Reactions of chlorine with water and sodium hydroxide
... ½Cl2 + OH- → HOCl + eAs chlorine has been both oxidised and reduced it is said to have disproportionated. ...
... ½Cl2 + OH- → HOCl + eAs chlorine has been both oxidised and reduced it is said to have disproportionated. ...
visual problems - Western Oregon University
... Assume that the values of ∆H°rxn and ∆S°rxn do not change appreciably with temperature. 12.61. Use the data in Appendix 4 to calculate ∆H° and ∆S° for the vaporization of hydrogen peroxide: H2O2(ℓ) → H2O2(g) Assuming that the calculated values are independent of temperature, what is the boiling poin ...
... Assume that the values of ∆H°rxn and ∆S°rxn do not change appreciably with temperature. 12.61. Use the data in Appendix 4 to calculate ∆H° and ∆S° for the vaporization of hydrogen peroxide: H2O2(ℓ) → H2O2(g) Assuming that the calculated values are independent of temperature, what is the boiling poin ...
AMINES
... Ans) Though both have intermolecular H bond .The H bond between alcohol molecules are stronger owing to the higher polarity of O – H bond compared to N – H bond. Q9) Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than NH3. Ans) In both NH3 and amines there is an unshared pair of electrons on N atom due to whic ...
... Ans) Though both have intermolecular H bond .The H bond between alcohol molecules are stronger owing to the higher polarity of O – H bond compared to N – H bond. Q9) Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than NH3. Ans) In both NH3 and amines there is an unshared pair of electrons on N atom due to whic ...
Ch 12 Solutions
... - Substances will mix and become disordered if no forces prevent them from doing so. - If only London forces are present, then there are no large differences in attractions. The molecules will move freely together as long as T is much less than their boiling points. - The same is true of polar molec ...
... - Substances will mix and become disordered if no forces prevent them from doing so. - If only London forces are present, then there are no large differences in attractions. The molecules will move freely together as long as T is much less than their boiling points. - The same is true of polar molec ...
Chapter 21: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3. Nitrogen
... The nitrogen of arylamines (aniline) is slightly flatten, reflecting resonance interactions with the aromatic ring. ...
... The nitrogen of arylamines (aniline) is slightly flatten, reflecting resonance interactions with the aromatic ring. ...
Document
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
Unit 7 Homework and Lab Packet
... -Design and conduct scientific investigations -Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and communications. -Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models using logic and evidence. -Understand and apply knowledge of chemical reactions ...
... -Design and conduct scientific investigations -Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and communications. -Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models using logic and evidence. -Understand and apply knowledge of chemical reactions ...
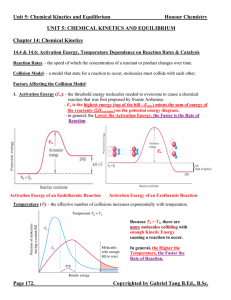
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
... 9. Each set of equilibrium concentrations is called an ______________________________. 10. There is only __________ equilibrium constant for a particular system at a particular temperature, but there are an ____________________ number of equilibrium positions. 11. The specific equilibrium position a ...
... 9. Each set of equilibrium concentrations is called an ______________________________. 10. There is only __________ equilibrium constant for a particular system at a particular temperature, but there are an ____________________ number of equilibrium positions. 11. The specific equilibrium position a ...
Chapter 11: Reactions of Alcohols
... We have just seen that alcohol have a strongly basic leaving group (HO−) that cannot be displaced by a nucleophile. Therefore, an alcohol cannot undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction. ...
... We have just seen that alcohol have a strongly basic leaving group (HO−) that cannot be displaced by a nucleophile. Therefore, an alcohol cannot undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction. ...
BSA - Sigma
... BSA (N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide) is one of the most commonly used silylating reagents. Its reactivity is similar to that of BSTFA, readily silylating a wide range of acidic functional groups such as non-sterically hindered alcohols, amides, amines, amino acids, carboxylic acids, and enols. It ...
... BSA (N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide) is one of the most commonly used silylating reagents. Its reactivity is similar to that of BSTFA, readily silylating a wide range of acidic functional groups such as non-sterically hindered alcohols, amides, amines, amino acids, carboxylic acids, and enols. It ...
Chapter 1 – Reaction Kinetics Answer Key
... 3. The concentrations of pure solids and liquids are fixed. That is they do not change (appreciably for the liquid if it is the solvent and at all for the solid) during a chemical reaction. ...
... 3. The concentrations of pure solids and liquids are fixed. That is they do not change (appreciably for the liquid if it is the solvent and at all for the solid) during a chemical reaction. ...
Hubbard-U is necessary on ligand atom for predicting
... The oxide dianions (Oµ), and aliphatic N atoms pure σ-donors- have spin polarization opposite to that of the nearest Mn ion, in agreement with superexchange The aromatic N atoms have nearly zero spin-polarization. O atoms of the acetate cations have the same spin polarization as the nearest Mn catio ...
... The oxide dianions (Oµ), and aliphatic N atoms pure σ-donors- have spin polarization opposite to that of the nearest Mn ion, in agreement with superexchange The aromatic N atoms have nearly zero spin-polarization. O atoms of the acetate cations have the same spin polarization as the nearest Mn catio ...
entropy - KFUPM Faculty List
... For a given substance, the standard entropy is greater in the gas phase than in the liquid phase. For two monatomic species, the one with the larger molar mass has the greater standard entropy. ...
... For a given substance, the standard entropy is greater in the gas phase than in the liquid phase. For two monatomic species, the one with the larger molar mass has the greater standard entropy. ...
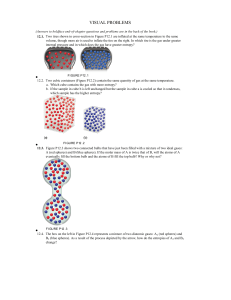
aq - Byron High School
... If you were to draw diagrams (such as that shown below) representing aqueous solutions of each of the following ionic compounds, how many anions would you show if the diagram contained six cations? (a) NiSO4, (b) Ca(NO3)2 , (c) Na3PO4, (d) ...
... If you were to draw diagrams (such as that shown below) representing aqueous solutions of each of the following ionic compounds, how many anions would you show if the diagram contained six cations? (a) NiSO4, (b) Ca(NO3)2 , (c) Na3PO4, (d) ...
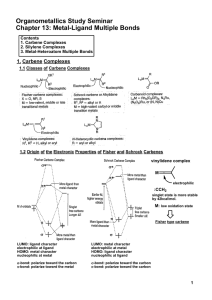
Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds
... LUMO: ligand character electrophilic at ligand HOMO: metal character nucleophilic at metal -bond: polarize toward the carbon -bond: polarize toward the metal ...
... LUMO: ligand character electrophilic at ligand HOMO: metal character nucleophilic at metal -bond: polarize toward the carbon -bond: polarize toward the metal ...