Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... Thermodynamics • Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy in a chemical or physical process. – We introduced the thermodynamic property of enthalpy, H, in Chapter 6. – We noted that the change in enthalpy equals the heat of reaction at constant pressure ...
... Thermodynamics • Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy in a chemical or physical process. – We introduced the thermodynamic property of enthalpy, H, in Chapter 6. – We noted that the change in enthalpy equals the heat of reaction at constant pressure ...
ppt
... examples of physical and chemical equilibrium systems. Explain the concept of chemical equilibrium and how it applies to the concentration of reactants and products in a chemical reaction at equilibrium. Create and complete an ICE table for an equilibrium system. Draw graphs of c vs. t to illustrate ...
... examples of physical and chemical equilibrium systems. Explain the concept of chemical equilibrium and how it applies to the concentration of reactants and products in a chemical reaction at equilibrium. Create and complete an ICE table for an equilibrium system. Draw graphs of c vs. t to illustrate ...
CHEM 494 Lecture 10b - UIC Department of Chemistry
... substances currently known by the names of alkalis, but alkaloids, since some of their properties they differ from alkalis considerably, and would thus find their place before the plant acids in the field of plant chemistry. ...
... substances currently known by the names of alkalis, but alkaloids, since some of their properties they differ from alkalis considerably, and would thus find their place before the plant acids in the field of plant chemistry. ...
Sample Exercise 2.1
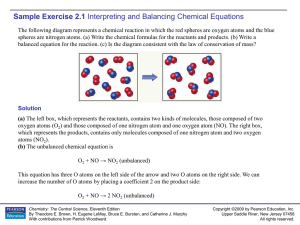
... Now there are two N atoms and four O atoms on the right. Placing the coefficient 2 in front of NO balances both the number of N atoms and O atoms: O2 + 2 NO → 2 NO2 (balanced) (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each ...
... Now there are two N atoms and four O atoms on the right. Placing the coefficient 2 in front of NO balances both the number of N atoms and O atoms: O2 + 2 NO → 2 NO2 (balanced) (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each ...
3 ON THE THERMODYNAMICS OF FATTY ACID OXIDATION
... and so, combined with (3), the limiting yield of ATP is about 0.5 mol g-1. The oxidation of the FAs from human fat or rattite or seed oils yields about 0.41 mol ATP g-1 (9) despite quite different FA compositions (Table 1). Naturally, the ATP yield increases with n and decreases only slightly with ...
... and so, combined with (3), the limiting yield of ATP is about 0.5 mol g-1. The oxidation of the FAs from human fat or rattite or seed oils yields about 0.41 mol ATP g-1 (9) despite quite different FA compositions (Table 1). Naturally, the ATP yield increases with n and decreases only slightly with ...
Sample Exam #2 Answer Key
... thiols. Finally, alcohols are much more water soluble than thiols due to their greater polarity and hydrogen bonding. 2) Compare the molecular structure and physical properties of aldehydes and ketones. Include descriptions of geometry, orbital hybridization, hydrogen bonding, relative melting point ...
... thiols. Finally, alcohols are much more water soluble than thiols due to their greater polarity and hydrogen bonding. 2) Compare the molecular structure and physical properties of aldehydes and ketones. Include descriptions of geometry, orbital hybridization, hydrogen bonding, relative melting point ...
AS and A-level Chemistry Specification Specifications for first
... An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and ...
... An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Adding this coefficient balances H but gives four O atoms in the products. Because there are only three O atoms in the reactants, we are not finished. We can place the 3/2 coefficient in front of O2 to give four O Atoms in the reactants (3/2 x 2 = 3 O atoms in 3/2 O2) CH3OH(l) + 3/2O2(g) CO2(g) + ...
... Adding this coefficient balances H but gives four O atoms in the products. Because there are only three O atoms in the reactants, we are not finished. We can place the 3/2 coefficient in front of O2 to give four O Atoms in the reactants (3/2 x 2 = 3 O atoms in 3/2 O2) CH3OH(l) + 3/2O2(g) CO2(g) + ...
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones – Nucleophilic Addition
... The negative charge of the enolate anion is distributed on both oxygen and carbon, the ion can combine with a proton at either site. ...
... The negative charge of the enolate anion is distributed on both oxygen and carbon, the ion can combine with a proton at either site. ...
Spring 2005
... a. (3 pts) What action should you take? b. (3 pts) What action should your lab partner take? 19. (6 pts) Draw the Lewis structure for H2SO4 including any resonance structures. 20. (10 pts) Ammonia is produced commercially by the Haber process: 3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) ! 2 NH3 (g) The yield from this reacti ...
... a. (3 pts) What action should you take? b. (3 pts) What action should your lab partner take? 19. (6 pts) Draw the Lewis structure for H2SO4 including any resonance structures. 20. (10 pts) Ammonia is produced commercially by the Haber process: 3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) ! 2 NH3 (g) The yield from this reacti ...
CHAPTER-7
... Ans. a) Effect of pressure: increase in pressure increases rate of forward reaction since it is accompanied by decrease in no. of gaseous moles; hence equilibrium shifts to right side decrease in pressure increases rate of backward reaction. b) Effect of concentration: Increase in concentration of r ...
... Ans. a) Effect of pressure: increase in pressure increases rate of forward reaction since it is accompanied by decrease in no. of gaseous moles; hence equilibrium shifts to right side decrease in pressure increases rate of backward reaction. b) Effect of concentration: Increase in concentration of r ...
Regents Chemistry - New York Science Teacher
... (4) The concentration of the products and the concentration of the reactants are correct constant. ...
... (4) The concentration of the products and the concentration of the reactants are correct constant. ...