Populations and Communities Study Guide Populations
... What is a habitat? What basic needs are provided by an organism’s habitat? Why do different organisms live in different habitats? What might happen to an organism if its habitat could not meet one of its needs? What are biotic factors? What are abiotic factors? Why are water and sunlight important t ...
... What is a habitat? What basic needs are provided by an organism’s habitat? Why do different organisms live in different habitats? What might happen to an organism if its habitat could not meet one of its needs? What are biotic factors? What are abiotic factors? Why are water and sunlight important t ...
10:4 Review Test
... You are trying to identify an animal. It is triploblastic, it has a dorsal hollow nerve cord, and post anal tail. You found it sitting on a nest of eggs near a river. It seems to have nipples along its belly. This animal is a... a) Reptile b) Mammal c) Monotreme d) Eutherian e) B and D f) B and C ...
... You are trying to identify an animal. It is triploblastic, it has a dorsal hollow nerve cord, and post anal tail. You found it sitting on a nest of eggs near a river. It seems to have nipples along its belly. This animal is a... a) Reptile b) Mammal c) Monotreme d) Eutherian e) B and D f) B and C ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary - Flushing Community Schools
... material and returns the nutrients so they are available to other organisms ...
... material and returns the nutrients so they are available to other organisms ...
Introduction to Animals
... organs in the adult body. a. ectoderm: outer-layer- outer layer of skin, nervous system, sense organs b. endoderm: inner-layer- lining of digestive tract, respiratory system, urinary bladder, digestive organs such as liver, and many other glands. c. Mesoderm: Separates inner and outer layer- Most of ...
... organs in the adult body. a. ectoderm: outer-layer- outer layer of skin, nervous system, sense organs b. endoderm: inner-layer- lining of digestive tract, respiratory system, urinary bladder, digestive organs such as liver, and many other glands. c. Mesoderm: Separates inner and outer layer- Most of ...
Unit 3 Sustainability and Interdependence Glossary
... alliance link between individuals in a primate social group which can increase social status Altruistic behaviour behaviour that harms the donor but benefits the recipient annual weed weed plant that completes its life cycle in 1 year ATP synthase membrane-bound enzyme that synthesises ATP back-cros ...
... alliance link between individuals in a primate social group which can increase social status Altruistic behaviour behaviour that harms the donor but benefits the recipient annual weed weed plant that completes its life cycle in 1 year ATP synthase membrane-bound enzyme that synthesises ATP back-cros ...
Introduction to Marine Ecology Lecture Notes
... Marine Ecology The oceans are populated by uncounted millions of species, most of which have not yet been identified. Marine ecology is the study of relationships between species and their environments. The marine environment consists of nonliving abiotic factors such as water, light, temperature, p ...
... Marine Ecology The oceans are populated by uncounted millions of species, most of which have not yet been identified. Marine ecology is the study of relationships between species and their environments. The marine environment consists of nonliving abiotic factors such as water, light, temperature, p ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... Proteins that have specific bonding sites for certain antigens that have been identified previously in the body Anything that prompts a response or action An action that is prompted by a stimulus The act of multiple body systems working together to establish various tasks Anything capable of causing ...
... Proteins that have specific bonding sites for certain antigens that have been identified previously in the body Anything that prompts a response or action An action that is prompted by a stimulus The act of multiple body systems working together to establish various tasks Anything capable of causing ...
8.L.5- Energy in Living Organisms - NHCS
... organisms, including humans, are multi-cellular. Cells carry on the many functions needed to sustain life. They grow and divide (mitosis or meiosis), thereby producing more cells. This requires that they take in nutrients, which they use to provide energy for the work that cells do and to make the m ...
... organisms, including humans, are multi-cellular. Cells carry on the many functions needed to sustain life. They grow and divide (mitosis or meiosis), thereby producing more cells. This requires that they take in nutrients, which they use to provide energy for the work that cells do and to make the m ...
Ecology
... Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) ...
... Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) ...
Chp 20 Webs - AdventuresinScienceEducation
... level. Producers are level 1, herbivores are level 2, first order consumers feeding on the herbivores are level 3 etc. • The food chains that make up a food web tend to have no more than 5 links, as the system is inefficient and there isn’t enough energy to sustain more than 5 trophic levels. ...
... level. Producers are level 1, herbivores are level 2, first order consumers feeding on the herbivores are level 3 etc. • The food chains that make up a food web tend to have no more than 5 links, as the system is inefficient and there isn’t enough energy to sustain more than 5 trophic levels. ...
Ch4 Revision - Population Ecology
... Environment: All the organisms (biotic) and the conditions (abiotic) which exist in an area Abiotic factors: all the non-living factors in an environment, such as rainfall, temperature, soil. Biotic factors: All the living organisms in an area – such as producers, predators and parasites. Population ...
