Warm-up
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
Notes for Newton
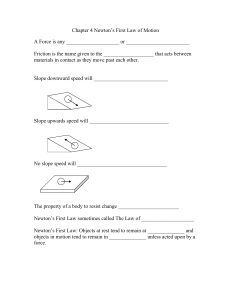
... 1. An object in motion will remain in motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of ...
... 1. An object in motion will remain in motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of ...
Kinematics, Momentum and Energy
... Newton’s First Law Inertia An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an external force. ...
... Newton’s First Law Inertia An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an external force. ...
Newtons 1st Law notes
... Balanced Forces Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
... Balanced Forces Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
Magic Square Vocabulary Game Combinations
... G. Friction H. 3rd Law of Motion I. Gravitational Force ...
... G. Friction H. 3rd Law of Motion I. Gravitational Force ...
Newton`s Second Law 1 PPT
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
Newton`s law clickview worksheet File
... Explain why a table cloth pulled slowly moves an object with it but when pulled quickly slides from underneath the object? ...
... Explain why a table cloth pulled slowly moves an object with it but when pulled quickly slides from underneath the object? ...
Newton`s Second Law
... An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). The kicked ball rolls u ...
... An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). The kicked ball rolls u ...
Newton`s Second and Third Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion Force is proportional to mass and ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion Force is proportional to mass and ...
ENERGY- Is the ability to do work
... WORK - Is performed when a force is applied through a distance You can tell something has moved when it has changed _POSITION_. To calculate speed, you must know _TIME_ and _DISTANCE_. FRICTION_ -A force between objects that slows an object down. ACCELERATION_ -A change in speed or direction. INERTI ...
... WORK - Is performed when a force is applied through a distance You can tell something has moved when it has changed _POSITION_. To calculate speed, you must know _TIME_ and _DISTANCE_. FRICTION_ -A force between objects that slows an object down. ACCELERATION_ -A change in speed or direction. INERTI ...
Newton`s Laws Vocabulary
... Newton (N) – the unit for the amount of force an object contains. Traction – a kind of friction that allows wheels to turn without slipping on a surface. Weight – a measure of the heaviness of an object. ...
... Newton (N) – the unit for the amount of force an object contains. Traction – a kind of friction that allows wheels to turn without slipping on a surface. Weight – a measure of the heaviness of an object. ...
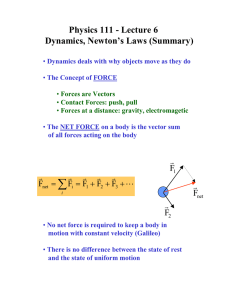
Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary)
... • No net force is required to keep a body in motion with constant velocity (Galileo) • There is no difference between the state of rest and the state of uniform motion ...
... • No net force is required to keep a body in motion with constant velocity (Galileo) • There is no difference between the state of rest and the state of uniform motion ...