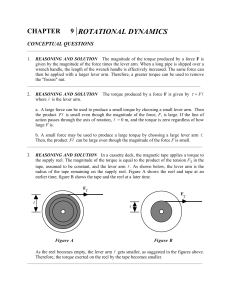
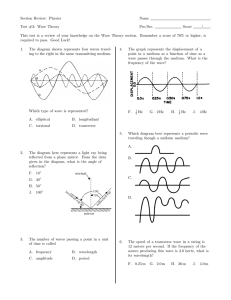
Chapter 07 Test A - Marian High School
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
A x - Description
... • Now consider gently pushing the brick to the right, as shown. • The horizontal frictional force is caused by microscopic bonds between the surfaces in contact. • As you push the brick, the net effect of these microscopic forces is to hold the brick in place. • As you increase your push force, this ...
... • Now consider gently pushing the brick to the right, as shown. • The horizontal frictional force is caused by microscopic bonds between the surfaces in contact. • As you push the brick, the net effect of these microscopic forces is to hold the brick in place. • As you increase your push force, this ...
Oaks_Park - TuHS Physics Homepage
... C) Dynamics Using Newton's second law, calculate the force the tracks must exert on the train to accelerate it. (Use the whole mass of the train for this!) Also calculate what the coefficient of friction has to be in order for the locomotive to do this. (The normal force would be due to the mass of ...
... C) Dynamics Using Newton's second law, calculate the force the tracks must exert on the train to accelerate it. (Use the whole mass of the train for this!) Also calculate what the coefficient of friction has to be in order for the locomotive to do this. (The normal force would be due to the mass of ...
physics and technology i - OCExternal
... understanding physics much easier and much more enjoyable for you. 1. Always read the assignment for the next lesson and lab prior to the class. Also, try to work ALL of the assigned problems. If you are able to understand the reading and to work all the problems, you are well prepared for the labor ...
... understanding physics much easier and much more enjoyable for you. 1. Always read the assignment for the next lesson and lab prior to the class. Also, try to work ALL of the assigned problems. If you are able to understand the reading and to work all the problems, you are well prepared for the labor ...
The Law of Momentum Conservation
... In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum. If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. Yet, the total momentum of the two objects (object 1 plus object 2) is the same befo ...
... In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum. If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. Yet, the total momentum of the two objects (object 1 plus object 2) is the same befo ...
The Modified Theory of Central-Force Motion Edison A. Enaibe,(Ph.D.)
... The number of independent ways in which a mechanical system can move without violating any constraints which may be imposed is called the number of degrees of freedom of the system. The number of degrees of freedom is the number of quantities which must be specified in order to determine the velocit ...
... The number of independent ways in which a mechanical system can move without violating any constraints which may be imposed is called the number of degrees of freedom of the system. The number of degrees of freedom is the number of quantities which must be specified in order to determine the velocit ...
Physics - Pakchoicez.com
... In inelastic collision the kinetic energy of the system will __________ conserved. If a massive body will collide elastically with a lighter body at rest then the lighter body will start to move with a velocity equal to __________ first body. ...
... In inelastic collision the kinetic energy of the system will __________ conserved. If a massive body will collide elastically with a lighter body at rest then the lighter body will start to move with a velocity equal to __________ first body. ...
Notes on (algebra based) Physics
... Our immediate interest would be to predict the position of an object. The position of an object (in space), relative to another point, is unambiguously specified as x. The position is a function of time, that is, x(t). Newtonian mechanics, the subject of discussion, proposes a strategy to determine ...
... Our immediate interest would be to predict the position of an object. The position of an object (in space), relative to another point, is unambiguously specified as x. The position is a function of time, that is, x(t). Newtonian mechanics, the subject of discussion, proposes a strategy to determine ...