... Environment: All the organisms (biotic) and the conditions (abiotic) which exist in an area Abiotic factors: all the non-living factors in an environment, such as rainfall, temperature, soil. Biotic factors: All the living organisms in an area – such as producers, predators and parasites. Population ...
Ecology > Text reference: Chapter 2
... transfers these microscopic larva as it bites. During the next few months, these larva migrate through the dogs body arriving at the heart several months later where they become adults. ...
... transfers these microscopic larva as it bites. During the next few months, these larva migrate through the dogs body arriving at the heart several months later where they become adults. ...
ecology - MrsStowSupport
... • Area where an organism lives, includes both the biotic and abiotic factors ...
... • Area where an organism lives, includes both the biotic and abiotic factors ...
Insecta
... Most numerous and diverse of all the groups of arthropods. • (There are more species of insects than species in all the other classes of animals combined!!) » Have three pairs of legs » Usually have two pairs of wings on the thoracic region of the body, (although some have one pair of wings, or none ...
... Most numerous and diverse of all the groups of arthropods. • (There are more species of insects than species in all the other classes of animals combined!!) » Have three pairs of legs » Usually have two pairs of wings on the thoracic region of the body, (although some have one pair of wings, or none ...
8th Grade 100 Facts Matter 1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of
... 69. Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. 70. Cells carry on the many functions needed to sustain life. 71. Through the process of cellular respiration , cells convert energy (glucose) to a usable form of energy (ATP). 72. Matter moves withi ...
... 69. Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. 70. Cells carry on the many functions needed to sustain life. 71. Through the process of cellular respiration , cells convert energy (glucose) to a usable form of energy (ATP). 72. Matter moves withi ...
organ challenge - powerpoint - Curriculum for Excellence Science
... Organ Challenge! In a pair, or trio, draw around the outline of one person using a BLACK pen onto paper. Draw and cut out the organs from different coloured paper as stated below. ...
... Organ Challenge! In a pair, or trio, draw around the outline of one person using a BLACK pen onto paper. Draw and cut out the organs from different coloured paper as stated below. ...
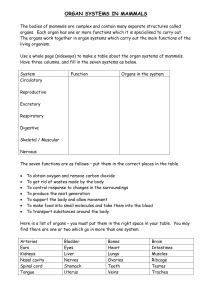
doc Organ systems table Table to fill in which will
... Nervous The seven functions are as follows – put them in the correct places in the table. ...
... Nervous The seven functions are as follows – put them in the correct places in the table. ...
11.1: Respiratory Systems of Animals in Aquatic or Moist
... Insects have a system of branching respiratory tubes (spiracles and trachea) that connect body cells directly with environment. Oxygen enters the body through spiracles and diffuses into tracheae. Gas exchange occurs throughout the body, close to all body cells. Carbon dioxide exits the body in the ...
... Insects have a system of branching respiratory tubes (spiracles and trachea) that connect body cells directly with environment. Oxygen enters the body through spiracles and diffuses into tracheae. Gas exchange occurs throughout the body, close to all body cells. Carbon dioxide exits the body in the ...
3.2 Energy Flow
... Each step in a food chain or food web Producers = 1st trophic level Consumers = 2nd, trophic level (3rd, 4th, etc) Only about 10% of the energy available within one trophic level is transferred to organisms at the next trophic level ...
... Each step in a food chain or food web Producers = 1st trophic level Consumers = 2nd, trophic level (3rd, 4th, etc) Only about 10% of the energy available within one trophic level is transferred to organisms at the next trophic level ...
Population- a group of organisms of the same species living
... Producers - An organism that is able to make its own food by using a source of energy to turn simple raw materials into food Food Webs - A diagram that consists of many different food chains Competition - An interaction in which organisms struggle with one another to get resources Commensalism - A f ...
... Producers - An organism that is able to make its own food by using a source of energy to turn simple raw materials into food Food Webs - A diagram that consists of many different food chains Competition - An interaction in which organisms struggle with one another to get resources Commensalism - A f ...
Ch 2 m definitions
... only eats plants 13. Heterotroph – organism that eats to get energy 14. Omnivore - organism that eats both plants/animals 15. Biogeochemical cycle – a series of physical and biological processes by which nutrients are cycled through the ...
... only eats plants 13. Heterotroph – organism that eats to get energy 14. Omnivore - organism that eats both plants/animals 15. Biogeochemical cycle – a series of physical and biological processes by which nutrients are cycled through the ...
Word
... The heart chamber into which newly oxygenated blood flows from the lungs. The largest and strongest heart chamber; its strong muscular walls pump blood out through your blood vessels to all of your body tissues. The largest artery of the body. The process by which cells use fuels and oxygen to make ...
... The heart chamber into which newly oxygenated blood flows from the lungs. The largest and strongest heart chamber; its strong muscular walls pump blood out through your blood vessels to all of your body tissues. The largest artery of the body. The process by which cells use fuels and oxygen to make ...