Moles
... Steps to Balancing Equations 1.Compare the numbers of atoms on each side of the equation 2.Start with the most complicated molecules FIRST! 3.Leave H and O until the end 4.Place COEFFICIENTS in front of the compound to try and balance the atoms 5.Check your answer to see if: - The numbers of atoms ...
... Steps to Balancing Equations 1.Compare the numbers of atoms on each side of the equation 2.Start with the most complicated molecules FIRST! 3.Leave H and O until the end 4.Place COEFFICIENTS in front of the compound to try and balance the atoms 5.Check your answer to see if: - The numbers of atoms ...
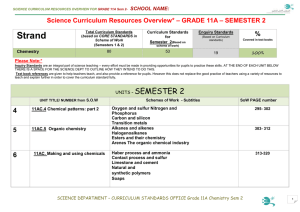
Science Curriculum Resources Overview* – GRADE 11A
... Know the main properties and uses of nitrates and understand their environmental impact Know why nitrogen and phosphorus exhibit two common oxidation states in their compounds and how this leads to two series of compounds. Recognise the importance of nitrogen and phosphorus to living things. Compare ...
... Know the main properties and uses of nitrates and understand their environmental impact Know why nitrogen and phosphorus exhibit two common oxidation states in their compounds and how this leads to two series of compounds. Recognise the importance of nitrogen and phosphorus to living things. Compare ...
1 Bite Angle Effects of Diphosphines in Carbonylation Reactions
... systematic studies using diphosphines was by Unruh [23] who used substituted dppf. Both rate and selectivity increase when the w-value of the ligands increase. There are two possible reasons: electrons preference for linear alkyl complex formation when the p-back-donation to the phosphine increases ...
... systematic studies using diphosphines was by Unruh [23] who used substituted dppf. Both rate and selectivity increase when the w-value of the ligands increase. There are two possible reasons: electrons preference for linear alkyl complex formation when the p-back-donation to the phosphine increases ...
Stoichiometry PP
... Energy Energy is measured in Joules or calories Every reaction has an energy change associated with it Exothermic reactions release energy, usually in the form of heat. Endothermic reactions absorb energy Energy is stored in bonds between atoms ...
... Energy Energy is measured in Joules or calories Every reaction has an energy change associated with it Exothermic reactions release energy, usually in the form of heat. Endothermic reactions absorb energy Energy is stored in bonds between atoms ...
Chemistry 162 Workbook 10.6
... may choose to grade the exam during a normal session while the student works on other materials (such as worksheets) and return the graded exam to the student. Alternatively, a tutor co ...
... may choose to grade the exam during a normal session while the student works on other materials (such as worksheets) and return the graded exam to the student. Alternatively, a tutor co ...
EQUILIBRIUM
... Thus the amount of solid NH4HS present does not affect the equilibrium. b) two points The equilibrium pressure of NH3 gas would decrease. In order for the pressure equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = ...
... Thus the amount of solid NH4HS present does not affect the equilibrium. b) two points The equilibrium pressure of NH3 gas would decrease. In order for the pressure equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
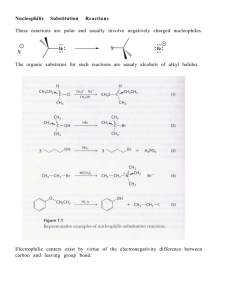
... Since the SN1 reaction involves carbocations that are formed in the RDS, then only those substrates that form relatively stable carbocations will undergo this reaction. What makes for a stabilized ...
... Since the SN1 reaction involves carbocations that are formed in the RDS, then only those substrates that form relatively stable carbocations will undergo this reaction. What makes for a stabilized ...
5.111 Principles of Chemical Science
... The ratio of protonated aspirin to its conjugate base is 79 to 1. So one-eightieth (1/80) of the total aspirin taken will be in the conjugate base form and available for immediate absorption in the stomach: 2 x 325 mg x (1/80) = 8.75 mg 9 mg (b) Would you expect more or less aspirin to be absorbed ...
