MATH 231 Kepler`s Second Law
... magnitude of the cross product of the radius vector with the velocity vector. But the cross product of the radius vector with the radial component of the velocity will be zero, since these are parallel. On the other hand, the magnitude of the tangential component of the velocity vector is easily see ...
... magnitude of the cross product of the radius vector with the velocity vector. But the cross product of the radius vector with the radial component of the velocity will be zero, since these are parallel. On the other hand, the magnitude of the tangential component of the velocity vector is easily see ...
Guide_Test1
... 2. The following equations will be provided. Solve the given problems using these. ...
... 2. The following equations will be provided. Solve the given problems using these. ...
1 Introduction - Mechanics - College of Engineering
... geometric properties of bodies (size, shape, etc.) Time – describes succession of events Mass – measures resistance of bodies to a change in velocity (=acceleration) Force – describes action of one body on another. It is a vector quantity. Distinguished as contact or volumetric ...
... geometric properties of bodies (size, shape, etc.) Time – describes succession of events Mass – measures resistance of bodies to a change in velocity (=acceleration) Force – describes action of one body on another. It is a vector quantity. Distinguished as contact or volumetric ...
mg - UF Physics
... Draw a FBD to show all the forces acting on the object Choose a coordinate system. If the direction of the net force is known, choose axes so that the net force (and acceleration) are along one of the axes Find the net force by adding the forces as vectors Use Newton’s second law to relate the net f ...
... Draw a FBD to show all the forces acting on the object Choose a coordinate system. If the direction of the net force is known, choose axes so that the net force (and acceleration) are along one of the axes Find the net force by adding the forces as vectors Use Newton’s second law to relate the net f ...
Rotational Mechanics
... and goal-line runner," Tomlin said. "And that's been solid for us. We don't pretend that it's something mystical. We've just got to formulate good plans, call good plays and execute them." ...
... and goal-line runner," Tomlin said. "And that's been solid for us. We don't pretend that it's something mystical. We've just got to formulate good plans, call good plays and execute them." ...
CLASSICAL MECHANICS II - Makerere University Courses
... Special Relativity Lorentz transformation matrix; space and time four vectors; force and energy in relativistic mechanics The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Generalized coordinates; Lagrangian formulation and applications; Hamiltonian and application to simple problems including central orbits and small ...
... Special Relativity Lorentz transformation matrix; space and time four vectors; force and energy in relativistic mechanics The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Generalized coordinates; Lagrangian formulation and applications; Hamiltonian and application to simple problems including central orbits and small ...
Document
... We write an equation like this for every particle in the body and then add all these equations: ...
... We write an equation like this for every particle in the body and then add all these equations: ...
rotational kinetic energy
... platform begin to rotate if the man moves from the edge to the centre? (a) 22 rpm ...
... platform begin to rotate if the man moves from the edge to the centre? (a) 22 rpm ...
File
... the resistance of an object to changes in its rotational motion. (rotating objects keep rotating, non-rotating objects tend to stay still) • The further the mass is located from the axis of rotation, the greater the rotational inertia. • Greater rotational inertia means more laziness per mass. ...
... the resistance of an object to changes in its rotational motion. (rotating objects keep rotating, non-rotating objects tend to stay still) • The further the mass is located from the axis of rotation, the greater the rotational inertia. • Greater rotational inertia means more laziness per mass. ...
Newton`s Law of Motion.
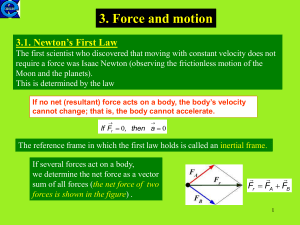
... • The law states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. • Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. • According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanc ...
... • The law states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. • Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. • According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanc ...
PPT - Modeling & Simulation Lab.
... His aim was to generalize complex numbers to three dimensions. Numbers of the form a+ib+jc, where a,b,c are real numbers and i2=j2=-1. He never succeeded in making this generalization. It has later been proven that the set of three-dimensional numbers is not closed under multiplication. Four num ...
... His aim was to generalize complex numbers to three dimensions. Numbers of the form a+ib+jc, where a,b,c are real numbers and i2=j2=-1. He never succeeded in making this generalization. It has later been proven that the set of three-dimensional numbers is not closed under multiplication. Four num ...
Physics 121 Exam Sheet - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Newton’s Third Law – The Third Law of Motion: If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B exerts a force, equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction, on body A, i.e.., FAB = FBA, where FAB is the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA is the force exerted on body A by body B. This law is ...
... Newton’s Third Law – The Third Law of Motion: If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B exerts a force, equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction, on body A, i.e.., FAB = FBA, where FAB is the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA is the force exerted on body A by body B. This law is ...
File
... Hence moment of inertia of a body about a given the axis is numerically equal to torque acting on the body rotating with unit angular acceleration about it. We may rewrite equation (9) in vector form as τ =Iα This equation is called Fundamental equation of rotation or law of rotation.This correspon ...
... Hence moment of inertia of a body about a given the axis is numerically equal to torque acting on the body rotating with unit angular acceleration about it. We may rewrite equation (9) in vector form as τ =Iα This equation is called Fundamental equation of rotation or law of rotation.This correspon ...
racing - MathinScience.info
... occurred in a situation. Motion can be determined by using the frame of reference to measure from point A to point B. The most common frame of reference is the horizon. ...
... occurred in a situation. Motion can be determined by using the frame of reference to measure from point A to point B. The most common frame of reference is the horizon. ...
PHYSICS SAE 4
... Newton’s Second Law Second Law – acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass. -the direction is in the direction of the net force Easier to see as an equation more commonly written ...
... Newton’s Second Law Second Law – acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass. -the direction is in the direction of the net force Easier to see as an equation more commonly written ...