Acceleration of a Pulled Spool
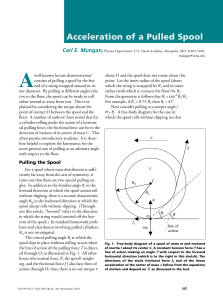
... These results can be applied to an introductory physics course in two ways. On the one hand, a three-part homework problem can be constructed. The students are given the freebody diagram in Fig. 1. In the first step, the students are asked to write down the horizontal component and rotational analog ...
... These results can be applied to an introductory physics course in two ways. On the one hand, a three-part homework problem can be constructed. The students are given the freebody diagram in Fig. 1. In the first step, the students are asked to write down the horizontal component and rotational analog ...
Momentum and Impulse Unit Notes
... The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum We’ve seen that if you want to change the momentum of an object or a system of objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum of ...
... The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum We’ve seen that if you want to change the momentum of an object or a system of objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum of ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Newton*s Law of Gravitation
... force is the result of their interaction at a distance r. Note that the field formula has just one mass – namely the mass that “sets up” the local field in the space surrounding it. It “curves” it. The field view of the universe (spatial disruption by a single mass) is currently preferred over the ...
... force is the result of their interaction at a distance r. Note that the field formula has just one mass – namely the mass that “sets up” the local field in the space surrounding it. It “curves” it. The field view of the universe (spatial disruption by a single mass) is currently preferred over the ...
9.1
... determined completely by their magnitude—for example, length, mass, area, temperature, and energy. We speak of a length of 5 m or a mass of 3 kg; only one number is needed to describe each of these quantities. Such a quantity is called a scalar. On the other hand, to describe the displacement of an ...
... determined completely by their magnitude—for example, length, mass, area, temperature, and energy. We speak of a length of 5 m or a mass of 3 kg; only one number is needed to describe each of these quantities. Such a quantity is called a scalar. On the other hand, to describe the displacement of an ...
Relative Motion in Two Dimensions
... Centrifugal “Force” • According to Newton’s first law, you will continue moving with the same velocity unless there is a net force acting on you. • The passenger in the car would continue to move straight ahead if it were not for the force of the car acting in the direction of the acceleration. ...
... Centrifugal “Force” • According to Newton’s first law, you will continue moving with the same velocity unless there is a net force acting on you. • The passenger in the car would continue to move straight ahead if it were not for the force of the car acting in the direction of the acceleration. ...
chapter11
... The instantaneous angular momentum L of a particle relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... The instantaneous angular momentum L of a particle relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... c. If there is no friction, the ball will never stop. ...
... c. If there is no friction, the ball will never stop. ...
lecture1437132938
... (a) Sliding pair: If two links have a sliding motion relative to each other, they form a sliding pair. (b) Turning pair: When one link has a turning or revolving motion relative to the other, they constitute a turning or revolving pair. (c) Rolling Pair: When the links of a pair have a rolling motio ...
... (a) Sliding pair: If two links have a sliding motion relative to each other, they form a sliding pair. (b) Turning pair: When one link has a turning or revolving motion relative to the other, they constitute a turning or revolving pair. (c) Rolling Pair: When the links of a pair have a rolling motio ...
ch13
... A spring is used to stop a 60 kg package which is sliding on a horizontal surface. The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the ...
... A spring is used to stop a 60 kg package which is sliding on a horizontal surface. The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the ...