Amusement Park Ride Project
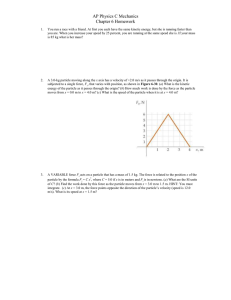
... at an angular speed of 150 rad/s or less, and the top toppled after spinning for 45 seconds, what was the initial angular velocity of the top? ...
... at an angular speed of 150 rad/s or less, and the top toppled after spinning for 45 seconds, what was the initial angular velocity of the top? ...
Chapter_6_In-class_problems_(section_by_section_notes)
... 2000 m. At a certain instant in time, the jet’s speedometer reads 300 m/s and his scale reads 5000N. Find the angle between the back of the pilots seat and the vertical at this instant in time. 6. In the previous problem, it is assumed that the pilot’s head was constantly pointing inward, towards th ...
... 2000 m. At a certain instant in time, the jet’s speedometer reads 300 m/s and his scale reads 5000N. Find the angle between the back of the pilots seat and the vertical at this instant in time. 6. In the previous problem, it is assumed that the pilot’s head was constantly pointing inward, towards th ...
laws of motion
... For object sliding on a smooth inclined plane • The acceleration depends on the inclination of the plane only. It does not depend on the mass. Objects of different masses slide on the inclined plane with the same acceleration. • The acceleration always points down-slope, independent of the directio ...
... For object sliding on a smooth inclined plane • The acceleration depends on the inclination of the plane only. It does not depend on the mass. Objects of different masses slide on the inclined plane with the same acceleration. • The acceleration always points down-slope, independent of the directio ...
Bellringer
... A. 0 mph B. 400 mph If someone gets up and walks to the front of the plane at 8 mph what is their speed relative to the plane? Relative to an observer on the ground? A. 8 mph B. 408 mph If they now turn around and walk back to their seat, what is their speed relative to an observer on the ground ...
... A. 0 mph B. 400 mph If someone gets up and walks to the front of the plane at 8 mph what is their speed relative to the plane? Relative to an observer on the ground? A. 8 mph B. 408 mph If they now turn around and walk back to their seat, what is their speed relative to an observer on the ground ...
chapter 7 notes - School District of La Crosse
... being launched B. trajectory-The path the projectile follows. ...
... being launched B. trajectory-The path the projectile follows. ...
A P COURSE AUDIT
... predict between m and T? Is it a linear, square or square root, inverse or logarithmic? How will you find out? By trial and error method, derive the formula for T and see that T2 vs. m is a straight line. Read both intercepts and interpret them. Can you predict the mass of the spring? 10. Find the ...
... predict between m and T? Is it a linear, square or square root, inverse or logarithmic? How will you find out? By trial and error method, derive the formula for T and see that T2 vs. m is a straight line. Read both intercepts and interpret them. Can you predict the mass of the spring? 10. Find the ...
Document
... If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It will translate and rotate. Why does it rotate? It rotates due to the frictional force at the point of contact, that is in a direction opposite to the direction the wheel would slip. The rolli ...
... If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It will translate and rotate. Why does it rotate? It rotates due to the frictional force at the point of contact, that is in a direction opposite to the direction the wheel would slip. The rolli ...
When the Acceleration is g
... Mass and Weight On the Moon the gravitational force is only 1/6 as strong as on the Earth. In space you are “weightless” but not “massless”. Your mass does not depend on where your are. • (e.g. Earth, Moon, or space). ...
... Mass and Weight On the Moon the gravitational force is only 1/6 as strong as on the Earth. In space you are “weightless” but not “massless”. Your mass does not depend on where your are. • (e.g. Earth, Moon, or space). ...
Forces Physical Science Chapter 2
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... 18. A student investigates the speed of a trolley as it rolls down a slope, as illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
... 18. A student investigates the speed of a trolley as it rolls down a slope, as illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
calculusreview3
... |u × v| = |u| |v| sin θ where θ is angle CCW from u to v Interpretation: Magnitude of u × v = area of parallelogram spanned by u and v Direction of u × v is perpendicular to both u and v (Use right hand rule to find which way: make fingers of RH go the short way from u into v; the thumb then points ...
... |u × v| = |u| |v| sin θ where θ is angle CCW from u to v Interpretation: Magnitude of u × v = area of parallelogram spanned by u and v Direction of u × v is perpendicular to both u and v (Use right hand rule to find which way: make fingers of RH go the short way from u into v; the thumb then points ...
Standards SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between
... SP3. Students will evaluate the forms and transformations of energy. a. Analyze, evaluate, and apply the principle of conservation of energy and measure the components of work-‐energy theorem by • d ...
... SP3. Students will evaluate the forms and transformations of energy. a. Analyze, evaluate, and apply the principle of conservation of energy and measure the components of work-‐energy theorem by • d ...
Study Guide for Conceptual Physics
... a. A train travels 6 meters in the first second of travel, 6 meters again during the second second of travel, and 6 meters again during the third second. What is the acceleration? b. A car starts from rest and after 7 seconds it is moving at 42 m/s. What is the car’s average acceleration? c. A Dave ...
... a. A train travels 6 meters in the first second of travel, 6 meters again during the second second of travel, and 6 meters again during the third second. What is the acceleration? b. A car starts from rest and after 7 seconds it is moving at 42 m/s. What is the car’s average acceleration? c. A Dave ...