* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz 7
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
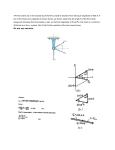
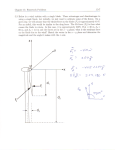
Quiz 7 Multiple-choice questions on forces acting at a point 1. A physical quantity which has direction as well as magnitude is known as a: (a) force (b) vector (c) scalar (d) weight 2. Which of the following is not a scalar quantity? (a) velocity (b) potential energy (c) work (d) kinetic energy 3. Which of the following is not a vector quantity? (a) displacement (b) density (c) velocity (d) acceleration 4. 5. 6. 7. Which of the following statements is false? (a) Scalar quantities have size or magnitude only (b) Vector quantities have both magnitude and direction (c) Mass, length and time are all scalar quantities (d) Distance, velocity and acceleration are all vector quantities If the centre of gravity of an object which is slightly disturbed is raised and the object returns to its original position when the disturbing force is removed, the object is said to be in (a) neutral equilibrium (b) stable equilibrium (c) static equilibrium (d) unstable equilibrium Which of the following statements is false? (a) The centre of gravity of a lamina is at its point of balance (b) The centre of gravity of a circular lamina is at its centre (c) The centre of gravity of a rectangular lamina is at the point of intersection of its two sides (d) The centre of gravity of a thin uniform rod is halfway along the rod The magnitude of the resultant of the vectors shown in Figure 19.29 is: (a) 2 N (b) 12 N (c) 35 N (d) −2 N 5N 7N Figure 19.29 Science for Engineering. 978-1-138-82688-5, © John Bird. Published by Taylor & Francis. All rights reserved. 8. The magnitude of the resultant of the vectors shown in Figure 19.30 is: (a) 7 N (b) 5 N (c) 1 N (d) 12 N 4N 3N Figure 19.30 9. 10. 11. Which of the following statements is false ? (a) There is always a resultant vector required to close a vector diagram representing a system of coplanar forces acting at a point, which are not in equilibrium (b) A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction (c) A vector diagram representing a system of coplanar forces acting at a point when in equilibrium does not close (d) Concurrent forces are those which act at the same time at the same point Which of the following statements is false? (a) The resultant of coplanar forces of 1 N, 2 N and 3 N acting at a point can be 4 N (b) The resultant of forces of 6 N and 3 N acting in the same line of action but opposite in sense is 3 N (c) The resultant of forces of 6 N and 3 N acting in the same sense and having the same line of action is 9N (d) The resultant of coplanar forces of 4 N at 0◦ , 3 N at 90◦ and 8 N at 180◦ is 15 N A space diagram of a force system is shown in Figure 19.31. Which of the vector diagrams in Figure 19.32 does not represent this force system? 10 N 30 N 20 N Figure 19.31 12. With reference to Figure 19.33, which of the following statements is false? (a) The horizontal component of FA is 8.66 N (b) The vertical component of FB is 10 N (c) The horizontal component of FC is 0 (d) The vertical component of FD is 4 N 13. The resultant of two forces of 3 N and 4 N can never be equal to: (a) 2.5 N (b) 4.5 N (c) 6.5 N (d) 7.5 N The magnitude of the resultant of the vectors shown in Figure 19.34 is: (a) 5 N (b) 13 N (c) 1 N (d) 63 N 10 N R = 1 esu 7. ltan 32 t N 30 N 30 N 10 N 10 N R = 1 esu 7.3 ltan 2N t 20 N 10 N 20 N 20 N 30 N (c) (b) (a) Scale 0 10 20 nt ta ul 2 N es 3 R 17. = R = esu 17 lta .3 nt 2 N 30 N 20 N (d) 30 N Figure 19.32 FB = 20 N FA = 10 N 150° 30° 60° FC = 5 N FD = 8 N Figure 19.33 3N 3N 7N Figure 19.34 1. (b) 2. (a) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (b) 8. (b) 9. (c) 10. (d) 11. (c) 12. (d) 13. (d) 14. (a) Answers 14.