2. Laws of Motion
... What is Newton’s second law? If the resultant force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the o ...
... What is Newton’s second law? If the resultant force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the o ...
Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
... Conservation of angular momentum means that the total angular momentum around any axis must be constant. This is why gyroscopes are so stable. ...
... Conservation of angular momentum means that the total angular momentum around any axis must be constant. This is why gyroscopes are so stable. ...
Document
... positions, and not on the path taken. (True or False) 19. Whenever a force is applied, and there is non-zero displacement then work is always done. (True or False). ...
... positions, and not on the path taken. (True or False) 19. Whenever a force is applied, and there is non-zero displacement then work is always done. (True or False). ...
Chapter 5 Summary
... --If you can, use the resulting expression to solve for the unknown you are seeking. If not, and you find more unknowns in the relationship than you have equations, either repeat the process along the other coordinate axis or, if that doesn't help, pick another body in the system and start the whole ...
... --If you can, use the resulting expression to solve for the unknown you are seeking. If not, and you find more unknowns in the relationship than you have equations, either repeat the process along the other coordinate axis or, if that doesn't help, pick another body in the system and start the whole ...
Newton`s Law Review Problems
... San Francisco: simply ascent in a helicopter high over Washington and wait three hours until San Francisco passes below. Is this person correct? Explain No. Objects that are on the ground are still moving forward with the Earth, including the helicopter. As it lifts off, no external forces act upon ...
... San Francisco: simply ascent in a helicopter high over Washington and wait three hours until San Francisco passes below. Is this person correct? Explain No. Objects that are on the ground are still moving forward with the Earth, including the helicopter. As it lifts off, no external forces act upon ...
以人为本 深化改革 努力探索实验室开放的新路子
... To explain this phenomenon, an inertial force is introduced into its force diagram: ...
... To explain this phenomenon, an inertial force is introduced into its force diagram: ...
Newton`s Laws
... normal force on an object that is being supported by a surface is the component of the supporting force that is perpendicular to the surface. ...
... normal force on an object that is being supported by a surface is the component of the supporting force that is perpendicular to the surface. ...
Circular Motion HW-4
... The L-shaped object in Figure 1 consists of three masses connected by light rods. What net torque must be applied to this object to give it an angular acceleration of 1.20 rad/s2 if it is rotated about (a) the x axis, (b) the y axis, or (c) the z axis (which is through the origin & perpendicular to ...
... The L-shaped object in Figure 1 consists of three masses connected by light rods. What net torque must be applied to this object to give it an angular acceleration of 1.20 rad/s2 if it is rotated about (a) the x axis, (b) the y axis, or (c) the z axis (which is through the origin & perpendicular to ...
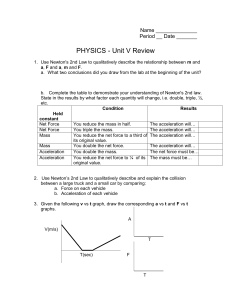
Unit V review
... b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve quantitative problems involving forces, mass and acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law. a. Having determined the net force (as in #3), and given the mas ...
... b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve quantitative problems involving forces, mass and acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law. a. Having determined the net force (as in #3), and given the mas ...
Physics - Partners4results
... B. rate at which something turns C. measure of how much an object weighs D. not given 8. An object’s resistance to change in rotational motion is ____. A. torque B. centripetal force C. rotational inertia D. angular acceleration 9. Among the following, the largest torque is the one provided by ____. ...
... B. rate at which something turns C. measure of how much an object weighs D. not given 8. An object’s resistance to change in rotational motion is ____. A. torque B. centripetal force C. rotational inertia D. angular acceleration 9. Among the following, the largest torque is the one provided by ____. ...
The Galaxy Education System S. N. Kansagra School Sub: Physics
... 15) Prove that F = ma. State the condition when it holds true. 16) Define (i) balanced forces (ii) unbalanced forces. 17) Name the SI unit of (i) linear momentum (ii) rate of change of momentum. 18) State the relationship between Force, mass and acceleration. Draw graphs showing the relationship bet ...
... 15) Prove that F = ma. State the condition when it holds true. 16) Define (i) balanced forces (ii) unbalanced forces. 17) Name the SI unit of (i) linear momentum (ii) rate of change of momentum. 18) State the relationship between Force, mass and acceleration. Draw graphs showing the relationship bet ...
Physics Final Exam Review Packet
... Tangential Acceleration What units should be used for angular displacement? ...
... Tangential Acceleration What units should be used for angular displacement? ...
2009 JC1 H2 Physics
... (iii) when the helicopter is ascending vertically with a constant acceleration of 1.4 m s-2. Since the helicopter is ascending vertically with a constant acceleration, there must be a resultant force acting on the helicopter. Consider the vertical direction, Fnet = ma T cos 30 + T cos 30 + (- W) = ...
... (iii) when the helicopter is ascending vertically with a constant acceleration of 1.4 m s-2. Since the helicopter is ascending vertically with a constant acceleration, there must be a resultant force acting on the helicopter. Consider the vertical direction, Fnet = ma T cos 30 + T cos 30 + (- W) = ...