The Physics of Renewable Energy
... A. The momentum of an object always remains constant. B. The momentum of a closed system always remains constant. C. Momentum can be stored in objects such as a spring. D. All of the above. ...
... A. The momentum of an object always remains constant. B. The momentum of a closed system always remains constant. C. Momentum can be stored in objects such as a spring. D. All of the above. ...
LCP1 INTUITIVE PHYSICS
... LCP1 begins with the intuitive understanding of motion, then continues to discuss motion in qualitative terms first, before appealing to the Galileo’s kinematics and Newton’s dynamics in quantitative terms. We will continue discussing these laws in LCP 2 by following the history of the concepts abou ...
... LCP1 begins with the intuitive understanding of motion, then continues to discuss motion in qualitative terms first, before appealing to the Galileo’s kinematics and Newton’s dynamics in quantitative terms. We will continue discussing these laws in LCP 2 by following the history of the concepts abou ...
chapter 3 part 1
... identified: the distinction between forces that act on an object and forces that act by the object. This leads to his Third Law of Motion: For every force by a first object on a second object, there is a force by the second object on the first object with the same magnitude but in the opposite direc ...
... identified: the distinction between forces that act on an object and forces that act by the object. This leads to his Third Law of Motion: For every force by a first object on a second object, there is a force by the second object on the first object with the same magnitude but in the opposite direc ...
Giancoli Ch 8.Word
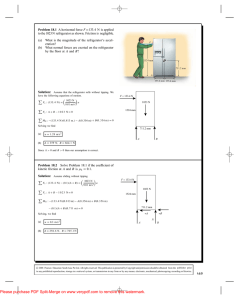
... 33. The force to produce the required torque is Fwrench = /L = (80 m · N)/(0.30 m) = 2.7 102 N. Because this torque is balanced by the torque produced by the bolt on the wrench, an equal torque is produced on the bolt. Because there are six points where a force is applied to the bolt, we have Fbo ...
... 33. The force to produce the required torque is Fwrench = /L = (80 m · N)/(0.30 m) = 2.7 102 N. Because this torque is balanced by the torque produced by the bolt on the wrench, an equal torque is produced on the bolt. Because there are six points where a force is applied to the bolt, we have Fbo ...
CHAPTER 8
... 33. The force to produce the required torque is Fwrench = /L = (80 m · N)/(0.30 m) = 2.7 102 N. Because this torque is balanced by the torque produced by the bolt on the wrench, an equal torque is produced on the bolt. Because there are six points where a force is applied to the bolt, we have Fbo ...
... 33. The force to produce the required torque is Fwrench = /L = (80 m · N)/(0.30 m) = 2.7 102 N. Because this torque is balanced by the torque produced by the bolt on the wrench, an equal torque is produced on the bolt. Because there are six points where a force is applied to the bolt, we have Fbo ...
03_PearsonPhysics_ch03_1
... object without considering the cause. When designing a structure, the kinematics quantities that an architect considers are displacement, velocity, and acceleration. But to predict how and explain why a structure moves, an architect must understand dynamics. Dynamics deals with the effects of forces ...
... object without considering the cause. When designing a structure, the kinematics quantities that an architect considers are displacement, velocity, and acceleration. But to predict how and explain why a structure moves, an architect must understand dynamics. Dynamics deals with the effects of forces ...
Acceleration
... During part of the journey the car is driven at a constant speed for five minutes. Which one of the equations links distance travelled, speed and time? ...
... During part of the journey the car is driven at a constant speed for five minutes. Which one of the equations links distance travelled, speed and time? ...
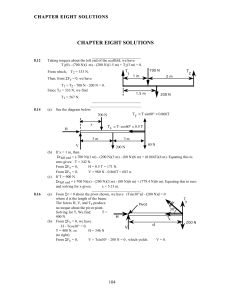
chapter eight solutions - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
... First, apply the above equation about the x axis. We have, Ix = (3 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(4kg)(9 m2) = 99.0 kg m2. About the y axis, we have Iy = (3 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (4kg)(4 m2) = 44.0 kg m2. The distance, r, (from an axis through O and perpendicular to the pag ...
... First, apply the above equation about the x axis. We have, Ix = (3 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(4kg)(9 m2) = 99.0 kg m2. About the y axis, we have Iy = (3 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (4kg)(4 m2) = 44.0 kg m2. The distance, r, (from an axis through O and perpendicular to the pag ...