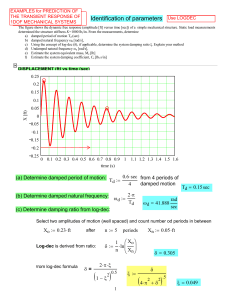
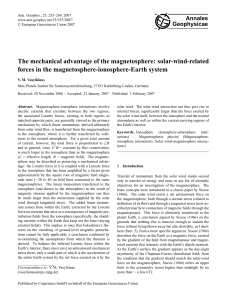
LCP1 INTUITIVE PHYSICS
... ideas only. A good way to start would be to model our first attempt toward understanding motion after Galileo, the first scientist to successfully challenge Aristotle's ideas about motion. He was the first to understand and describe motion the way physicists do today. Galileo began his study of moti ...
... ideas only. A good way to start would be to model our first attempt toward understanding motion after Galileo, the first scientist to successfully challenge Aristotle's ideas about motion. He was the first to understand and describe motion the way physicists do today. Galileo began his study of moti ...
canim-11 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... • As springs apply equal and opposite forces to two particles, they should obey conservation of momentum • As it happens, the springs will also conserve energy, as the kinetic energy of motion can be stored in the deformation energy of the spring and later restored • In practice, our simple implemen ...
... • As springs apply equal and opposite forces to two particles, they should obey conservation of momentum • As it happens, the springs will also conserve energy, as the kinetic energy of motion can be stored in the deformation energy of the spring and later restored • In practice, our simple implemen ...
1 - OnCourse
... 1. Students will gain an understanding of light and how images are formed using different optical devices. Special and General Relativity: The laws of physics apply to all reference frames. Whether an observer is moving or not, the speed of light is constant. 1. Students will gain an understanding o ...
... 1. Students will gain an understanding of light and how images are formed using different optical devices. Special and General Relativity: The laws of physics apply to all reference frames. Whether an observer is moving or not, the speed of light is constant. 1. Students will gain an understanding o ...
Module P2.6 Circular motion
... above the Earth’s surface, air resistance and the non-spherical shape of the Earth would be unimportant and a circular path would be feasible. This is similar to an artificial Earth satellite (often abbreviated to ‘satellite’) being put into orbit. If it is sent up in a rocket to the desired height ...
... above the Earth’s surface, air resistance and the non-spherical shape of the Earth would be unimportant and a circular path would be feasible. This is similar to an artificial Earth satellite (often abbreviated to ‘satellite’) being put into orbit. If it is sent up in a rocket to the desired height ...
SECTION7.2 Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... Orbits of Planets and Satellites (cont.) • The equations for speed and period of a satellite can be used for any object in orbit about another. Central body mass will replace mE, and r will be the distance between the centers of the orbiting body and the central body. • If the mass of the central bo ...
... Orbits of Planets and Satellites (cont.) • The equations for speed and period of a satellite can be used for any object in orbit about another. Central body mass will replace mE, and r will be the distance between the centers of the orbiting body and the central body. • If the mass of the central bo ...
Lesson 1: Vectors - Fundamentals and Operations
... 3. To determine the length of the side opposite the indicated angle, use the sine function. Substitute the magnitude of the vector for the length of the hypotenuse. 4. Repeat the above step using the cosine function to determine the length of the side adjacent to the indicated ...
... 3. To determine the length of the side opposite the indicated angle, use the sine function. Substitute the magnitude of the vector for the length of the hypotenuse. 4. Repeat the above step using the cosine function to determine the length of the side adjacent to the indicated ...
4.6 Elastic potential Energy and simple harmonic Motion
... Simple Harmonic Motion Suppose a block is connected to a spring and both are resting on a frictionless surface. The block is at equilibrium when it is resting at its initial position, x 5 0, as shown in Figure 7(a). In Figure 7(b), the spring is stretched to its maximum limit, or amplitude, A; displ ...
... Simple Harmonic Motion Suppose a block is connected to a spring and both are resting on a frictionless surface. The block is at equilibrium when it is resting at its initial position, x 5 0, as shown in Figure 7(a). In Figure 7(b), the spring is stretched to its maximum limit, or amplitude, A; displ ...
Ch 5 Solutions Glencoe 2013
... 20. Thomas sits on a small rug on a polished wooden floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rug and the slippery wooden floor is only 0.12. If Thomas weighs 650 N, what horizontal force is needed to pull the rug and Thomas across the floor at a constant speed? SOLUTION: At constant ...
... 20. Thomas sits on a small rug on a polished wooden floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rug and the slippery wooden floor is only 0.12. If Thomas weighs 650 N, what horizontal force is needed to pull the rug and Thomas across the floor at a constant speed? SOLUTION: At constant ...
Freehold Regional High School District
... The Medical Science AP Physics B course will begin with observations of objects in motion, focusing on multiple representations of motion, the mechanics of moving objects and using the scientific method to solve real world problems. As the course progresses, the students will gain an understanding t ...
... The Medical Science AP Physics B course will begin with observations of objects in motion, focusing on multiple representations of motion, the mechanics of moving objects and using the scientific method to solve real world problems. As the course progresses, the students will gain an understanding t ...
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line Position
... moving in a magnetic field. Since a moving charge produces a magnetic field it should come as no surprise that a moving charge placed in an external magnetic field will feel a magnetic force. (Because of the pole law). Furthermore, a stationary charge in a magnetic field will feel no magnetic forc ...
... moving in a magnetic field. Since a moving charge produces a magnetic field it should come as no surprise that a moving charge placed in an external magnetic field will feel a magnetic force. (Because of the pole law). Furthermore, a stationary charge in a magnetic field will feel no magnetic forc ...
PSI AP Physics I
... the record rotates, compare the linear displacement (arc length, s) to the angular displacement of the two bugs. 5. For a rotating disc, what are the two types of linear acceleration? How do their magnitudes depend on how far an object on the disc is from the center of the disc? 6. You are stepping ...
... the record rotates, compare the linear displacement (arc length, s) to the angular displacement of the two bugs. 5. For a rotating disc, what are the two types of linear acceleration? How do their magnitudes depend on how far an object on the disc is from the center of the disc? 6. You are stepping ...