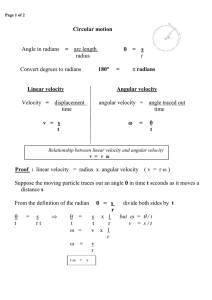
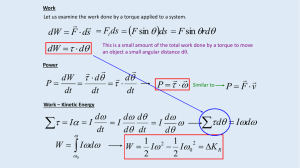
Rotational Kinetic Energy
... Angular Momentum Angular momentum-the product of the angular velocity of a body and its moment of inertia about the axis of rotation. Depends on the mass of the object and how it is distributed ...
... Angular Momentum Angular momentum-the product of the angular velocity of a body and its moment of inertia about the axis of rotation. Depends on the mass of the object and how it is distributed ...
Chapter 13 - AJRomanello
... FΔt = mΔV In an angular system the change in angular momentum is given by: FrΔt = IΔω or ΤΔt = IΔω ...
... FΔt = mΔV In an angular system the change in angular momentum is given by: FrΔt = IΔω or ΤΔt = IΔω ...
Study Notes
... on a planet that spins about its axis (big merry-go-round) so he is accelerating. The planet is also orbiting the sun which is rotating in the Milky Way galaxy, etc. To a physicist prior to the 1900’s the solution was to attach a reference frame to the luminiferous eather (the invisible, stationary ...
... on a planet that spins about its axis (big merry-go-round) so he is accelerating. The planet is also orbiting the sun which is rotating in the Milky Way galaxy, etc. To a physicist prior to the 1900’s the solution was to attach a reference frame to the luminiferous eather (the invisible, stationary ...
Answers - jpsaos
... MC The moment of inertia of a rigid body (a) depends on the axis of rotation, (b) cannot be zero, (c) depends on mass distribution, (d) all of the preceding. (d) MC Which of the following best describes the physical quantity called torque: (a) rotational analogue of force, (b) energy due to rotation ...
... MC The moment of inertia of a rigid body (a) depends on the axis of rotation, (b) cannot be zero, (c) depends on mass distribution, (d) all of the preceding. (d) MC Which of the following best describes the physical quantity called torque: (a) rotational analogue of force, (b) energy due to rotation ...
Lecture 6
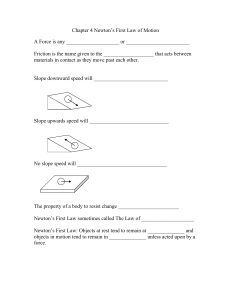
... First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle is not zero, the particle experiences an acceleration in the same direction ...
... First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle is not zero, the particle experiences an acceleration in the same direction ...
Conceptual Physics
... Volume is a measure of how much ________________ and object occupies. ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: ...
... Volume is a measure of how much ________________ and object occupies. ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: ...
Holt Physics--Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Dynasmics
... *the units for moments of inertia are (kg)(m2) ...
... *the units for moments of inertia are (kg)(m2) ...
Forces in Mechanical Systems
... Line of action – line along the applied force that extends in both directions. ...
... Line of action – line along the applied force that extends in both directions. ...
Document
... It rotates due to the frictional force at the point of contact, that is in a direction opposite to the direction the wheel would slip. The rolling motion associated with this wheel can be modeled as if all parts of the wheel rotate about the point of contact. Using this model, what can we say about ...
... It rotates due to the frictional force at the point of contact, that is in a direction opposite to the direction the wheel would slip. The rolling motion associated with this wheel can be modeled as if all parts of the wheel rotate about the point of contact. Using this model, what can we say about ...
17AP_Physics_C_-_Rotational_Motion_II
... equal to ZERO and thus the ANGULAR MOMENTUM is CONSERVED. Here is a common example. An ice skater begins a spin with his arms out. His angular velocity at the beginning of the spin is 2.0 rad/s and his moment of inertia is 6 kgm2. As the spin proceeds he pulls in his arms decreasing his moment of in ...
... equal to ZERO and thus the ANGULAR MOMENTUM is CONSERVED. Here is a common example. An ice skater begins a spin with his arms out. His angular velocity at the beginning of the spin is 2.0 rad/s and his moment of inertia is 6 kgm2. As the spin proceeds he pulls in his arms decreasing his moment of in ...
Relevant Equations
... U1-2: Work of a non-conservative variable force ΔT = change in kinetic energy ΔVg = change in potential energy ΔVe = change in potential energy (for a spring) g = gravitational constant (9.81 meters per second squared or 32.2 feet per second squared) h = height above or below reference datum (can be ...
... U1-2: Work of a non-conservative variable force ΔT = change in kinetic energy ΔVg = change in potential energy ΔVe = change in potential energy (for a spring) g = gravitational constant (9.81 meters per second squared or 32.2 feet per second squared) h = height above or below reference datum (can be ...
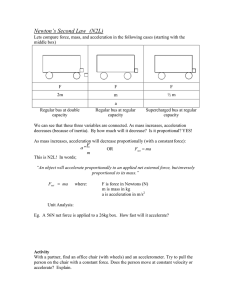
Newton`s Second Law
... 11. A woman astronaut has a mass of 60 kg. What will be her weight on the moon? ...
... 11. A woman astronaut has a mass of 60 kg. What will be her weight on the moon? ...
Inertia and Mass
... In each of the following situations, represent the object with a dot. Sketch all the forces acting upon the object, making the length of each vector represent the magnitude of the force. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). Describe the net force and acceleration. ...
... In each of the following situations, represent the object with a dot. Sketch all the forces acting upon the object, making the length of each vector represent the magnitude of the force. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). Describe the net force and acceleration. ...