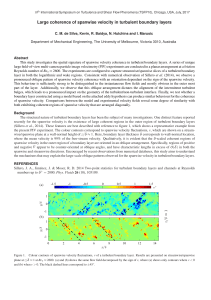
Momentum Review - KEY
... 1. Distinguish between mass and momentum. Which is inertia and which is inertia in motion. (7.1) An objects inertia is basically defined by its mass. An objects momentum is its mass multiplied by its velocity. This means that Mass is Inertia and Momentum is inertia in motion. 2. a. Which has the gre ...
... 1. Distinguish between mass and momentum. Which is inertia and which is inertia in motion. (7.1) An objects inertia is basically defined by its mass. An objects momentum is its mass multiplied by its velocity. This means that Mass is Inertia and Momentum is inertia in motion. 2. a. Which has the gre ...
Forces - Ateneonline
... •A coordinate system is a must. •Do not include fictitious forces. Remember that ma is itself not a force! •You may indicate the direction of the body’s acceleration or direction of motion if you wish, but it must be done well off to the side of the free body diagram. ...
... •A coordinate system is a must. •Do not include fictitious forces. Remember that ma is itself not a force! •You may indicate the direction of the body’s acceleration or direction of motion if you wish, but it must be done well off to the side of the free body diagram. ...
Chapter 6-10 Resources
... 6. The object described in the Question 5 has a velocity vector v1 at the beginning of the time interval and v2 at the end of the time interval. Write an algebraic expression that describes the object’s average acceleration during this time interval. ...
... 6. The object described in the Question 5 has a velocity vector v1 at the beginning of the time interval and v2 at the end of the time interval. Write an algebraic expression that describes the object’s average acceleration during this time interval. ...
F - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Fnet = ma (or F = ma ) Newton’s second law EXAMPLE: An object has a mass of 25 kg. A tension of R 50 n and a friction force of 30 n are acting on it as shown. What is its acceleration? 50 n SOLUTION: Ff The vertical forces W and R 30 n cancel out. W The net force is thus Fnet = 50 – 30 = 20 n (+x ...
... Fnet = ma (or F = ma ) Newton’s second law EXAMPLE: An object has a mass of 25 kg. A tension of R 50 n and a friction force of 30 n are acting on it as shown. What is its acceleration? 50 n SOLUTION: Ff The vertical forces W and R 30 n cancel out. W The net force is thus Fnet = 50 – 30 = 20 n (+x ...
Gr. 11 Physics Forces
... We will use a spring scale to measure the size of forces. First you need to calibrate the spring scale. Hold the scale horizontally or vertically just as you will use it when measuring, but without pulling on the hook. Adjust the scale (a sliding cover or nut at the top) so it reads zero. The scale ...
... We will use a spring scale to measure the size of forces. First you need to calibrate the spring scale. Hold the scale horizontally or vertically just as you will use it when measuring, but without pulling on the hook. Adjust the scale (a sliding cover or nut at the top) so it reads zero. The scale ...
Stacey Carpenter - University of Hawaii System
... Everyone uses the term momentum, but what is it? How is it defined in physics? If you were playing football, and someone was about to tackle you, what are the two main things you'd think about? Probably how big they are and how fast they're moving. The word momentum is often used to describe somethi ...
... Everyone uses the term momentum, but what is it? How is it defined in physics? If you were playing football, and someone was about to tackle you, what are the two main things you'd think about? Probably how big they are and how fast they're moving. The word momentum is often used to describe somethi ...
Work and Kinetic Energy
... he concept of energy is one of the most important topics in science and engineering. In everyday life, we think of energy in terms of fuel for transportation and heating, electricity for lights and appliances, and foods for consumption. However, these ideas do not really define energy. They merely te ...
... he concept of energy is one of the most important topics in science and engineering. In everyday life, we think of energy in terms of fuel for transportation and heating, electricity for lights and appliances, and foods for consumption. However, these ideas do not really define energy. They merely te ...
Momentum - Net Start Class
... Impulse explains the operation of air bags, etc. An air bag increases the time that the change in momentum occurs over. The product of the force and t must equal the change in momentum. If t is increased, then the force must be decreased in order for their product to be constant. Angular momentum ...
... Impulse explains the operation of air bags, etc. An air bag increases the time that the change in momentum occurs over. The product of the force and t must equal the change in momentum. If t is increased, then the force must be decreased in order for their product to be constant. Angular momentum ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... Systems can contain any number of objects, and the objects can stick together or come apart in a collision. Under these conditions, the law of conservation of momentum states that the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not change. This law will enable you to make a connection between condi ...
... Systems can contain any number of objects, and the objects can stick together or come apart in a collision. Under these conditions, the law of conservation of momentum states that the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not change. This law will enable you to make a connection between condi ...
Lectures 5-12
... Let us consider rewriting Newton’s law in terms of the new coordinate . Note that ...
... Let us consider rewriting Newton’s law in terms of the new coordinate . Note that ...