forces
... Timmy hits the gas petal of his car and it provides 5000 N of force onto the road. If his car and he have a mass of 1850 kg, then how quickly do they accelerate? ...
... Timmy hits the gas petal of his car and it provides 5000 N of force onto the road. If his car and he have a mass of 1850 kg, then how quickly do they accelerate? ...
T3F2008
... C. In the figure below, two blocks, of masses m1 and m2, are connected by a massless cord that is wrapped around a uniform disk of rotational inertia, I and radius R. The disk can rotate without friction about a fixed horizontal axis through its center; the cord cannot slip on the disk. The system i ...
... C. In the figure below, two blocks, of masses m1 and m2, are connected by a massless cord that is wrapped around a uniform disk of rotational inertia, I and radius R. The disk can rotate without friction about a fixed horizontal axis through its center; the cord cannot slip on the disk. The system i ...
Phys. 1st Sem Rev 95-96
... Examples: Review the various Opus worksheets. 1. If an object, falling from rest, takes 4.0 s to reach the ground a. how fast is it going at impact? b. from what height was it dropped? 2. If the same object were thrown downwards at 10 m/s, what would be the answers to a and b above? 3. A ball is thr ...
... Examples: Review the various Opus worksheets. 1. If an object, falling from rest, takes 4.0 s to reach the ground a. how fast is it going at impact? b. from what height was it dropped? 2. If the same object were thrown downwards at 10 m/s, what would be the answers to a and b above? 3. A ball is thr ...
May 2011 - Maths Genie
... the ends of a light inextensible string. The string passes over a small smooth pulley which is fixed at the top of a fixed rough plane. The plane is inclined to the horizontal at an angle , where tan = 34 . The coefficient of friction between P and the plane is 12 . The string lies in a vertical ...
... the ends of a light inextensible string. The string passes over a small smooth pulley which is fixed at the top of a fixed rough plane. The plane is inclined to the horizontal at an angle , where tan = 34 . The coefficient of friction between P and the plane is 12 . The string lies in a vertical ...
End-semester Examination 2013 Mechanics (PHY102A/N
... 1. Imagine an isolated system with two particles interacting with each other via a central force. For this system, which of the following quantities are conserved. ! (a) √ Total energy! (b) Total kinetic energy ! (c) √ Total angular momentum ! (d) √ Total linear momentum. ! 2. Which of the following ...
... 1. Imagine an isolated system with two particles interacting with each other via a central force. For this system, which of the following quantities are conserved. ! (a) √ Total energy! (b) Total kinetic energy ! (c) √ Total angular momentum ! (d) √ Total linear momentum. ! 2. Which of the following ...
Document
... 18. What is the force of gravity on a falling object called? How do you find it? Will it be different for objects with different masses? 19. What will be the acceleration of all falling objects on earth? 20. Why do all falling objects on earth have the same the same acceleration? 21. How does an inc ...
... 18. What is the force of gravity on a falling object called? How do you find it? Will it be different for objects with different masses? 19. What will be the acceleration of all falling objects on earth? 20. Why do all falling objects on earth have the same the same acceleration? 21. How does an inc ...
motion
... table]connected by a light string. what is the tension in the string? Does the answer depend on which mass the pull is being applied?[333.3 N, 166.7N] [5] 2 objects of masses 3kg and 4Kg are connected by a weightless string which passes over a frictionless pulley. The objects are initially held at a ...
... table]connected by a light string. what is the tension in the string? Does the answer depend on which mass the pull is being applied?[333.3 N, 166.7N] [5] 2 objects of masses 3kg and 4Kg are connected by a weightless string which passes over a frictionless pulley. The objects are initially held at a ...
Document
... A force at right angles to the direction of motion will make an object start to move in a circle. ...
... A force at right angles to the direction of motion will make an object start to move in a circle. ...
ert146 lect kinetic of motion
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
4.1 Force
... acted on the body, which would then maintain its motion with constant velocity, until it was disturbed, i.e., an unbalanced force was then applied to the body to change its state of motion. L7-s5,9 ...
... acted on the body, which would then maintain its motion with constant velocity, until it was disturbed, i.e., an unbalanced force was then applied to the body to change its state of motion. L7-s5,9 ...
General Description of Motion
... • torque measured for each step rotation was 44 pN-nm, • calculated the work done by this rotary motor in each step rotation: a step rotation angle of q = 120o = (2p/3) • they found that W = (2p/3)(44 pN-nm) = 92 pN-nm = 92 x 10-21 J. • This value is very close to the energy liberated by one ATP m ...
... • torque measured for each step rotation was 44 pN-nm, • calculated the work done by this rotary motor in each step rotation: a step rotation angle of q = 120o = (2p/3) • they found that W = (2p/3)(44 pN-nm) = 92 pN-nm = 92 x 10-21 J. • This value is very close to the energy liberated by one ATP m ...
Y12 Mechanics Notes - Cashmere
... This is done by drawing them “head to tail”. The result is a vector called a resultant. The resultant has the same effect as the 2 vectors ...
... This is done by drawing them “head to tail”. The result is a vector called a resultant. The resultant has the same effect as the 2 vectors ...
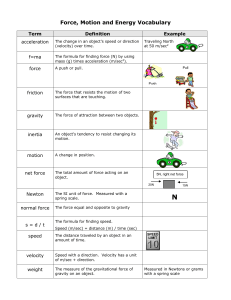
FORCE and MOTION UNIT VOCABULARY
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
Motion Characteristics for Circular Motion
... circular motion is moving in a circle with a constant speed. uniform: not changing in form or character; remaining the same in all cases and at all times ...
... circular motion is moving in a circle with a constant speed. uniform: not changing in form or character; remaining the same in all cases and at all times ...
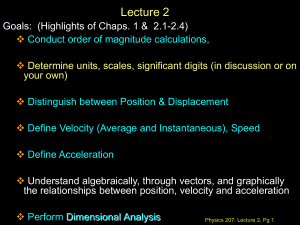
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Displacement, position, velocity & acceleration are the main quantities that we will discuss today. Which of these 4 quantities have the same units A. Velocity & position B. Velocity & acceleration C. Acceleration & displacement D. Position & displacement E. Position & acceleration ...
... Displacement, position, velocity & acceleration are the main quantities that we will discuss today. Which of these 4 quantities have the same units A. Velocity & position B. Velocity & acceleration C. Acceleration & displacement D. Position & displacement E. Position & acceleration ...
Laws of Motion
... Or, the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass: acceleration = force ÷ mass a=F÷m ...
... Or, the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass: acceleration = force ÷ mass a=F÷m ...
Instructions - People Server at UNCW
... d. A person pulls a toboggan for a distance of 35 m along the j. A recording engineer works in a soundproofed room that is 40.0 snow with a rope directed at 60o above the snow. The tension in dB quieter than outside. If the intensity in the room is the rope is 100 N. How much work is done on the tob ...
... d. A person pulls a toboggan for a distance of 35 m along the j. A recording engineer works in a soundproofed room that is 40.0 snow with a rope directed at 60o above the snow. The tension in dB quieter than outside. If the intensity in the room is the rope is 100 N. How much work is done on the tob ...