* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force and Motion Force: a push or a pull that causes a change in
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
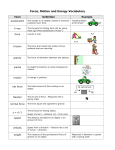
Force and Motion Force: a push or a pull that causes a change in movement or shape Example: Pushing a baby stroller Pulling on a rope Motion: the change in position of an object as compared to a fixed point - Distance: length of the actual path traveled by an object - Speed: distance traveled by an object in a given amount of time - Velocity: object’s speed in a given direction Velocity (v) = distance (d) / time (t) Example: Speed = 80 miles per hour Velocity = 80 miles per hour NORTH Acceleration: a change in velocity over time. - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or more objects; Weight is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. Rate of acceleration (free fall) is constant because of gravity’s pull. 3) Upward Force: a force used to support something. Example: If a book is resting on a table, the table is exerting an upward force on the book. Example with all three Forces: r = upward force of ramp g = gravity’s pull down f = friction between car and ramp Other Forces Net Force: the sum of all the forces acting on an object. Balanced Forces: when the total of all forces equal zero; no change in motion. Net Force = ZERO Unbalanced Forces: when the total of all forces DOES NOT equal zero; produce a change in motion Net Force = greater than zero Forces must be unbalanced to change an object’s motion.