Chapter 13, sections 13.5 - Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
... • higher boiling points than alkanes and ethers of similar mass. • lower boiling points than alcohols of similar mass. ...
... • higher boiling points than alkanes and ethers of similar mass. • lower boiling points than alcohols of similar mass. ...
19_03_05rw
... First stage of mechanism (formation of tetrahedral intermediate) is analogous to nucleophilic addition to C=O of aldehydes and ketones. ...
... First stage of mechanism (formation of tetrahedral intermediate) is analogous to nucleophilic addition to C=O of aldehydes and ketones. ...
Acid derivatives
... individual steps in these mechanisms vary, but the essential characteristic of the overall transformation is that of addition followed by elimination. Acid catalysts act to increase the electrophilicity of the acyl reactant; whereas, base catalysts act on the nucleophilic reactant to increase its re ...
... individual steps in these mechanisms vary, but the essential characteristic of the overall transformation is that of addition followed by elimination. Acid catalysts act to increase the electrophilicity of the acyl reactant; whereas, base catalysts act on the nucleophilic reactant to increase its re ...
C - Deans Community High School
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
CBSEGuess.com
... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Why sulphuric acid is not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI? 2. Explain swarts reaction. 3. How o- and p- niterophenols are separated? 4. Conert (a) eth ...
... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Why sulphuric acid is not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI? 2. Explain swarts reaction. 3. How o- and p- niterophenols are separated? 4. Conert (a) eth ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in society
... Industrial processes are designed to maximise profit and minimise the impact on the environment. "The Chemical Industry is not in existence to manufacture chemicals: like any other industry it exists to create wealth and wealth can only be created if it can make profits." So, the major determinant i ...
... Industrial processes are designed to maximise profit and minimise the impact on the environment. "The Chemical Industry is not in existence to manufacture chemicals: like any other industry it exists to create wealth and wealth can only be created if it can make profits." So, the major determinant i ...
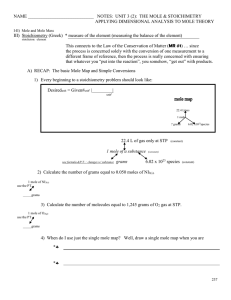
Stoichiometry and the Mole - 2012 Book Archive
... 1. Think back to the pound cake recipe. What possible conversion factors can you construct relating the components of the recipe? 2. Think back to the pancake recipe. What possible conversion factors can you construct relating the components of the recipe? 3. What are all the conversion factors that ...
... 1. Think back to the pound cake recipe. What possible conversion factors can you construct relating the components of the recipe? 2. Think back to the pancake recipe. What possible conversion factors can you construct relating the components of the recipe? 3. What are all the conversion factors that ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society
... After a look at general factors which influence the design of industrial processes, this topic looks at stoichiometry, the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products, and studies equilibrium in reversible reactions. ...
... After a look at general factors which influence the design of industrial processes, this topic looks at stoichiometry, the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products, and studies equilibrium in reversible reactions. ...
quantitative_chemistry
... This quantity is approximately 300 billion times more than the current human population of the earth! The comparison serves as a reminder of just how tiny molecules must be if that many are required to make up half a gram. Knowing that the average molecular mass of aspirin is 180.2 amu, a chemist at ...
... This quantity is approximately 300 billion times more than the current human population of the earth! The comparison serves as a reminder of just how tiny molecules must be if that many are required to make up half a gram. Knowing that the average molecular mass of aspirin is 180.2 amu, a chemist at ...
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic compounds; Identify the names and structures of groups of simple ...
... transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic compounds; Identify the names and structures of groups of simple ...
Fluorine – A Vital Element in the Medicine Chest
... In addition, fluorine can make a good arsenal of anticancer drugs. replacement for oxygen. The van der The popularity of fluorine as a Waals radii of fluorine, at 1.35 Å and component of drug molecules has oxygen at 1.40 Å are not that different, spiralled since then, with very many and their electr ...
... In addition, fluorine can make a good arsenal of anticancer drugs. replacement for oxygen. The van der The popularity of fluorine as a Waals radii of fluorine, at 1.35 Å and component of drug molecules has oxygen at 1.40 Å are not that different, spiralled since then, with very many and their electr ...
ppt
... of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the -electrons of the aromatic ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation. Substitutents can greatly influence the basicity of the aniline. The effect is dependent upon the nature and ...
... of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the -electrons of the aromatic ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation. Substitutents can greatly influence the basicity of the aniline. The effect is dependent upon the nature and ...
104 Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3
... of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the π-electrons of the aromatic ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation. Substitutents can greatly influence the basicity of the aniline. The effect is dependent upon the nature and ...
... of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the π-electrons of the aromatic ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation. Substitutents can greatly influence the basicity of the aniline. The effect is dependent upon the nature and ...
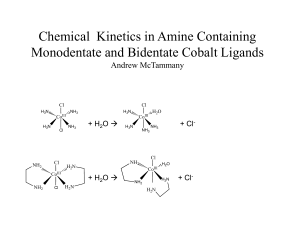
Chemical Kinetics in Monodentate and Bidentate Cobalt Compounds
... repeated. The trans-Co(NH3)4Cl2 should be synthesized using a lower temperature and lower concentration of acid. A mixture of HCl and H2SO4 could be used instead. From there the effect of different ligands can be ...
... repeated. The trans-Co(NH3)4Cl2 should be synthesized using a lower temperature and lower concentration of acid. A mixture of HCl and H2SO4 could be used instead. From there the effect of different ligands can be ...
CHE 110 Dr. Nicholas Bizier Office DS 337b email
... From this information you can calculate the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the sample. However since oxygen is in excess you must find oxygen through indirect means (the mass comes from what is not accounted for by carbon and hydrogen, in a sample that only contains CHO). ...
... From this information you can calculate the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the sample. However since oxygen is in excess you must find oxygen through indirect means (the mass comes from what is not accounted for by carbon and hydrogen, in a sample that only contains CHO). ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reactions). ...
... They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reactions). ...
Competing Intramolecular vs. Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds in
... relative free energies; solute dimerization ...
... relative free energies; solute dimerization ...