What are adaptations?
... » Many animals’ only line of defense is their colors. » The warning colors of red, yellow, orange, and bright blue warn others that these animals might be dangerous and should be avoided! ...
... » Many animals’ only line of defense is their colors. » The warning colors of red, yellow, orange, and bright blue warn others that these animals might be dangerous and should be avoided! ...
Name: Biology Quarter Test 1 Review Scientific Method What is a
... What does abiotic mean? Give 2 examples of abiotic factors in an ecosystem. Abiotic means nonliving. Air currents, water, temperature and rocks are examples of abiotic factors. What does biotic mean? Give 2 examples of biotic factors in an ecosystem. Biotic means living. Trees, grass and any organis ...
... What does abiotic mean? Give 2 examples of abiotic factors in an ecosystem. Abiotic means nonliving. Air currents, water, temperature and rocks are examples of abiotic factors. What does biotic mean? Give 2 examples of biotic factors in an ecosystem. Biotic means living. Trees, grass and any organis ...
Levels of Organization in the Ecosystem
... • All the different populations in a specific area or region at a certain time. • Communities involve many types of interactions among the populations. • Some of these interactions involve the obtaining and use of food, space, or other environmental resources. › Example – all of the living organisms ...
... • All the different populations in a specific area or region at a certain time. • Communities involve many types of interactions among the populations. • Some of these interactions involve the obtaining and use of food, space, or other environmental resources. › Example – all of the living organisms ...
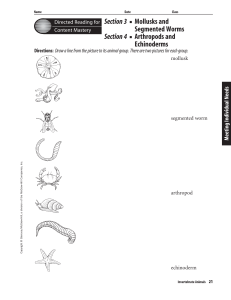
Chapter 6 Resource: Invertebrate Animals
... 7. circulatory system in which blood is not in vessels but surrounds organs 10. bell-shaped body plan, like that of a jellyfish 12. joint-footed animal 14. organs that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with water 15. tongue-like organ in mollusks that works like a file 16. remaining attached to one ...
... 7. circulatory system in which blood is not in vessels but surrounds organs 10. bell-shaped body plan, like that of a jellyfish 12. joint-footed animal 14. organs that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with water 15. tongue-like organ in mollusks that works like a file 16. remaining attached to one ...
Ecology Vocabulary Words
... You will choose 3 options; one of which must be the middle. *You cannot use the same words for your 2nd and 3rd choices. Create a “meme” for ten words that helps explain what the word means. Be sure to include the term ...
... You will choose 3 options; one of which must be the middle. *You cannot use the same words for your 2nd and 3rd choices. Create a “meme” for ten words that helps explain what the word means. Be sure to include the term ...
Ecology - One Day Enrichment
... • Population density – the number of individuals per unit area • Population growth – increase in size of a population • Population size can be affected by: – Number of births – Number of deaths – Immigration – organisms moving into an area – Emigration – organisms moving out of an area ...
... • Population density – the number of individuals per unit area • Population growth – increase in size of a population • Population size can be affected by: – Number of births – Number of deaths – Immigration – organisms moving into an area – Emigration – organisms moving out of an area ...
File
... 3. When cells divide to create 2 identical cells, they reproduce by __________________ 4. Name the 2 types of reproduction _____________________, ______________________ 5. Which one is used to make new bone cells ________________, a baby whale_____________ 6. Which type of reproduction has genetic v ...
... 3. When cells divide to create 2 identical cells, they reproduce by __________________ 4. Name the 2 types of reproduction _____________________, ______________________ 5. Which one is used to make new bone cells ________________, a baby whale_____________ 6. Which type of reproduction has genetic v ...
Chapter 14 Interactions in Ecosystems Review
... 1. __Habitat_ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives 2. ___Abiotic_or Density-Independent___ factors are non-living factors--temperature, rainfall, etc.. 3. __Biotic or Density-Dependent___ factors are living factors---plants and animals 4. __Ecological Niche___ includes all of the fa ...
