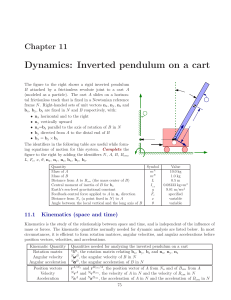
Document
... Section 2 (Linear Motion) Consider an object undergoing a constant acceleration motion, its kinematics variable can be obtained through: v u at ...
... Section 2 (Linear Motion) Consider an object undergoing a constant acceleration motion, its kinematics variable can be obtained through: v u at ...
Honors Final Review
... 11. A pool ball traveling 10 m/s collides head on with a pool ball at rest. If they have the same mass and the first ball travels at 8 m/s at a 30 degree angle above the horizontal, how fast and in what direction does the second ball travel? ...
... 11. A pool ball traveling 10 m/s collides head on with a pool ball at rest. If they have the same mass and the first ball travels at 8 m/s at a 30 degree angle above the horizontal, how fast and in what direction does the second ball travel? ...
Unit 2a Force and Motion Study Guide Label the following with the
... 15. Force is measured in a. Newtons b. Kg c. m/s/s d. kg/hr 16. __________ is a push or a pull. 17. __________ can cause an object to change direction, stop or accelerate. 18. __________ is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. 19. True or False __________ Friction is i ...
... 15. Force is measured in a. Newtons b. Kg c. m/s/s d. kg/hr 16. __________ is a push or a pull. 17. __________ can cause an object to change direction, stop or accelerate. 18. __________ is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. 19. True or False __________ Friction is i ...
patterns of motion and equilibrium - SCIENCE
... Sliding friction: the object moves. Lubricated friction: Needs a lubricant to start moving. • Fluid friction: resistance in liquids. • Air resistance: resistance of an object to move in the air. ...
... Sliding friction: the object moves. Lubricated friction: Needs a lubricant to start moving. • Fluid friction: resistance in liquids. • Air resistance: resistance of an object to move in the air. ...
waves
... 2 m/s. Which of the following must the 250 g toy car have in order to maintain the same momentum as the cart? F An acceleration of 5 m/s2 for 2 seconds G A potential energy of 20 J H A constant velocity of 4 m/s J An applied force of 5 N for 5 seconds ...
... 2 m/s. Which of the following must the 250 g toy car have in order to maintain the same momentum as the cart? F An acceleration of 5 m/s2 for 2 seconds G A potential energy of 20 J H A constant velocity of 4 m/s J An applied force of 5 N for 5 seconds ...
Matter and Forces in Motion (2a-2c)
... 22. For any object, the greater the force that's applied to it, the greater its acceleration will be. 23. The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and distance between them. 24.As you get farther from the center of Earth, your weight will decrease. 25.When a fo ...
... 22. For any object, the greater the force that's applied to it, the greater its acceleration will be. 23. The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and distance between them. 24.As you get farther from the center of Earth, your weight will decrease. 25.When a fo ...
del
... (sometimes called the divergence theorem). We start with: A dV = [(Ax /x) + (Ay /y) + (Az /z)] dx dy dz = [(Ax /x)dx dydz + (Ay /y)dy dxdz + (Az /z)dz dxdy] We can see that each term as written in the last expression gives the value of the change in vector A that cuts perpe ...
... (sometimes called the divergence theorem). We start with: A dV = [(Ax /x) + (Ay /y) + (Az /z)] dx dy dz = [(Ax /x)dx dydz + (Ay /y)dy dxdz + (Az /z)dz dxdy] We can see that each term as written in the last expression gives the value of the change in vector A that cuts perpe ...
Measuring Motion
... Change in velocity= change in speed or direction Combining Velocities Combine two velocities in same direction= add together Combine two velocities in opposite directions= subtract smaller velocity from larger velocity ...
... Change in velocity= change in speed or direction Combining Velocities Combine two velocities in same direction= add together Combine two velocities in opposite directions= subtract smaller velocity from larger velocity ...
v(t) = v0 + at
... Motion down a ramp 2 (with forces!) Sketch Velocity, acceleration and net force vs. time graphs for the car moving away from the motion detector and slowing down at a steady rate. v0 ...
... Motion down a ramp 2 (with forces!) Sketch Velocity, acceleration and net force vs. time graphs for the car moving away from the motion detector and slowing down at a steady rate. v0 ...
PHYS 307 LECTURE NOTES, Daniel W. Koon, St. Lawrence Univ.
... are Burning by Midnight Oil, 1986 SECTION 2: ROTATION COORDINATE SYSTEMS There is an awful lot of mathematics here. Read the book and try to follow it. The most important part of this is to realize that if you take the time derivative of some quantity in a fixed coordinate system, calculating the ti ...
... are Burning by Midnight Oil, 1986 SECTION 2: ROTATION COORDINATE SYSTEMS There is an awful lot of mathematics here. Read the book and try to follow it. The most important part of this is to realize that if you take the time derivative of some quantity in a fixed coordinate system, calculating the ti ...
Physics 117
... velocity), unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force impressed upon it.” The property of material objects to resist changes in their state of motion is called inertia ...
... velocity), unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force impressed upon it.” The property of material objects to resist changes in their state of motion is called inertia ...
Blank Jeopardy - the Mining Quiz List
... The equation for centripetal force is just which equation rewritten? Newton’s Second Law ...
... The equation for centripetal force is just which equation rewritten? Newton’s Second Law ...
Lecture8 (Equilibrium)
... covered" during its motion. • Displacement s 位移 is a vector quantity which refers to "how far out of place an object is"; it is the object's change in position. ...
... covered" during its motion. • Displacement s 位移 is a vector quantity which refers to "how far out of place an object is"; it is the object's change in position. ...
Physics of Soccer
... Newton's Laws of physics Mass Velocity Acceleration Inertia Momentum Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravity ...
... Newton's Laws of physics Mass Velocity Acceleration Inertia Momentum Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravity ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... Questions for Thought An insect inside a bus flies from the back toward the front at 5.0 miles/hour. The bus is moving in a straight line at 50 miles/hour. What is the speed of the insect? The speed of the insect relative to the ground is the 50.0 mi/hr of the bus plus the 5.0 mi/hr of the insect ...
... Questions for Thought An insect inside a bus flies from the back toward the front at 5.0 miles/hour. The bus is moving in a straight line at 50 miles/hour. What is the speed of the insect? The speed of the insect relative to the ground is the 50.0 mi/hr of the bus plus the 5.0 mi/hr of the insect ...