Static Electricity
... electrons to or receive electrons from the object being charged. The charged object serves to polarize the object being charged. 3. The object being charged is touched by a ground; electrons are transferred between the ground and the object being charged (either into the object or out of it). 4. The ...
... electrons to or receive electrons from the object being charged. The charged object serves to polarize the object being charged. 3. The object being charged is touched by a ground; electrons are transferred between the ground and the object being charged (either into the object or out of it). 4. The ...
- Lake Fenton Community School District
... Information: Scientific Notation “Scientific notation” is used to make very large or very small numbers easier to handle. For example the number 45,000,000,000,000,000 can be written as “4.5 x 1016 ”. The “16” tells you that there are sixteen decimal places between the right side of the four and the ...
... Information: Scientific Notation “Scientific notation” is used to make very large or very small numbers easier to handle. For example the number 45,000,000,000,000,000 can be written as “4.5 x 1016 ”. The “16” tells you that there are sixteen decimal places between the right side of the four and the ...
Electrostatics - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
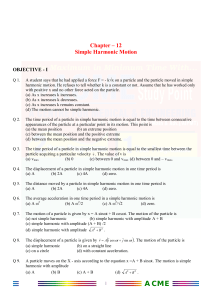
... (2) System : A collection of any number of particles interacting with one another and are under consideration during analysis of a situation are said to form a system. (3) Internal forces : All the forces exerted by various particles of the system on one another are called internal forces. These for ...
... (2) System : A collection of any number of particles interacting with one another and are under consideration during analysis of a situation are said to form a system. (3) Internal forces : All the forces exerted by various particles of the system on one another are called internal forces. These for ...
Phys11U_Unit 2_Ch4_CE_ms_for_Questions
... You can measure the force of friction acting on a stationary object by pulling on it with a spring scale or a force meter. If you measure the largest force required to move the object, you will determine the maximum amount of friction the surface exerts on the object just before it starts to move. I ...
... You can measure the force of friction acting on a stationary object by pulling on it with a spring scale or a force meter. If you measure the largest force required to move the object, you will determine the maximum amount of friction the surface exerts on the object just before it starts to move. I ...
ch 5 - Applying Newton`s Laws
... • It’s not hard to state Newton’s laws well; how should we apply them to everyday situations? • We can start with forces balanced, nothing moving (statics). • Next, we’ll study unbalanced forces causing motion (dynamics). • We’ll end Chapter 5 considering the role of forces in circular motion. Copyr ...
... • It’s not hard to state Newton’s laws well; how should we apply them to everyday situations? • We can start with forces balanced, nothing moving (statics). • Next, we’ll study unbalanced forces causing motion (dynamics). • We’ll end Chapter 5 considering the role of forces in circular motion. Copyr ...
4.3 Centripetal Acceleration
... OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0‡ ...
... OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0‡ ...
1 - Weebly
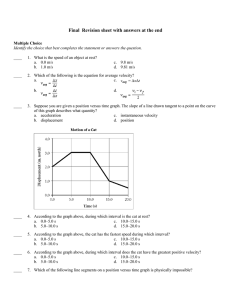
... a. 2.5 m/s to the left b. 2.5 m/s to the right c. 3.0 m/s to the left d. 3.0 m/s to the right ______ 5. For a given change in momentum (constant), if the net force that is applied to an object increases, what happens to the time interval over which the force is applied? a. The time interval increase ...
... a. 2.5 m/s to the left b. 2.5 m/s to the right c. 3.0 m/s to the left d. 3.0 m/s to the right ______ 5. For a given change in momentum (constant), if the net force that is applied to an object increases, what happens to the time interval over which the force is applied? a. The time interval increase ...
Seesaws 9 Balanced Seesaw
... A body at rest tends to remain at rest A body that’s rotating tends to keep rotating ...
... A body at rest tends to remain at rest A body that’s rotating tends to keep rotating ...
Physics
... b. gravitational pressure. c. fluid pressure. d. constant pressure. 23. If an object floats, the volume of displaced water is equal to the volume of a. the entire object. b. the portion of the object that is above water. c. the portion of the object that is submerged. d. exactly half of the object. ...
... b. gravitational pressure. c. fluid pressure. d. constant pressure. 23. If an object floats, the volume of displaced water is equal to the volume of a. the entire object. b. the portion of the object that is above water. c. the portion of the object that is submerged. d. exactly half of the object. ...