MOTION: Describing and Measuring Motion
... To help with motion sickness, try to look forward at a point far in the distance and stay focused on that. ...
... To help with motion sickness, try to look forward at a point far in the distance and stay focused on that. ...
Chapter 7
... • He went on to conclude that there is a mutual gravitational force between all particles of matter. • From that he saw that the attractive force was universal to all objects based on their mass and the distance they are apart from each other. • Because of its universal nature, there is a constant o ...
... • He went on to conclude that there is a mutual gravitational force between all particles of matter. • From that he saw that the attractive force was universal to all objects based on their mass and the distance they are apart from each other. • Because of its universal nature, there is a constant o ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... smaller force on the smaller object but it’s easier to move, these two factors will equal out and both objects will hit at the same time. ...
... smaller force on the smaller object but it’s easier to move, these two factors will equal out and both objects will hit at the same time. ...
Monday, Sept. 22, 2008
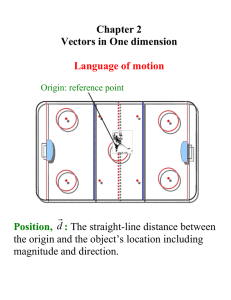
... Results of physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
... Results of physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 10. An astronaut drops a moon rock from 3.5 m above the surface of the moon. If the acceleration of gravity on the moon is 1.62 m/s2 downward, how long does it take the rock to hit the moon’s surface? ...
... 10. An astronaut drops a moon rock from 3.5 m above the surface of the moon. If the acceleration of gravity on the moon is 1.62 m/s2 downward, how long does it take the rock to hit the moon’s surface? ...
Tri A Final Review Packet
... 10) A ball is thrown perfectly horizontally off of the same cliff at 20m/s and lands 4.0s later. (Fill in the table) What is the initial horizontal velocity? What is the horizontal acceleration? What is the final horizontal velocity? Now that the ball is moving horizontally, list here which of the v ...
... 10) A ball is thrown perfectly horizontally off of the same cliff at 20m/s and lands 4.0s later. (Fill in the table) What is the initial horizontal velocity? What is the horizontal acceleration? What is the final horizontal velocity? Now that the ball is moving horizontally, list here which of the v ...
Recitation 1
... Problem 12.5. A particle moving along the x axis in simple harmonic motion starts from its equilibrium position, the origin, at t = 0 and moves to the right. The amplitude of its motion is 2.00 cm and the frequency is 1.50 Hz. (a) show that the position of the particle is given by x = (2.00 cm) sin( ...
... Problem 12.5. A particle moving along the x axis in simple harmonic motion starts from its equilibrium position, the origin, at t = 0 and moves to the right. The amplitude of its motion is 2.00 cm and the frequency is 1.50 Hz. (a) show that the position of the particle is given by x = (2.00 cm) sin( ...
All Kinematics Worksheet
... paratrooper’s speed to a safe 5.00 m/s? (In real life, the acceleration is not constant in this case, but the equations of constant acceleration provide an easy estimate.) (b) How far does the paratrooper fall during this time interval? 18. The brakes are applied to a car traveling on a dry, level h ...
... paratrooper’s speed to a safe 5.00 m/s? (In real life, the acceleration is not constant in this case, but the equations of constant acceleration provide an easy estimate.) (b) How far does the paratrooper fall during this time interval? 18. The brakes are applied to a car traveling on a dry, level h ...
what is physics
... Simply put, the study of motion is the study of anything that moves. In physics, the study of motion is called mechanics. BRANCHES OF MECHANICS Mechanics is divided into two branches: kinematics and dynamics. Essentially, kinematics is the “how of motion” (descriptive) and dynamics is the “why of mo ...
... Simply put, the study of motion is the study of anything that moves. In physics, the study of motion is called mechanics. BRANCHES OF MECHANICS Mechanics is divided into two branches: kinematics and dynamics. Essentially, kinematics is the “how of motion” (descriptive) and dynamics is the “why of mo ...
neet test paper 05 - Sigma Physics Centre
... The image formed by an objective of a compound microscope is : (a) virtual and diminished (b) real and diminished (c) real and enlarged (d) virtual and enlarged The earth radiates in the infra-red region of the spectrum. The spectrum is correctly given by : (a) Rayleigh Jeans law (b) Planck’s law of ...
... The image formed by an objective of a compound microscope is : (a) virtual and diminished (b) real and diminished (c) real and enlarged (d) virtual and enlarged The earth radiates in the infra-red region of the spectrum. The spectrum is correctly given by : (a) Rayleigh Jeans law (b) Planck’s law of ...
student notes - science
... His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x ...
... His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x ...
Dynamics
... The ratio of the applied force to the resulting acceleration is the inertia (or mass) of the body. If a torque acts on a body that can rotate freely about some axis, the body will undergo an angular acceleration. The ratio of the applied torque to the resulting angular acceleration is the rotational ...
... The ratio of the applied force to the resulting acceleration is the inertia (or mass) of the body. If a torque acts on a body that can rotate freely about some axis, the body will undergo an angular acceleration. The ratio of the applied torque to the resulting angular acceleration is the rotational ...
Paper : IIT-JEE Physics Question Paper Of Year 1999
... A particle of mass m, positive charge q and velocity V0i travels along x-axis and enters the region of the magnetic field. Neglect the gravity throughout the question. (a) Find the value of L is fthe particle emerges from the region of magnetic field with its final velocity at an angle 300 to its in ...
... A particle of mass m, positive charge q and velocity V0i travels along x-axis and enters the region of the magnetic field. Neglect the gravity throughout the question. (a) Find the value of L is fthe particle emerges from the region of magnetic field with its final velocity at an angle 300 to its in ...
L#4
... --Query : This particle goes faster and faster as it moves out. Why isn't it conserving energy? Answer: N is doing work on the particle! N dot v = (2m r& ω ) (r ω) = m ω2 dr2/dt ≠ 0. Something is doing work on the system and a little reflection indicates that there must be a motor that is maintainin ...
... --Query : This particle goes faster and faster as it moves out. Why isn't it conserving energy? Answer: N is doing work on the particle! N dot v = (2m r& ω ) (r ω) = m ω2 dr2/dt ≠ 0. Something is doing work on the system and a little reflection indicates that there must be a motor that is maintainin ...
FY016_2012
... A circular, horizontal pipe uniformly tapers from a diameter of 160 mm to a diameter of 70 mm. Hydraulic oil, of density 1200 kgm-3, flows through the pipe from the greater diameter cross-section to the smaller diameter cross-section. The pressure at the greater diameter cross-section is 160 kPa whi ...
... A circular, horizontal pipe uniformly tapers from a diameter of 160 mm to a diameter of 70 mm. Hydraulic oil, of density 1200 kgm-3, flows through the pipe from the greater diameter cross-section to the smaller diameter cross-section. The pressure at the greater diameter cross-section is 160 kPa whi ...
The Physics of Orbits
... because they change direction satellites are undergoing acceleration. This is called Centripetal Acceleration, and it is: (copy formula) ...
... because they change direction satellites are undergoing acceleration. This is called Centripetal Acceleration, and it is: (copy formula) ...