... The ratio of protonated aspirin to its conjugate base is 79 to 1. So one-eightieth (1/80) of the total aspirin taken will be in the conjugate base form and available for immediate absorption in the stomach: 2 x 325 mg x (1/80) = 8.75 mg 9 mg (b) Would you expect more or less aspirin to be absorbed ...
Chemistry 11 - Correspondence Studies
... Stoichiometry deals with the mass-mass or molemole relationship among reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. It answers questions like how much of one reactant will react with a given amount of another reactant and how much product will be formed. Whether a compound is being prepare ...
... Stoichiometry deals with the mass-mass or molemole relationship among reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. It answers questions like how much of one reactant will react with a given amount of another reactant and how much product will be formed. Whether a compound is being prepare ...
Biomimetic Organic Synthesis. 2 Volume Set Brochure
... atoms into highly complex structures. Therefore, biomimetic total syntheses of natural products (in which biosynthesis considerations guide the synthetic strategy) constitute the major focus of this book, with emphasis on the developments of the last 10 to 15 years. Important key definitions and gen ...
... atoms into highly complex structures. Therefore, biomimetic total syntheses of natural products (in which biosynthesis considerations guide the synthetic strategy) constitute the major focus of this book, with emphasis on the developments of the last 10 to 15 years. Important key definitions and gen ...
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
... Breaking Elements Apart with Nuclear Fission .................... 52 Mass defect: Where does all that energy come from? .................................................... 52 Chain reactions and critical mass ............................... 53 Coming Together with Nuclear Fusion.................... ...
... Breaking Elements Apart with Nuclear Fission .................... 52 Mass defect: Where does all that energy come from? .................................................... 52 Chain reactions and critical mass ............................... 53 Coming Together with Nuclear Fusion.................... ...
chapter27
... • Each carbon atom in a C C bond is sp hybridized. – Each sp hybrid contains two bonds and two p bonds. – The carbon atom will have one single bond and one triple bond. ...
... • Each carbon atom in a C C bond is sp hybridized. – Each sp hybrid contains two bonds and two p bonds. – The carbon atom will have one single bond and one triple bond. ...
unit 7 hw packet File - District 196 e
... This website will help you out in your quest to understand chemistry. Explanations are at the introductory level and give some detail --- but not too much. Even the humor is well above average. You need to check this out. ChemTeam www.chemteam.info (chemical equations and reaction types) This webs ...
... This website will help you out in your quest to understand chemistry. Explanations are at the introductory level and give some detail --- but not too much. Even the humor is well above average. You need to check this out. ChemTeam www.chemteam.info (chemical equations and reaction types) This webs ...
Reactions of Alcohol
... Reactions of Alcohols In biological reactions the coenzyme NAD+ is often used as the oxidizing agent. The NAD+ takes the ...
... Reactions of Alcohols In biological reactions the coenzyme NAD+ is often used as the oxidizing agent. The NAD+ takes the ...
Student Solutions Manual Errata
... The relative atomic mass of boron is 10.81 amu. Since boron exists as either boron-10 or boron-11, the relative abundance of boron-11 will be much higher. Of the choices given only two make sense: 20% boron-10 and 80% boron-11 (correct answer) 5.0% boron-10 and 95.0% boron-11 The best answer can be ...
... The relative atomic mass of boron is 10.81 amu. Since boron exists as either boron-10 or boron-11, the relative abundance of boron-11 will be much higher. Of the choices given only two make sense: 20% boron-10 and 80% boron-11 (correct answer) 5.0% boron-10 and 95.0% boron-11 The best answer can be ...
Stoichiometric Conversions
... gas, the two will combust and form carbon dioxide and water CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O How many moles of H2O will be formed when 28.0 g of methane combusts? ...
... gas, the two will combust and form carbon dioxide and water CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O How many moles of H2O will be formed when 28.0 g of methane combusts? ...