Frames of Reference
... (non-inertial) frame of reference. •From fixed frame no unbalanced force is seen. •Objects moving in a circle have an acceleration toward the center called centripetal force. •Centrifugal force is the fictitious force that balances this by being exerted away from the ...
... (non-inertial) frame of reference. •From fixed frame no unbalanced force is seen. •Objects moving in a circle have an acceleration toward the center called centripetal force. •Centrifugal force is the fictitious force that balances this by being exerted away from the ...
Chp_ 13-2 notes - South Pointe Middle
... • An object is orbiting when it is moving around another object in space. • Centripetal force is the unbalanced force that makes an object move in a circular path around another object. • Gravity provides the centripetal force on the planets and their moons that keeps them in orbit ...
... • An object is orbiting when it is moving around another object in space. • Centripetal force is the unbalanced force that makes an object move in a circular path around another object. • Gravity provides the centripetal force on the planets and their moons that keeps them in orbit ...
Unit 2a Force and Motion Study Guide Label the following with the
... 15. Force is measured in a. Newtons b. Kg c. m/s/s d. kg/hr 16. ___Force__ is a push or a pull. 17. __Force___ can cause an object to change direction, stop or accelerate. 18. _Friction_ is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. 19. True or False __False___ Friction is i ...
... 15. Force is measured in a. Newtons b. Kg c. m/s/s d. kg/hr 16. ___Force__ is a push or a pull. 17. __Force___ can cause an object to change direction, stop or accelerate. 18. _Friction_ is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. 19. True or False __False___ Friction is i ...
Chapter Eight
... • A balance scale consisting of a weightless rod has a mass of 0.1 kg on the right side 0.2 m from the pivot point. See Fig. 8-2. (a) How far from the pivot point on the left must 0.4 kg be placed so that a balance is achieved? (b) If the 0.4-kg mass is suddenly removed, what is the instantaneous ro ...
... • A balance scale consisting of a weightless rod has a mass of 0.1 kg on the right side 0.2 m from the pivot point. See Fig. 8-2. (a) How far from the pivot point on the left must 0.4 kg be placed so that a balance is achieved? (b) If the 0.4-kg mass is suddenly removed, what is the instantaneous ro ...
Chapter 4 Rotating Coordinate Systems and the Equations of Motion
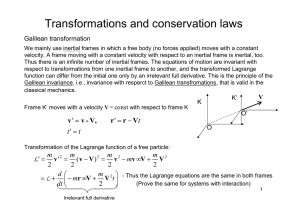
... rotating with the planet and hence, because of the rotation, a frame of reference that is not inertial. It is necessary , therefore, to examine how the equations of motion must be altered to take this into account. The earth rotates with an angular velocity Ω which we will take, for our purposes to ...
... rotating with the planet and hence, because of the rotation, a frame of reference that is not inertial. It is necessary , therefore, to examine how the equations of motion must be altered to take this into account. The earth rotates with an angular velocity Ω which we will take, for our purposes to ...
8th PS 9-Weeks 3 Exam
... The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their ____. a. frictional forces b. inertia c. masses and the distance between them d. speed and direction A feather will fall through the air more slowly than a brick because of ____. a. air resistance c. inertia b. gravity d. momen ...
... The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their ____. a. frictional forces b. inertia c. masses and the distance between them d. speed and direction A feather will fall through the air more slowly than a brick because of ____. a. air resistance c. inertia b. gravity d. momen ...
Semester 1 Final Exam Review
... review, and add things to your notes that may be missing. You may not use this review itself on the final exam, or other assignments, only what’s in your notes. The problems are pretty much in the order we covered them. Show your work on separate paper! ...
... review, and add things to your notes that may be missing. You may not use this review itself on the final exam, or other assignments, only what’s in your notes. The problems are pretty much in the order we covered them. Show your work on separate paper! ...
Newton`s 2nd Law - fhssciencerocks
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average speed: __________________________________________ ...
... 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average speed: __________________________________________ ...
Uniform circular motion
... • tension, F • bung mass m • radius r • periodic time, T Calculate mv2/r and compare with F. VPLab simulation Circular motion ...
... • tension, F • bung mass m • radius r • periodic time, T Calculate mv2/r and compare with F. VPLab simulation Circular motion ...
Honors Physics - Practice Final Exam
... C. They would hit the ground at the same time. D. They would be suspended in a vacuum. 25. Which of the following is a physical quantity that has a magnitude but no direction? A. vector C. resultant B. scalar D. frame of reference 26. Identify the following quantities as scalar or vector: the speed ...
... C. They would hit the ground at the same time. D. They would be suspended in a vacuum. 25. Which of the following is a physical quantity that has a magnitude but no direction? A. vector C. resultant B. scalar D. frame of reference 26. Identify the following quantities as scalar or vector: the speed ...