Lecture 16 - Circular Motion
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. (This required inventing Calculus). He wo ...
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. (This required inventing Calculus). He wo ...
Paper Reference(s)
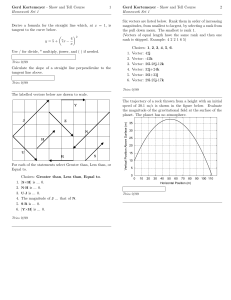
... ceiling. The particle hangs in equilibrium with AC and BC inclined to the horizontal at 30 and 60 respectively, as shown in Fig.1. Given the tension in AC is 50 N, calculate (a) the tension in BC, to 3 significant figures, (b) the value of W. ...
... ceiling. The particle hangs in equilibrium with AC and BC inclined to the horizontal at 30 and 60 respectively, as shown in Fig.1. Given the tension in AC is 50 N, calculate (a) the tension in BC, to 3 significant figures, (b) the value of W. ...
Physics Final
... Bill’s motorcycle can accelerate at 7.05m/s2 at a certain RPM and gear. How far, starting from rest, will Bill travel in the first 2.50s? ...
... Bill’s motorcycle can accelerate at 7.05m/s2 at a certain RPM and gear. How far, starting from rest, will Bill travel in the first 2.50s? ...
Centripetal Force
... provides part of the cpforce at the top of the loop ( ST ) • The rest of the cpforce is provided by the weight of the rider ...
... provides part of the cpforce at the top of the loop ( ST ) • The rest of the cpforce is provided by the weight of the rider ...
Falling Objects and Gravity
... 1. Acceleration due to gravity “g” near the earth’s surface is CONSTANT (i.e., NOT varying with TIME) and has a value of 9.8 m/s2. 2. An object in free fall will INCREASE its VELOCITY UNIFORMLY with time. (v = g t) 3. The distance fallen in a unit of time will INCREASE RAPIDLY with time as the objec ...
... 1. Acceleration due to gravity “g” near the earth’s surface is CONSTANT (i.e., NOT varying with TIME) and has a value of 9.8 m/s2. 2. An object in free fall will INCREASE its VELOCITY UNIFORMLY with time. (v = g t) 3. The distance fallen in a unit of time will INCREASE RAPIDLY with time as the objec ...
Unit 1 - CElliott
... the tension in the rope connecting the two cats. 3. You attach two cats (A with a mass of 5.5kg and B with a mass of 3.7kg) to opposite ends of a rope suspended over a pulley. If there is no friction in the pulley system, find the acceleration of the system and the tension in the rope. 4. A cat (m=5 ...
... the tension in the rope connecting the two cats. 3. You attach two cats (A with a mass of 5.5kg and B with a mass of 3.7kg) to opposite ends of a rope suspended over a pulley. If there is no friction in the pulley system, find the acceleration of the system and the tension in the rope. 4. A cat (m=5 ...
Forces and Motion Commotion 2012
... Part A: Motion and Speed of Objects 1. Describe and measure motion using the concept of a reference point. 2. Describe and measure speed and be able to calculate speed. (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time ...
... Part A: Motion and Speed of Objects 1. Describe and measure motion using the concept of a reference point. 2. Describe and measure speed and be able to calculate speed. (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time ...
Section B: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING – Answer ALL questions
... A vacuum chamber which forms part of a linear accelerator contains both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field. When a charged particle is fired into the chamber it experiences an instantaneous force F1 (newtons) due to the electric field, and F2 (newtons) due to the magnetic field, a ...
... A vacuum chamber which forms part of a linear accelerator contains both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field. When a charged particle is fired into the chamber it experiences an instantaneous force F1 (newtons) due to the electric field, and F2 (newtons) due to the magnetic field, a ...
Linear and Rotational Kinematics
... about its center, and it has a moment of inertia I. a) Draw freebody diagrams for the wheel and the block, block and write Newton Newton’ss second law appropriate to each object. b) When the mass m is released from rest,, it falls a distance D in time t. Find the acceleration of the block and the an ...
... about its center, and it has a moment of inertia I. a) Draw freebody diagrams for the wheel and the block, block and write Newton Newton’ss second law appropriate to each object. b) When the mass m is released from rest,, it falls a distance D in time t. Find the acceleration of the block and the an ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 1 Notes
... angular velocity and acceleration are vector quantities. So far we only talked about the magnitude of these vectors. But as vectors they also have a direction. Both angular velocity and acceleration point along the rotation axis. ...
... angular velocity and acceleration are vector quantities. So far we only talked about the magnitude of these vectors. But as vectors they also have a direction. Both angular velocity and acceleration point along the rotation axis. ...
Test #4 - Wando High School
... 12) A boat traveling due east at 6.00 m/s crosses a 98.0 m wide river flowing due southward at 3.40 m/s. a) What will the boat’s velocity be? (remember that velocity, like all vectors, has both a magnitude and direction). b) How far downstream will the boat be when it reaches the opposite shore? c) ...
... 12) A boat traveling due east at 6.00 m/s crosses a 98.0 m wide river flowing due southward at 3.40 m/s. a) What will the boat’s velocity be? (remember that velocity, like all vectors, has both a magnitude and direction). b) How far downstream will the boat be when it reaches the opposite shore? c) ...
MOTION
... rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
... rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
practice for midterm, part 3 - West Windsor
... a) Draw a motion diagram for a moving object b) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram. c) Interpret x vs t and v vs t graphs in terms of position, velocity, displacement, and acceleration. 1. Are you moving while sitting on a train that is leaving the station? 2. Describe th ...
... a) Draw a motion diagram for a moving object b) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram. c) Interpret x vs t and v vs t graphs in terms of position, velocity, displacement, and acceleration. 1. Are you moving while sitting on a train that is leaving the station? 2. Describe th ...