Ch#8 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q5. A projectile of mass m = 0.200 kg is fired at an angle of 60.0 degrees above the horizontal with a speed of 20.0 m/s. Find the work done on the projectile by the gravitational force during its flight from its firing point to the highest point on its trajectory. (A: –30.0 J) Q6. A 0.500-kg block ...
... Q5. A projectile of mass m = 0.200 kg is fired at an angle of 60.0 degrees above the horizontal with a speed of 20.0 m/s. Find the work done on the projectile by the gravitational force during its flight from its firing point to the highest point on its trajectory. (A: –30.0 J) Q6. A 0.500-kg block ...
Chapter 19
... given by F = qvB sin θ , where v is the speed of the particle and θ is the angle between the direction of the particle’s velocity and the direction of the magnetic field. If either v = 0 [choice (e)] or sin θ = 0 [choice (c)], this force has zero magnitude. All other choices are false, so the correc ...
... given by F = qvB sin θ , where v is the speed of the particle and θ is the angle between the direction of the particle’s velocity and the direction of the magnetic field. If either v = 0 [choice (e)] or sin θ = 0 [choice (c)], this force has zero magnitude. All other choices are false, so the correc ...
SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR XI CLASS PHYSICS
... One Dimensional Motion. The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion if only one out of the three coordinates specifying the position of the object changes with respect to times. (an object moves along any of the three axes X, Y or Z). ...
... One Dimensional Motion. The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion if only one out of the three coordinates specifying the position of the object changes with respect to times. (an object moves along any of the three axes X, Y or Z). ...
Newtons Lesson 10
... 21. A 2.00 kg pendulum hangs in an elevator. Calculate the tension in the string supporting the pendulum if the elevator moves: a. with zero velocity b. downward at a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s c. upward at a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s d. downward at a constant acceleration of 2.00 m/s2 e. upwa ...
... 21. A 2.00 kg pendulum hangs in an elevator. Calculate the tension in the string supporting the pendulum if the elevator moves: a. with zero velocity b. downward at a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s c. upward at a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s d. downward at a constant acceleration of 2.00 m/s2 e. upwa ...
circular motion
... A train is moving towards North. At one place it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that (A) the radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner rail (B) the radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater (C) the radius of curvature of inner rail will be grea ...
... A train is moving towards North. At one place it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that (A) the radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner rail (B) the radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater (C) the radius of curvature of inner rail will be grea ...
Curriculum Map: AP Physics I MASH Science
... acceleration. Use force and mass to explain translational motion or simple harmonic motion of objects. Relate torque and rotational inertia to explain rotational motion. Standard – 3.2.P.B2: Explain the translation and simple harmonic motion of objects using conservation of energy and conservation o ...
... acceleration. Use force and mass to explain translational motion or simple harmonic motion of objects. Relate torque and rotational inertia to explain rotational motion. Standard – 3.2.P.B2: Explain the translation and simple harmonic motion of objects using conservation of energy and conservation o ...
Old Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... and m3 has a speed of 6.0 m/s in the direction of +ve y-axis. The momentum of the center of mass of the system is: (Ans: 6i+12j) Q11. A 0.20 kg steel ball, travels along the x-axis at 10 m/s, undergoes an elastic collision with a 0.50 kg steel ball traveling along the y-axis at 4.0 m/s. The total ki ...
... and m3 has a speed of 6.0 m/s in the direction of +ve y-axis. The momentum of the center of mass of the system is: (Ans: 6i+12j) Q11. A 0.20 kg steel ball, travels along the x-axis at 10 m/s, undergoes an elastic collision with a 0.50 kg steel ball traveling along the y-axis at 4.0 m/s. The total ki ...
Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... Conceptual Example Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Answe ...
... Conceptual Example Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Answe ...
Ch# 9 - KFUPM Faculty List
... and m3 has a speed of 6.0 m/s in the direction of +ve y-axis. The momentum of the center of mass of the system is: (Ans: 6i+12j) Q11. A 0.20 kg steel ball, travels along the x-axis at 10 m/s, undergoes an elastic collision with a 0.50 kg steel ball traveling along the y-axis at 4.0 m/s. The total ki ...
... and m3 has a speed of 6.0 m/s in the direction of +ve y-axis. The momentum of the center of mass of the system is: (Ans: 6i+12j) Q11. A 0.20 kg steel ball, travels along the x-axis at 10 m/s, undergoes an elastic collision with a 0.50 kg steel ball traveling along the y-axis at 4.0 m/s. The total ki ...
KINEMATICS DYNAMICS
... direction of the force acting on an object and the change in momentum caused by that force. [SP 4.1] 3.D.2.1: The student is able to justify the selection of routines for the calculation of the relationships between changes in momentum of an object, average force, impulse, and time of interaction. [ ...
... direction of the force acting on an object and the change in momentum caused by that force. [SP 4.1] 3.D.2.1: The student is able to justify the selection of routines for the calculation of the relationships between changes in momentum of an object, average force, impulse, and time of interaction. [ ...
1st semester EXAM review and key
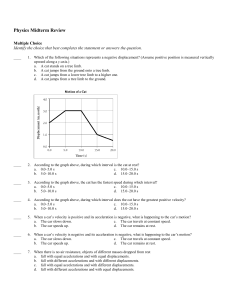
... 38. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 39. Why is force not a scalar quantity? 40. A block of wood supported by two concrete blocks is chopped in half by a k ...
... 38. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 39. Why is force not a scalar quantity? 40. A block of wood supported by two concrete blocks is chopped in half by a k ...
Document
... • An object at rest tends to remain at rest and an object in motion tends to remain in motion at the same speed and in the same direction unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... • An object at rest tends to remain at rest and an object in motion tends to remain in motion at the same speed and in the same direction unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...