* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide motion key
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
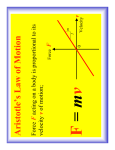
Study Guide - Motion Name Key Date Pd 1. An object is in ___motion_________ if it is changing position. 2. _Mass_____________ is a measurement of the amount of matter. 3. ____ ___Distance__ measures the length of the path that an object follows during its motion. ___Displacement_____________ is the change in position between the starting point and the ending point, as well as the ____direction________ from the start to end points. 4. If a student rides her bicycle on a straight road and does not speed up or slow down, she is traveling with a ___constant_________ _____speed____________. 5. Which of the following is a measurement of velocity? a. 16 m east c. 55 mi/h south b. 25 m/s2 d. 60 km/h 6. ___acceleration__________________ is a measure of how quickly velocity changes by speeding up, slowing down, or turning. 7. ___Velocity___________ includes the speed and __Direction______________ of motion. 8. The __Momentum_______ of an object is a measure of how hard it is to stop the object, a property of moving objects that depends on mass and velocity. 9. A __Force________ is a push or a pull. 10. The __Newton_____________ is the unit of force. 11. _Net___ _Force________________ is determined by combining forces. 12. __Static Friction___________ opposes motion between surfaces that are touching. 13. __Sliding__________________ friction is the force that slows a book moving across a table. 14. Which type of friction is important to walking? ___Static________________ ___Friction_______________ 15. An object in motion has __inertia________________, so it tends to stay in motion. 16. Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. moving objects. c. objects that are not moving. b. objects that are accelerating. d. both a and c 17. An object acted upon by a net force will accelerate in the direction of this force is Newton’s __2nd _____________________ law of motion. 18. __Gravity__________________ is a force of attraction between two objects. 19. If you are in a spacecraft that has been launched into space, your weight would (increase, decrease) because gravitational force is (increasing, decreasing). 20. Newton’s third law states that the forces two objects exert on each other are always ___equal ______________ but in ___opposite________________ directions. 21. When a soccer ball is kicked, the action and reaction forces do not cancel each other out because the forces are not __equal_____________________ in size. 22. Describe the relationship between motion and a reference point. The reference point determines if there is motion between two objects. 23. Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Velocity is different from speed, in that, velocity includes direction. 24. Explain the difference between distance and displacement. Displacement includes direction and is the shortest distance between two points, whereas distance follows the path of traveling. 25. How is it possible to be accelerating and traveling at a constant speed? If an object is traveling in a circular path it could be traveling at a constant speed but be constantly changing direction. 26. A golf ball and a bowling ball are moving at the same velocity. Which of the two has more momentum? Why? The bowling ball has more momentum because momentum is mass x velocity and the mass of the bowling ball is greater. 27. Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. Balanced forces acting on an object equal zero, unbalanced forces are when all the forces acting on an object do not equal zero. 28. Suppose you were on in-line skates and you toss a backpack full of heavy books toward your friend. What do you think will happen to you? Explain your answer in terms of Newton’s third law of motion. This will cause me to move in the opposite direction where my mass x velocity is equal the mass x velocity of the backpack. 29. Explain the relationship between mass and inertia. The greater mass an object has, the more difficult it will be to overcome its inertia. 30. Explain the difference between mass and weight. Unless gravity = 0, the greater the mass, the greater the weight. Mass does not change, weight may change depending on gravity 31. 50 N 100 N Net force ____50 N__________ 32. Direction ____Left___________ 30 N 100 N Net force ____130N__________ Direction ____Right___________ 33. A squirrel climbs to a branch 12m high at a rate of 3m/s. How long does it take for the squirrel to reach the branch? T=d/s t= 12m / 3m/s t=4s 34. A kangaroo hops 60m to the east in 5s. What is the Kangaroo’s speed? S=d/t s=60m / 5s s=12m/s 35. A car travels for half an hour at 50 km/h. How far does it travel? D=s x t d=50km/h x 0.5h d= 25km 36. If you exert a force of 9N on a 2kg object, what will its acceleration be? A=f/m a= 9N / 2kg a= 9(kgm/s2) / 2kg a=4.5m/s2 37. Find the average speed of a girl who swims 105m in 70s. Averaged speed = total distance/total time s=105m / 70s s=1.5m/s 38. What is the average acceleration of a subway train that speeds up from 9.6m/s to 12m/s in 0.8s on a straight section of track? A=(vf – vi)/t a=(12m/s – 9.6m/s)/0.8s a=3m/s2 39. Calculate the momentum of a 2.5kg puppy that is running with a velocity of 4.8m/s south. p=m x v p=2.5kg x 4.8m/s p=12kgm/s 40. What is the force necessary to accelerate a 70kg object at a rate of 4.2m/s/s? F = m x a f=70kg x 4.2m/s/s f= 294kgm/s2 f= 294N 41. What is the acceleration of a 7kg mass if a force of 68.6N is used to move it? a=f/m a= 68.6N / 7kg a= 68.6(kgm/s2) / 7kg a=9.8m/s2 42. A boy pulls a wagon with a force of 6N east as another boy pushes it with a force of 4N east. What is the net force? Fn = f1 +f2 Fn=6N + 4N Fn = 10N, east 43. If you travel 7.5km while walking for 1.5h, what is your average speed? Average speed = total distance/ total time s=7.5km / 1.5h s= 5km/h