* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
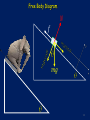
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
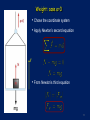
Lecture 12 Newton’s first Law If there are no external forces, the object does not change its velocity and direction. LAW of INERTIA!!! 2 Newton’s Second Law Acceleration Frame A 𝑣𝑣21≠=𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡 0 3 Newton’s Third Law 𝐹12 = −𝐹21 F12 F21 • Forces exist always in pairs. • These forces are called action-reaction forces • The action and reaction forces act on different objects 4 Examples • When you push the wall with force F then the wall pushes you with the same force 5 Action-reaction 6 Summary: Newton’s third Law • • Interacting objects exert equal forces upon each other These are called action reaction forces • Every action receives an equal but opposite reaction 7 The Gravitational Force - Weight 𝐹′ SI unit: 1 N= 1 kg m/s2 𝐹 = 𝑚𝑎 𝐹 𝑔 = 𝑚𝑔 𝑔 𝑊 = 𝑚𝑔 • • • 𝐹𝑔 𝐹𝑔 Weight and mass are NOT the same: Mass is an intrinsic property of the object determined by the type and amount of atoms The weight is the measure of the gravitational force and therefore dependence on the conditions how the force is measured 8 Weight: dependence on the environment No gravity Mass is not a weight!!! 9 Normal force • • Normal force is the force acting to the object due to the deformation of the surface. Normal force is always perpendicular to the surface 𝑁 𝑁 𝑁 𝑚𝑔 10 • • • Friction Friction is the resistance to the motion due to the interaction of the object with the environment The direction of frictional force is always opposite to the direction of motion Friction is always proportional to the normal force N 11 Tension • Tension is the force transmitted through a “rope” from one end to the other. • An ideal cord has zero mass, does not stretch, and the tension is the same throughout the cord. 12 Free Body Diagram 𝐹 = 𝑚𝑎 • Idealize (simplify) the system • Identify all the forces acting on the object • Choose an appropriate coordinate system Real life 𝑇 − 𝑚𝑔 = 0 𝑇 = 𝑚𝑔 Free body diagram 𝑇 y x 𝑚𝑔 13 Free Body Diagram 𝑁 𝑓 𝑚𝑔 14 Weight: case a=0 • Chose the coordinate system • Apply Newton’s second equation • From Newton’s third equation y 15 Weight: case a>0 y • The object become heaver 16 Weight: case a<0 y • • The object become lighter For a=g the object becomes weightless 17