Ch. 2-3
... 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is ___________________ to the mass of an object in motion. 6. Weight equals ___________ times the ____ ...
... 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is ___________________ to the mass of an object in motion. 6. Weight equals ___________ times the ____ ...
Forces and Motion Study Guide
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
Chapter 3: Forces and Motion
... ex hitting a ball with a bat, the result is a change in velocity (direction) *an interaction can lead to a change in magnitude or direction A force is any influence that can change the velocity of an object. *this definition agrees with the idea of forces as “pushes” or “pulls” contact force arise ...
... ex hitting a ball with a bat, the result is a change in velocity (direction) *an interaction can lead to a change in magnitude or direction A force is any influence that can change the velocity of an object. *this definition agrees with the idea of forces as “pushes” or “pulls” contact force arise ...
Document
... Friction is the resistance to the motion due to the interaction of the object with the environment The direction of frictional force is always opposite to the direction of ...
... Friction is the resistance to the motion due to the interaction of the object with the environment The direction of frictional force is always opposite to the direction of ...
Newton`s Law of Motion.
... object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. • Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. • According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanced force acting upon it. The presence of an unbalanc ...
... object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. • Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. • According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanced force acting upon it. The presence of an unbalanc ...
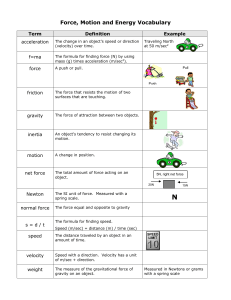
FORCE and MOTION UNIT VOCABULARY
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
Name ______ Period ______ Newton`s Laws Study Guide ______
... 9. The force of gravity is effected by: ___________________ and ____________________. A larger object has _________ gravity than a smaller object. Gravitational force ________ as the distance between the objects decreases. 10. The motion of a body when only gravity is acting on it is called ________ ...
... 9. The force of gravity is effected by: ___________________ and ____________________. A larger object has _________ gravity than a smaller object. Gravitational force ________ as the distance between the objects decreases. 10. The motion of a body when only gravity is acting on it is called ________ ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
... Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
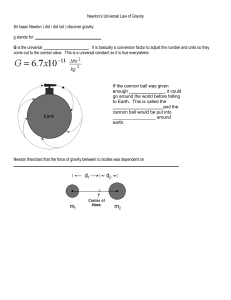
Newton`s Universal Law of Gravity
... Sir Isaac Newton ( did / did not ) discover gravity: g stands for: ________________________________ G is the universal ______________________. It is basically a conversion factor to adjust the number and units so they come out to the correct value. This is a universal constant so it is true everywhe ...
... Sir Isaac Newton ( did / did not ) discover gravity: g stands for: ________________________________ G is the universal ______________________. It is basically a conversion factor to adjust the number and units so they come out to the correct value. This is a universal constant so it is true everywhe ...