time When things change momentum, most of the time the object is changing its Velocity, and not its mass. Think about it… while walking down the hallway, if Wanted to change your momentum, would you change your mass or your s ...