* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
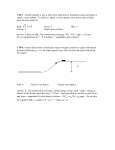
Ch 4 & 6 Review Test Multiple Choice: 1. If distance is increased by 2 times and the mass of one of the objects by 4 times, then the gravitational force of attraction between the two objects would (a) (b) (c) (d) Increase by four times Decrease by four times Increase by 2 times Will not change 2. A ball is shot at an angle of 450 to the horizontal. What happens to the magnitude of the ball’s vertical acceleration during the total time interval that the ball is in the air? a. it decreases, then increases b. it decreases, then remain the same a. it increases, then decreases d. It remains the same 3. A man standing on a scale in an elevator notices that the scale reads 0 N. Which type of movement of the elevator causes this ? Accelerating upward at 9.8 m/s2 Accelerating downward at 9.8 m/s2 Moving upward at constant speed Moving downward at constant speed a. b. c. d. 4. If Newton was holding a bag of apples of 1 kg mass in his hand at a height 10 m above the ground the net force on the apple is (a) (b) (c) (d) 9.8 N 0N 98 N impossible to tell 5. If a truck collides head on with a cycle, the force of impact on the cycle as compared to the truck is ____________. The deceleration of the truck is ____________ as compared to the cycle. (a) Larger (b) Smaller (c) Same 6. Action Reaction forces always act on the same object (True or False) 7. Two forces are applied to a 3 kg block on a frictionless surface. The acceleration of the block is 10 N 4N 3 kg (a) 2 m/s2 East (b) 6 m/s2 West (c) 6 m/s2 East (d) 2 m/s2 West 8. Suppose a worker has to move crates onto a ramp as shown below. The kinetic energy just before it coasts up the ramp is 24 J. At the top of the ramp the crate stops and has 10 J of potential energy. How much work was done by friction of the ramp? (a) -24 J (c) -14 J (b) 14 J (d) -34 J 9. In order to have maximum efficiency the worker should push the carts on the ground at an angle equal to (a) 0 degrees (d) 90 degrees (b) 45 degrees (d) 180 degrees 10. A 100 kg sail boat goes from rest to 10.0 m/s with a huge gust of wind. How much work did the wind do on the sailboat? (a) 5000 J (c) 40000 J (b) 10000 J (d) 500 J 11. If the sailboat went from 0.0 m/s to 10 in 5 s what power did the wind deliver? (a) 250 W (c) 4000 W (b) 1000 W (d) 2000 W 12. Suppose you toss a coin to help you make a decision on this test. If the 10 g quarter went 100 cm into the air. How much work did you do on the quarter with your hand ? (a) 0.98 J (b) 0.098 J (c) 19.6 J (d) 10 J 13. The amount of potential energy possessed by an elevated object is equal to (a) the distance it is lifted (b) the power used to lift it (c) the work done in lifting it (d) the value of the acceleration due to gravity (e) the force needed to lift it. 14. An arrow in a bow has 140J of elastic potential energy. Assuming frictional loss of - 40 J, how much kinetic energy will the arrow have after it has been shot? (a) 140 J (b) - 40 J (c) 40 J (d) 100 J (e) 0 J 15. Which requires more work: lifting a 40-kg sack vertically 3 meters or lifting a 20-kg sack vertically 6 meters? (a) Lifting the 40-kg sack (b) Lifting the 20-kg sack (c) Both require the same amount of work. 16. A job is done slowly, and an identical job is done quickly. Both jobs require the same amount of work but different amounts of _______________. (a) energy (b) power (c) both a and b (d) none of the above 17. Identify conservative and non conservative forces (a) Gravity (b) Kinetic Friction (c) Tension (d) Electric (e) Elastic 18. The work done by a non-conservative force only depends on the initial and final positions, and not on the path taken. (True or False) 19. Whenever a force is applied, and there is non-zero displacement then work is always done. (True or False). Free-Response: 1. Three simultaneous forces act on an object. The first force is 220 N @ 200 NE, the second is 149 N @ 390 NE and the third is 76 N @ 510 SE. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force and acceleration. Draw the vector diagram. Force X component Y component F1 F2 F3 Sum of forces Fx = Fy = 2. Two cable wires suspend a 105 N (weight) sign as shown in the drawing below. Draw the force vectors in the figure. T* 40 0 40 0 T T Welcome To Hogwarts (a) Identify all the known and unknown variables (b) Identify the equation(s) to be used (c) Find the tension with correct units and show your work 3. A particle starting from point A in the drawing below is projected down the curved runway. Upon leaving the runway at point B, the particle is traveling straight upward and reaches a height of 9.0 m above the floor before falling back down. Ignoring friction and air resistance, find the initial speed of the particle at point A. A vi 9.0 m 4.0 m B