* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review - Hingham Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
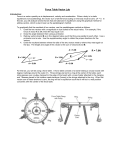
Review Test #4: Vectors & Two-Dimensional Forces Reading: Ch. 5, p.p. 118 - 139 Topics: Vector Addition, Equilibrium, Inclines Labs & Activities: Treasure Hunt Equations: Fg= mg a = Fnet m soh Ff = μFN cah c² = a² + b² toa Know a vector has magnitude and direction. Be able to draw vectors tip-to-tail. Know the resultant is the vector that points from the start to the finish when 2 or more vectors are drawn tip-to-tail. Be able to find the resultant graphically and algebraically. Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Be able to break forces at angles into components. Know an object is in equilibrium when the forces acting on the object are balanced. Know an object in equilibrium will move at a constant speed or not at all. Be able to identify forces that are balanced. With inclines, be able to break the force of gravity into components. Know the relationship between the angle of an incline and the components of gravity. Practice Questions & Problems 1. a. List four ways to describe the direction of the vector. b. Calculate the components of the vector shown. 20⁰ 15 N 2. A girl jogs 2.5 miles west and 5 miles north. Calculate her resultant displacement. 3. Two displacement vectors each with a y-component of 10 km are added together to form a resultant which makes an angle of 60º with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the resultant? 4. A hiker walks 25.5 km at 35º south of east. On the next day he walks 41 km at 65º north of east. What is his total displacement? 5. A man pulls a 0.85 kg book across a table with a force of 7 N at an angle of 24º to the horizontal. The coefficient of friction for the book on the table is 0.25. Calculate the book’s acceleration. 6. A 9800N railroad car is being pulled on tracks of negligible friction by ropes tied to two horses as shown in the top view below. The net force on the car is 500 N to the right. a) Calculate the tension in each rope. b) Calculate the car’s acceleration. 80⁰ 7. Calculate the tension in the cables shown. T T 10⁰ 10⁰ 20 kg 8. A 14 kg box is pushed along the floor with a force of 68 N that acts at an angle of 35º below the horizontal. The block accelerates to the right at 1.45 m/s². Find the coefficient of friction between the block and the floor. 9. An 80 kg sled is pulled up a hill that has an incline of 27 °. If the coefficient of friction between the sled and the snow is 0.12, how hard must a child pull the sled to accelerate it at 0.75 m/s² ? 10. A 5 kg block is held in equilibrium on a frictionless incline of 30° by a force, F, as shown. Find the magnitude of F and the normal force. F