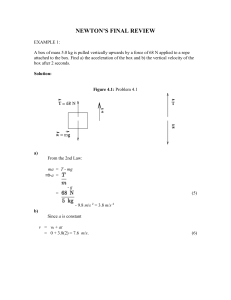
Final Newtons Review
... e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 3, then the new accelerati ...
... e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 3, then the new accelerati ...
Sample
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
Packet 8: Impulse Momentum
... By the time we finish this unit and all related activities you should be able to: 1. Define momentum; distinguish between momentum and velocity. 2. Calculate the momentum, impulse, or force exerted on an object. 3. Distinguish between elastic and inelastic collisions. 4. Use the law of conservation ...
... By the time we finish this unit and all related activities you should be able to: 1. Define momentum; distinguish between momentum and velocity. 2. Calculate the momentum, impulse, or force exerted on an object. 3. Distinguish between elastic and inelastic collisions. 4. Use the law of conservation ...
Physics I - Rose
... Solve: Only spring 2 touches the mass, so the net force on the mass is Fm F2 on m. Newton’s third law tells us that F2 on m Fm on 2 and that F2 on 1 F1 on 2. From Fnet ma, the net force on a massless spring is zero. Thus Fw on 1 F2 on 1 k1x1 and Fm on 2 F1 on 2 k2x2. Combining thes ...
... Solve: Only spring 2 touches the mass, so the net force on the mass is Fm F2 on m. Newton’s third law tells us that F2 on m Fm on 2 and that F2 on 1 F1 on 2. From Fnet ma, the net force on a massless spring is zero. Thus Fw on 1 F2 on 1 k1x1 and Fm on 2 F1 on 2 k2x2. Combining thes ...
Textbook Practice Problems
... Discuss balanced and unbalanced forces and how to find the net force on an object by drawing all the forces and their directions. Can the net force on an object be zero if only one force is acting on the object? (4D) Use the Promethean Interactive White Board Flip Chart - “Newton’s Laws of Motio ...
... Discuss balanced and unbalanced forces and how to find the net force on an object by drawing all the forces and their directions. Can the net force on an object be zero if only one force is acting on the object? (4D) Use the Promethean Interactive White Board Flip Chart - “Newton’s Laws of Motio ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... Galileo tested his idea by rolling balls along plane surfaces tilted at different angles. • A ball rolling down an inclined plane speeds up. • A ball rolling up an inclined plane—in a direction opposed by gravity—slows down. • A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal plane has almost ...
... Galileo tested his idea by rolling balls along plane surfaces tilted at different angles. • A ball rolling down an inclined plane speeds up. • A ball rolling up an inclined plane—in a direction opposed by gravity—slows down. • A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal plane has almost ...
FORCES AND NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... Q4.15. Reason: As your foot comes into contact with the floor the force of static friction acts in the direction necessary to prevent motion of the foot. The friction prevents your foot from slipping forward, so the direction of the force of the floor on your foot is backward. Assess: Static frictio ...
... Q4.15. Reason: As your foot comes into contact with the floor the force of static friction acts in the direction necessary to prevent motion of the foot. The friction prevents your foot from slipping forward, so the direction of the force of the floor on your foot is backward. Assess: Static frictio ...
Interim Assessment Sample Question
... motion. The student is expected to (A) develop and interpret a free body diagram for force analysis and (C) demonstrate the effects of forces on the motion of objects IPC TEKS 4 The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. The student is expected to (B) investigate and de ...
... motion. The student is expected to (A) develop and interpret a free body diagram for force analysis and (C) demonstrate the effects of forces on the motion of objects IPC TEKS 4 The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. The student is expected to (B) investigate and de ...
Higher Physics Scholar ODU 2015
... second before the ball starts moving downwards. When it is moving back towards the Earth, the velocity of the ball is negative, because we have defined upwards as the positive direction. We have described the difference between the scalar quantities distance and speed and the vector quantities displ ...
... second before the ball starts moving downwards. When it is moving back towards the Earth, the velocity of the ball is negative, because we have defined upwards as the positive direction. We have described the difference between the scalar quantities distance and speed and the vector quantities displ ...
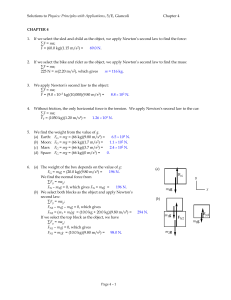
CHAPTER 4
... FTmax = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2) = 5.04104 N. The minimum tension will be exerted by the motor when the elevator is accelerating downward. We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the car: y-component: FTmin – mg = ma, or FTmin = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(– 0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2 ...
... FTmax = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2) = 5.04104 N. The minimum tension will be exerted by the motor when the elevator is accelerating downward. We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the car: y-component: FTmin – mg = ma, or FTmin = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(– 0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2 ...
Document
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
M: Chapter 2: Force and Newton`s Laws
... What is gravity? The force of gravity exists between any two objects that have mass. Gravity always is attractive and pulls objects toward each other. A gravitational attraction exists between you and every object in the universe that has mass. However, the force of gravity depends on the mass of th ...
... What is gravity? The force of gravity exists between any two objects that have mass. Gravity always is attractive and pulls objects toward each other. A gravitational attraction exists between you and every object in the universe that has mass. However, the force of gravity depends on the mass of th ...
Lecture 29: Friction Examples
... We can use the kinematic equation relating position to time, x = x0 + v0xt + 12axt2, to find the time of the sea lion’s sli be necessary, however, to first determine the acceleration of the sea lion in the x direction, ax. ...
... We can use the kinematic equation relating position to time, x = x0 + v0xt + 12axt2, to find the time of the sea lion’s sli be necessary, however, to first determine the acceleration of the sea lion in the x direction, ax. ...