... 1. __Habitat_ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives 2. ___Abiotic_or Density-Independent___ factors are non-living factors--temperature, rainfall, etc.. 3. __Biotic or Density-Dependent___ factors are living factors---plants and animals 4. __Ecological Niche___ includes all of the fa ...
Interactions in Communities
... _____ 1. predation _____ 2. commensalism _____ 3. coevolution _____ 4. mutualism _____ 5. symbiosis _____ 6. parasitism _____ 7. herbivory _____ 8. host _____ 9. prey ...
... _____ 1. predation _____ 2. commensalism _____ 3. coevolution _____ 4. mutualism _____ 5. symbiosis _____ 6. parasitism _____ 7. herbivory _____ 8. host _____ 9. prey ...
Niche & Community Interactions PPT
... survival. An example would be water. The Biological Aspects of the Niche involve the biotic factors that are required for survival. An example would reproduction and food. ...
... survival. An example would be water. The Biological Aspects of the Niche involve the biotic factors that are required for survival. An example would reproduction and food. ...
Insect Notes
... 2 Phylum of Animals: No backbone. - Examples are: insects, worms, sponges, mollusks, and etc. - Lack: bones, some have hard outer shells or exoskeletons - 95% of all animals - Insects make up 80% of all animals. Chordata- 5 divisions of chordata - Make up only 5% of all animals. ...
... 2 Phylum of Animals: No backbone. - Examples are: insects, worms, sponges, mollusks, and etc. - Lack: bones, some have hard outer shells or exoskeletons - 95% of all animals - Insects make up 80% of all animals. Chordata- 5 divisions of chordata - Make up only 5% of all animals. ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... survival and growth of an organism and the productivity of the ecosystem in which that organism lives. 4. A habitat is the area where an organism lives. B. The Niche 1. A niche is the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organisms use t ...
... survival and growth of an organism and the productivity of the ecosystem in which that organism lives. 4. A habitat is the area where an organism lives. B. The Niche 1. A niche is the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organisms use t ...
Day 1 Notes
... Day 1 Notes- 3 Green Anatomy- Structural components of an organism’s “body” and how it is built Physiology- The overall functioning of the body and all of its components (mostly chemical and electrical); PROCESSES 4 Themes for the Year: - “FFF”- Form Follows Function - Interdependence in Systems - H ...
... Day 1 Notes- 3 Green Anatomy- Structural components of an organism’s “body” and how it is built Physiology- The overall functioning of the body and all of its components (mostly chemical and electrical); PROCESSES 4 Themes for the Year: - “FFF”- Form Follows Function - Interdependence in Systems - H ...
1) Chapter 21 - Ecology Vocabulary
... Population – a group of the same type of organisms living in the same place at the same time. Community – all the populations that live in an ecosystem. Habitat – place where an organism lives, provides the food, shelter, moisture, temperature, and other factors required for the organism’s survival. ...
... Population – a group of the same type of organisms living in the same place at the same time. Community – all the populations that live in an ecosystem. Habitat – place where an organism lives, provides the food, shelter, moisture, temperature, and other factors required for the organism’s survival. ...
Ecology Unit - Houston ISD
... Trophic Level = represents an organism’s position in the transfer of energy Energy Pyramid = a diagram that compares energy used at each trophic level - as you increase up the pyramid 1) energy available decreases - only about 10% of the energy from previous level is obtained 2) biomass decreases 3) ...
... Trophic Level = represents an organism’s position in the transfer of energy Energy Pyramid = a diagram that compares energy used at each trophic level - as you increase up the pyramid 1) energy available decreases - only about 10% of the energy from previous level is obtained 2) biomass decreases 3) ...
Lecture #18 Date
... Energy expenditures per unit mass (kcal/kg•day). Comparing the daily energy expenditures per kg of body weight for the four animals reinforces two important concepts of bioenergetics. First, a small animal, such as a mouse, has a much greater energy demand per kg than does a large animal of the same ...
... Energy expenditures per unit mass (kcal/kg•day). Comparing the daily energy expenditures per kg of body weight for the four animals reinforces two important concepts of bioenergetics. First, a small animal, such as a mouse, has a much greater energy demand per kg than does a large animal of the same ...