Lab 9 - Suffolk County Community College
... (a) THE LINEAR MOMENTUM P for a mass m is defined to be the product of the mass m and the velocity v, i.e., P = mv. P is a vector quantity and its MKS unit is kg m/sec. A cart moving to the right on the air track is considered to have a positive momentum. (b) AN ELASTIC COLLISION between two objects ...
... (a) THE LINEAR MOMENTUM P for a mass m is defined to be the product of the mass m and the velocity v, i.e., P = mv. P is a vector quantity and its MKS unit is kg m/sec. A cart moving to the right on the air track is considered to have a positive momentum. (b) AN ELASTIC COLLISION between two objects ...
p - Effingham County Schools
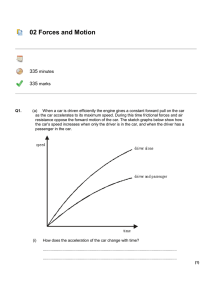
... Two cars enter an icy intersection. Car 1, with a mass of 2.50 x 103 kg, is heading east at 20.0 m/s, and car 2, with a mass of 1.45 x 103 kg is going north at 30.0 m/s. The two vehicles collide and stick together. What is the speed and direction of the cars as they skid away together ...
... Two cars enter an icy intersection. Car 1, with a mass of 2.50 x 103 kg, is heading east at 20.0 m/s, and car 2, with a mass of 1.45 x 103 kg is going north at 30.0 m/s. The two vehicles collide and stick together. What is the speed and direction of the cars as they skid away together ...
Momentum - eAcademy
... opposite the light cart at a low speed. Repeat but slide the heavier cart toward the lighter cart which is at rest. Observe the motion of the carts before, during, and after the elastic collision. The heavier cart continues its motion with a low speed and the lighter cart moves in the same direction ...
... opposite the light cart at a low speed. Repeat but slide the heavier cart toward the lighter cart which is at rest. Observe the motion of the carts before, during, and after the elastic collision. The heavier cart continues its motion with a low speed and the lighter cart moves in the same direction ...
General Physics I - Dr. David G. Simpson
... The Four Forces of Nature . Hooke’s Law. . . . . . . . Weight . . . . . . . . . . . Normal Force . . . . . . . Tension . . . . . . . . . . ...
... The Four Forces of Nature . Hooke’s Law. . . . . . . . Weight . . . . . . . . . . . Normal Force . . . . . . . Tension . . . . . . . . . . ...
battery. - SCHOOLinSITES
... • It takes a certain amount of force to overcome static friction and start the block moving (until the bonds between the block and the surface area are broken). • The force needed to put the block in motion is greater than the force needed to keep the block moving. L6 ...
... • It takes a certain amount of force to overcome static friction and start the block moving (until the bonds between the block and the surface area are broken). • The force needed to put the block in motion is greater than the force needed to keep the block moving. L6 ...
UserManual4Modules
... 2. Draw the path ( position versus time) of simultaneous fall of both balls 3. At each position show the direction of velocities of both balls 4. From the paths that you have drawn, is it possible for Ball A and ball B to hit 5. the ground at the same time? If yes, explain __________________________ ...
... 2. Draw the path ( position versus time) of simultaneous fall of both balls 3. At each position show the direction of velocities of both balls 4. From the paths that you have drawn, is it possible for Ball A and ball B to hit 5. the ground at the same time? If yes, explain __________________________ ...