Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit II Dynamics
... action force: a force initiated by object A on object B apparent weight: the negative of the normal force acting on an object coefficient of friction: proportionality constant relating the magnitude of the force of friction to the magnitude of the normal force field: a three-dimensional region of in ...
... action force: a force initiated by object A on object B apparent weight: the negative of the normal force acting on an object coefficient of friction: proportionality constant relating the magnitude of the force of friction to the magnitude of the normal force field: a three-dimensional region of in ...
Pacing Guide for Physics
... (tip-to-tail and parallelogram) to add 2 or more vectors together. Sticks of different lengths may also be utilized as the actual vectors. ...
... (tip-to-tail and parallelogram) to add 2 or more vectors together. Sticks of different lengths may also be utilized as the actual vectors. ...
Chapter 2 Review of Forces and Moments
... using Newton’s law of gravitation; electrostatic forces acting between charged particles are governed by Coulomb’s law; electromagnetic forces acting between current carrying wires are governed by Ampere’s law; buoyancy forces are governed by laws describing hydrostatic forces in fluids. Some of the ...
... using Newton’s law of gravitation; electrostatic forces acting between charged particles are governed by Coulomb’s law; electromagnetic forces acting between current carrying wires are governed by Ampere’s law; buoyancy forces are governed by laws describing hydrostatic forces in fluids. Some of the ...
Force Vectors
... 2.6 Addition/Subtraction of Cartesion vectors Since any vector in 3-D can be expressed as components in x,y,z directions, we just need to add the corresponding components since the components are scalars. ...
... 2.6 Addition/Subtraction of Cartesion vectors Since any vector in 3-D can be expressed as components in x,y,z directions, we just need to add the corresponding components since the components are scalars. ...
Ch 5 Solutions Glencoe 2013
... 20. Thomas sits on a small rug on a polished wooden floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rug and the slippery wooden floor is only 0.12. If Thomas weighs 650 N, what horizontal force is needed to pull the rug and Thomas across the floor at a constant speed? SOLUTION: At constant ...
... 20. Thomas sits on a small rug on a polished wooden floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rug and the slippery wooden floor is only 0.12. If Thomas weighs 650 N, what horizontal force is needed to pull the rug and Thomas across the floor at a constant speed? SOLUTION: At constant ...
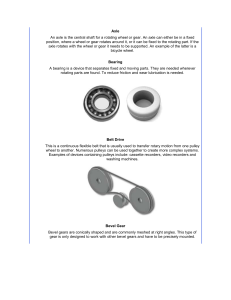
Axle
... surfaces to reduce friction. Typical examples of lubricants are oil and grease. Mechanical Advantage (MA) This is the amount by which a machine multiplies the effort put into it. For example; if you have a pulley system which requires 10lb. of effort to lift a 20lb. load the system has a mechanical ...
... surfaces to reduce friction. Typical examples of lubricants are oil and grease. Mechanical Advantage (MA) This is the amount by which a machine multiplies the effort put into it. For example; if you have a pulley system which requires 10lb. of effort to lift a 20lb. load the system has a mechanical ...
10 Circular Motion
... A heavy iron ball is attached by a spring to a rotating platform, as shown in the sketch. Two observers, one in the rotating frame and one on the ground at rest, observe its motion. Which observer sees the ball being pulled outward, stretching the spring? Which observer sees the spring pulling the b ...
... A heavy iron ball is attached by a spring to a rotating platform, as shown in the sketch. Two observers, one in the rotating frame and one on the ground at rest, observe its motion. Which observer sees the ball being pulled outward, stretching the spring? Which observer sees the spring pulling the b ...
10 Circular Motion
... A heavy iron ball is attached by a spring to a rotating platform, as shown in the sketch. Two observers, one in the rotating frame and one on the ground at rest, observe its motion. Which observer sees the ball being pulled outward, stretching the spring? Which observer sees the spring pulling the b ...
... A heavy iron ball is attached by a spring to a rotating platform, as shown in the sketch. Two observers, one in the rotating frame and one on the ground at rest, observe its motion. Which observer sees the ball being pulled outward, stretching the spring? Which observer sees the spring pulling the b ...
Exam 3 Review Questions PHY 2425 - Exam 3
... Section: 8–2 Topic: Kinetic Energy of a System Type: Conceptual 12 A golf ball and a Ping-Pong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber. When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed. B) potential energy. C) kinetic energy. D) momentum. E) speed, potential energy, kinetic ener ...
... Section: 8–2 Topic: Kinetic Energy of a System Type: Conceptual 12 A golf ball and a Ping-Pong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber. When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed. B) potential energy. C) kinetic energy. D) momentum. E) speed, potential energy, kinetic ener ...
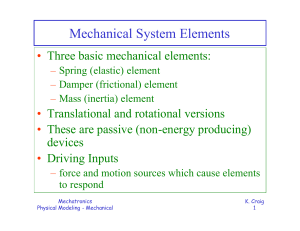
Mechanical System Elements
... – Real physical bodies never display ideal rigid behavior when being accelerated. – The pure / ideal inertia element is a model, not a real object. Mechatronics Physical Modeling - Mechanical ...
... – Real physical bodies never display ideal rigid behavior when being accelerated. – The pure / ideal inertia element is a model, not a real object. Mechatronics Physical Modeling - Mechanical ...
ch18
... 18.1 Kinetic Energy • Consider the rigid body as shown, which is represented here by a slab moving in the inertial x-y reference plane. • An arbitrary ith particle of the body, having a mass dm, is located at r from the arbitrary point P. • If at the instant shown the particle has a velocity vi, th ...
... 18.1 Kinetic Energy • Consider the rigid body as shown, which is represented here by a slab moving in the inertial x-y reference plane. • An arbitrary ith particle of the body, having a mass dm, is located at r from the arbitrary point P. • If at the instant shown the particle has a velocity vi, th ...
More Applications of Newton`s Laws
... 53. What is the Earth's gravitational force on a 4000 kg body orbiting 2800 km above the surface in N? The Earth’s radius is 6.37 × 10 6 m. a. 5.9 × 10 6 b. 3.9 × 10 4 c. 2.0 × 10 4 d. 1.9 × 10 4 e. 5.3 × 10 6 ANS: d 54. The Earth’s gravitational force must be included when calculating the centripet ...
... 53. What is the Earth's gravitational force on a 4000 kg body orbiting 2800 km above the surface in N? The Earth’s radius is 6.37 × 10 6 m. a. 5.9 × 10 6 b. 3.9 × 10 4 c. 2.0 × 10 4 d. 1.9 × 10 4 e. 5.3 × 10 6 ANS: d 54. The Earth’s gravitational force must be included when calculating the centripet ...