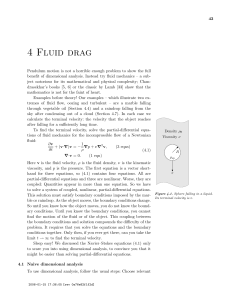
E - HayonPhysics
... An electron e and a proton p are simultaneously released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as shown above. Assume that the particles are sufficiently far apart so that the only force acting on each particle after it is released is that due to the electric field. At a later time when the parti ...
... An electron e and a proton p are simultaneously released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as shown above. Assume that the particles are sufficiently far apart so that the only force acting on each particle after it is released is that due to the electric field. At a later time when the parti ...
No Slide Title - myersparkphysics
... An electron e and a proton p are simultaneously released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as shown above. Assume that the particles are sufficiently far apart so that the only force acting on each particle after it is released is that due to the electric field. At a later time when the parti ...
... An electron e and a proton p are simultaneously released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as shown above. Assume that the particles are sufficiently far apart so that the only force acting on each particle after it is released is that due to the electric field. At a later time when the parti ...
Physics I
... object at rest or moving at constant velocity continues its current motion unless acted upon by an outside agent (force).) Given a diagram or a written description of the forces acting on an object.: 1. draw a force diagram for the object 2. resolve the forces into x and y components, then find the ...
... object at rest or moving at constant velocity continues its current motion unless acted upon by an outside agent (force).) Given a diagram or a written description of the forces acting on an object.: 1. draw a force diagram for the object 2. resolve the forces into x and y components, then find the ...
Momentum, Kinetic Energy, and Arrow Penetration
... The second line expresses the acceleration by its basic definition, a change in velocity divided by the change in time. The third line is arrived at through algebra, by multiplying each side of the equation by delta t (which is the symbol for change in time), canceling it on the right, effectively m ...
... The second line expresses the acceleration by its basic definition, a change in velocity divided by the change in time. The third line is arrived at through algebra, by multiplying each side of the equation by delta t (which is the symbol for change in time), canceling it on the right, effectively m ...
Momentum and Impulse Momentum and Impulse
... catches, and interceptions of the ball in soccer are examples of collisions in sports action. Players, such as Randy Ferbey, who are able to accurately predict the resulting motion of colliding objects have a better chance of helping their team win (Figure 9.1). When objects interact during a short ...
... catches, and interceptions of the ball in soccer are examples of collisions in sports action. Players, such as Randy Ferbey, who are able to accurately predict the resulting motion of colliding objects have a better chance of helping their team win (Figure 9.1). When objects interact during a short ...
Forces
... Patty was riding in her brother Chuck’s car at a city speed of 15.0 m/s. Patty thought that the speed was fairly slow, so she did not bother wearing a seatbelt. She figured that she could use her arms to exert a stopping force before she hit the dashboard 0.75 m away. Chuck’s attention was diverted ...
... Patty was riding in her brother Chuck’s car at a city speed of 15.0 m/s. Patty thought that the speed was fairly slow, so she did not bother wearing a seatbelt. She figured that she could use her arms to exert a stopping force before she hit the dashboard 0.75 m away. Chuck’s attention was diverted ...
Units and Dimensions - RIT
... A scalar is a quantity that has a value, but no direction. A scalar can be positive or negative. Scalar arithmetic is the usual stuff you learned through grade school: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising to a power. We can also take the absolute magnitude of a scalar. Normal ...
... A scalar is a quantity that has a value, but no direction. A scalar can be positive or negative. Scalar arithmetic is the usual stuff you learned through grade school: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising to a power. We can also take the absolute magnitude of a scalar. Normal ...




![5. [I] How many millimeters are in 10.0 km?](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007761429_2-9c678e889fd8013c5426d1283561544c-300x300.png)