* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conceptual Physics
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
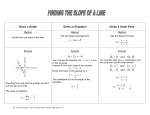
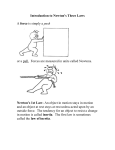
Chapter 4 Newton’s First Law of Motion A Force is any ____________________ or ________________________ Friction is the name given to the ___________________ that acts between materials in contact as they move past each other. Slope downward speed will ____________________________ Slope upwards speed will ______________________________ No slope speed will __________________________________ The property of a body to resist change _______________________ Newton’s First Law sometimes called The Law of ____________________ Newton’s First Law: Objects at rest tend to remain at ______________ and objects in motion tend to remain in ______________ unless acted upon by a force. Mass is a measure of ________________________ Volume is a measure of how much ________________ and object occupies. ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: W ______________________ m ______________________ g ______________________ The SI unit of Weight is the _________________________ The combination of all forces acting on an object is called the ___________________________. It is this force that changes an objects motion. Applied Force Net Force 6N 6N 12 N 12 N 6N 6N An object is said to be in ___________________________ when the net forces equal zero. Lets set a block on a table If the block is stationary the net force on the block is _________________ Support Force W = mg The support force is often called the _______________________________ The magnitude of the block’s weight must ______________ the magnitude of the support force. Another Example of Equilibrium 50 N 50 N 100 N Vector Addition of Forces Determine the reading on the scale: A 1kg B C 1kg 1kg