Ch 18 - SchemmScience.com
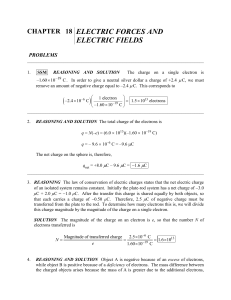
... magnitudes of these forces can be found by using Coulomb’s law. The magnitude and direction of the net force that acts on q1 can be determined by using the method of vector components. b. According to Newton’s second law, Equation 4.2b, the acceleration of q1 is equal to the net force divided by its ...
... magnitudes of these forces can be found by using Coulomb’s law. The magnitude and direction of the net force that acts on q1 can be determined by using the method of vector components. b. According to Newton’s second law, Equation 4.2b, the acceleration of q1 is equal to the net force divided by its ...
241.0 KB - NZTA Education Portal
... 1. Change the slope of the plank. Use stacking blocks or books to change the starting height of the trolley car. Make a prediction about any change in the trolley car’s motion before testing. Repeat your experiment three times, taking the average result under each condition as the speed or distance ...
... 1. Change the slope of the plank. Use stacking blocks or books to change the starting height of the trolley car. Make a prediction about any change in the trolley car’s motion before testing. Repeat your experiment three times, taking the average result under each condition as the speed or distance ...
ClassicalMechanics_4..
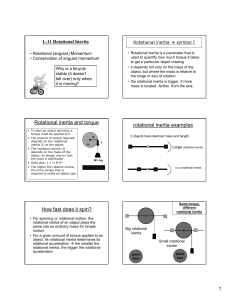
... Torque is provided by friction acting at the surface (otherwise the ball would just slide). Note that the normal force does not produce a torque (although it can with deformable surfaces and rolling friction). Semester 1 2008 ...
... Torque is provided by friction acting at the surface (otherwise the ball would just slide). Note that the normal force does not produce a torque (although it can with deformable surfaces and rolling friction). Semester 1 2008 ...
(1 Of 2) Air Track TEACHER
... (Addressed in Procedures A-H; the student uses this apparatus to observe and measure the forces acting on gliders on a near-frictionless environment, and use data collecting equipment to measure motion.) o Motions and Forces. An object that is not being subjected to a force will continue to move at ...
... (Addressed in Procedures A-H; the student uses this apparatus to observe and measure the forces acting on gliders on a near-frictionless environment, and use data collecting equipment to measure motion.) o Motions and Forces. An object that is not being subjected to a force will continue to move at ...
8 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... experienced the 0.56-N force of gravity, but that force was not due to the racquet). This problem could also be solved by first finding the acceleration and then using F net = ma , but one additional step would be required compared with the strategy used in this example. ...
... experienced the 0.56-N force of gravity, but that force was not due to the racquet). This problem could also be solved by first finding the acceleration and then using F net = ma , but one additional step would be required compared with the strategy used in this example. ...
Crumple Zone - cloudfront.net
... acceleration vs. time graph appear on the screen. See Figure 2. 5. Securely attach the accelerometer to the cart so that the arrow on the accelerometer points toward the front of the cart. To calibrate the probe using Logger Pro software, click Experiment on the toolbar, Calibrate. Click the Calibra ...
... acceleration vs. time graph appear on the screen. See Figure 2. 5. Securely attach the accelerometer to the cart so that the arrow on the accelerometer points toward the front of the cart. To calibrate the probe using Logger Pro software, click Experiment on the toolbar, Calibrate. Click the Calibra ...
The Casimir force: background, experiments, and
... intermolecular effects. Lifshitz [12]1 first developed in 1956 the theory for the attractive force between two plane surfaces made of a material with a generalized susceptibility. His work was motivated by experimental results from force measurements between dielectric bodies that were much smaller ...
... intermolecular effects. Lifshitz [12]1 first developed in 1956 the theory for the attractive force between two plane surfaces made of a material with a generalized susceptibility. His work was motivated by experimental results from force measurements between dielectric bodies that were much smaller ...